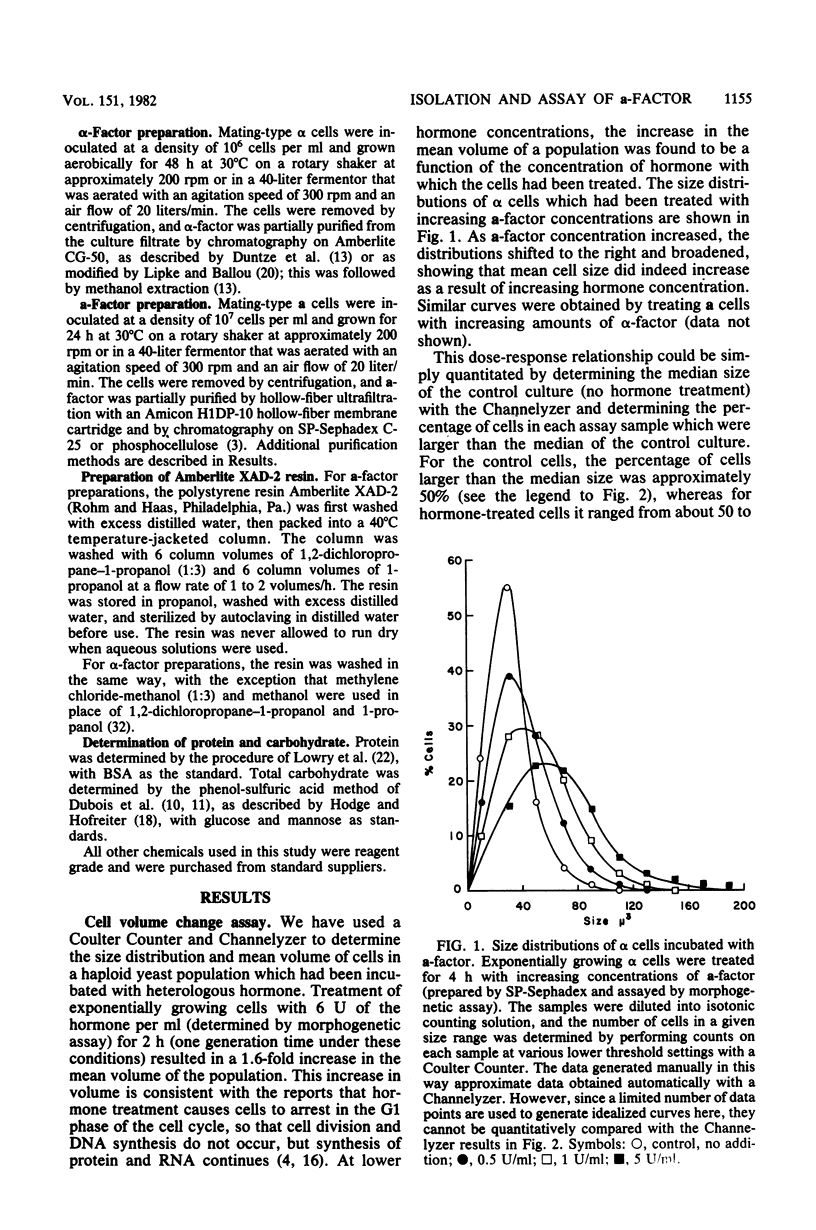
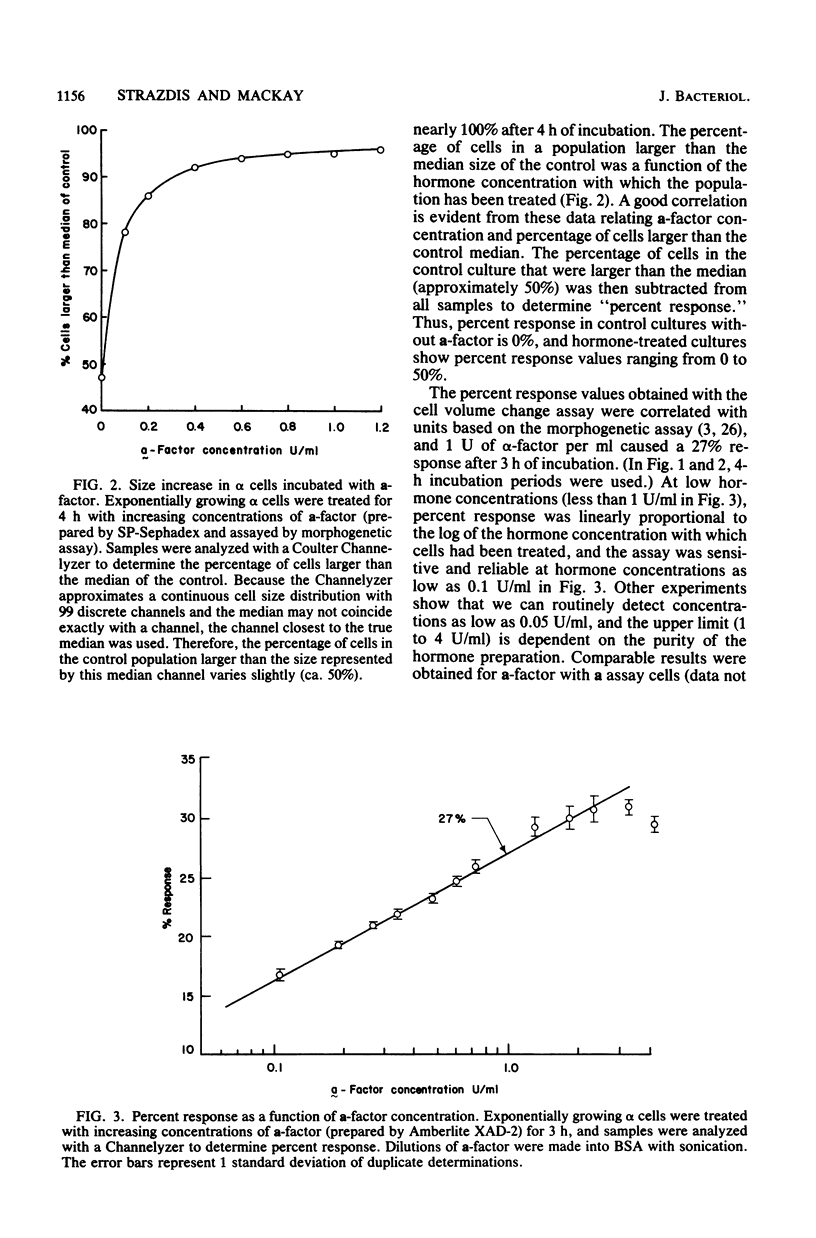
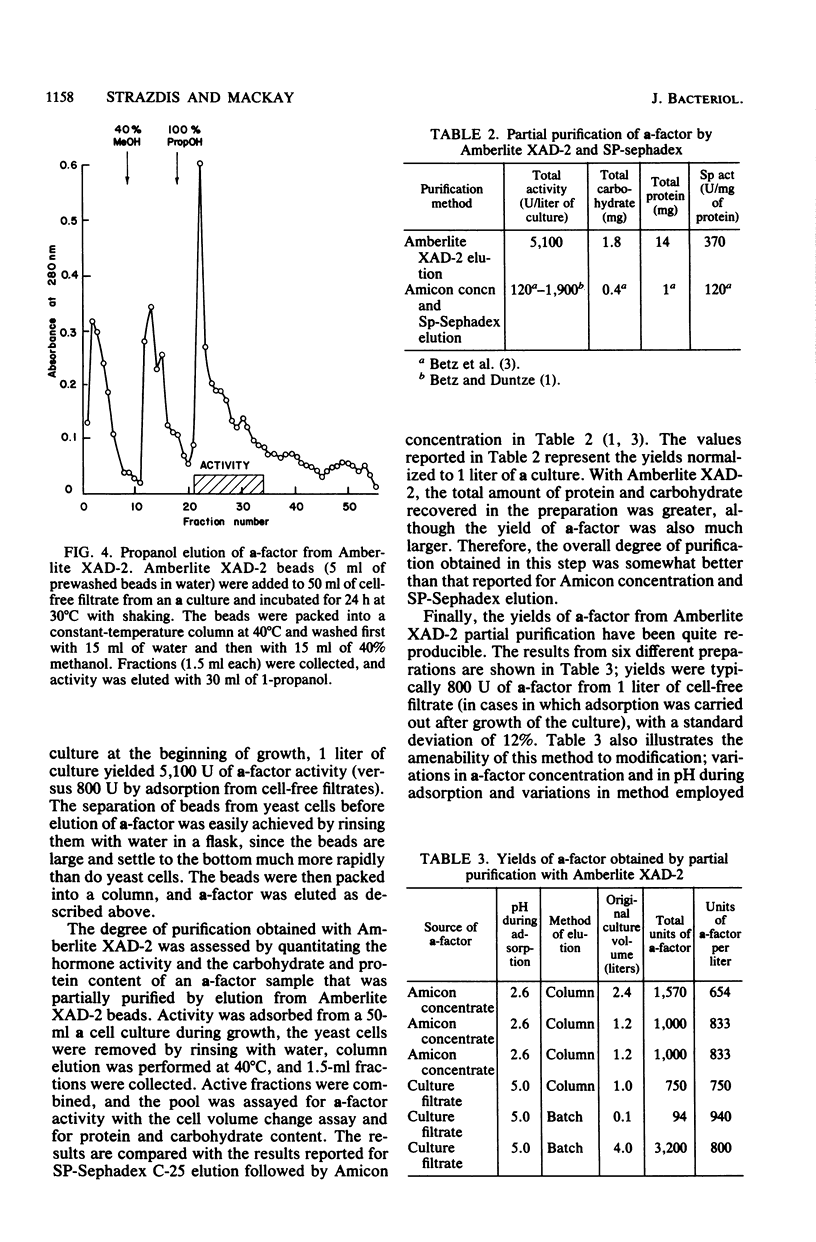
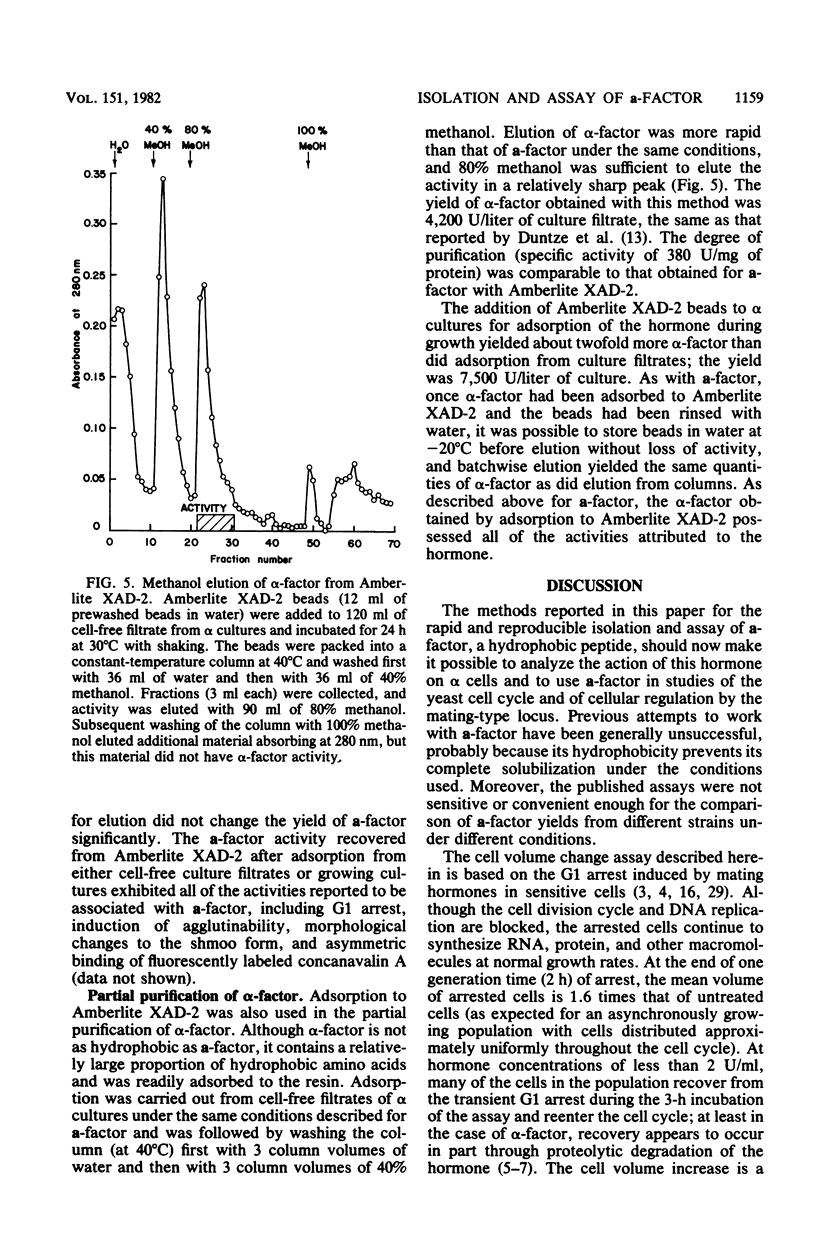
Abstract
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae mating hormone a-factor has been difficult to isolate reproducibly in sufficient yields by methods using ion-exchange chromatography, probably because of its pronounced hydrophobicity. In this work, a hydrophobic adsorbent (Amberlite XAD-2), in an insoluble bead from, was used to isolate larger (up to sixfold greater than previous reports) and quite reproducible (12% standard deviation) quantities of a-factor by adsorption from cell-free filtrates of a cultures. Moreover, when the beads were added to the cultures at the time of inoculation, sixfold greater yields were obtained than when a-factor was adsorbed to the beads from cell-free filtrates. a-Factor was readily eluted from the beads with 1-propanol. The same adsorbent could also be used in the partial purification of the less hydrophobic α-factor. Adsorption of both hormones by Amberlite XAD-2 gave a degree of purification comparable to that obtained by the first steps of previously published methods while providing larger yields of hormones. The present procedure is shorter, simpler, and, for a-factor, more reproducible. The activities of both hormones were quantitated by using an assay in which the size distribution of cells in the population was monitored after the addition of hormone of the opposite mating type. The extent of increase in cell size which accompanies hormone treatment is a function of the hormone concentration. To ensure solubilization of a-factor in the aqueous bioassay system, samples were diluted into bovine serum albumin solutions and sonicated before assaying. The resulting assay is most sensitive at hormone concentrations between 0.05 and 2 U/ml, can reliably detect as little as 0.16 ng of hormone, gave results reproducible within 16%, and is convenient for a large number (>100) of samples.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Betz R., Duntze W. Purification and partial characterization of a factor, a mating hormone produced by mating-type-a cells from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Apr;95(3):469–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12986.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz R., MacKay V. L., Duntze W. a-Factor from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: partial characterization of a mating hormone produced by cells of mating type a. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):462–472. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.462-472.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bücking-Throm E., Duntze W., Hartwell L. H., Manney T. R. Reversible arrest of haploid yeast cells in the initiation of DNA synthesis by a diffusible sex factor. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Jan;76(1):99–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90424-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R. K., Otte C. A. Isolation and genetic analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants supersensitive to G1 arrest by a factor and alpha factor pheromones. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;2(1):11–20. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R. K. Recovery of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mating-type a cells from G1 arrest by alpha factor. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):766–774. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.766-774.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciejek E., Thorner J., Geier M. Solid phase peptide synthesis of alpha-factor, a yeast mating pheromone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Oct 10;78(3):952–961. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90514-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciejek E., Thorner J. Recovery of S. cerevisiae a cells from G1 arrest by alpha factor pheromone requires endopeptidase action. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):623–635. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90117-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS M., GILLES K., HAMILTON J. K., REBERS P. A., SMITH F. A colorimetric method for the determination of sugars. Nature. 1951 Jul 28;168(4265):167–167. doi: 10.1038/168167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duntze W., MacKay V., Manney T. R. Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a diffusible sex factor. Science. 1970 Jun 19;168(3938):1472–1473. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3938.1472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duntze W., Stötzler D., Bücking-Throm E., Kalbitzer S. Purification and partial characterization of -factor, a mating-type specific inhibitor of cell reproduction from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jun;35(2):357–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehrenbacher G., Perry K., Thorner J. Cell-cell recognition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: regulation of mating-specific adhesion. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):893–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.893-901.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein D. B., Strausberg S. Metabolism of alpha-factor by a mating type cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 10;254(3):796–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae unresponsive to cell division control by polypeptide mating hormone. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):811–822. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Synchronization of haploid yeast cell cycles, a prelude to conjugation. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Jan;76(1):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90425-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keana J. F., Roman R. B. Improved synthesis of n-octyl-beta-D-glucoside: a nonionic detergent of considerable potential in membrane biochemistry. Membr Biochem. 1978;1(3-4):323–327. doi: 10.3109/09687687809063854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipke P. N., Ballou C. E. Altered immunochemical reactivity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae a-cells after alpha-factor-induced morphogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1170–1177. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1170-1177.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipke P. N., Taylor A., Ballou C. E. Morphogenic effects of alpha-factor on Saccharomyces cerevisiae a cells. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):610–618. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.610-618.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay V., Manney T. R. Mutations affecting sexual conjugation and related processes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. I. Isolation and phenotypic characterization of nonmating mutants. Genetics. 1974 Feb;76(2):255–271. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manney T. R., Woods V. Mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae resistant to the alpha mating-type factor. Genetics. 1976 Apr;82(4):639–644. doi: 10.1093/genetics/82.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masui Y., Chino N., Sakakibara S., Tanaka T., Murakami T., Kita H. Synthesis of the mating factor of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its truncated peptides : the structure-activity relationship. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 23;78(2):534–538. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90211-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stötzler D., Duntze W. Isolation and characterization of four related peptides exhibiting alpha factor activity from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1976 May 17;65(1):257–262. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkacz J. S., MacKay V. L. Sexual conjugation in yeast. Cell surface changes in response to the action of mating hormones. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):326–333. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickerham L. J. A Critical Evaluation of the Nitrogen Assimilation Tests Commonly Used in the Classification of Yeasts. J Bacteriol. 1946 Sep;52(3):293–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson L. E., Pringle J. R. Transient G1 arrest of S. cerevisiae cells of mating type alpha by a factor produced by cells of mating type a. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Nov;89(1):175–187. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90200-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



