Abstract
We have previously shown that allophanate acts as an inducer for five structural genes whose products participate in the degradation of allantoin by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. This observation led us to hypothesize that these genes might be controlled in common and to test the hypothesis by searching for mutants unable to induce production of the allantoin-degrading enzymes. Such mutants have been found. These strains grew poorly when provided with any of the allantoin pathway intermediates, but used other nitrogen sources normally. The mutations carried in these strains were recessive to wild-type alleles and complemented mutations in all known loci associated with the allantoin pathway. The locus containing the most thoroughly studied mutation (dal81-1) was not fund to be tightly linked to any of the allantoin pathway structural genes. The low basal levels of allantoin pathway enzymes observed in Dal81- strains remained the same whether or not the inducer was present in the growth medium. However, the levels of enzyme increased moderately when mutants were grown on poor nitrogen sources. From these observations, we conclude that dal81 mutant strains possess a defect in the induction of enzyme synthesis; enzyme production due to relief of nitrogen catabolite repression, however, appears normal. The observed epistatic relationships of mutations in the DAL80 and DAL81 loci suggest that their products may possess a reasonable degree of functional independence.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bossinger J., Cooper T. G. Molecular events associated with induction of arginase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):163–173. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.163-173.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossinger J., Cooper T. Possible failure of NADP-glutamate dehydrogenase to participate directly in nitrogen repression of the allantoin degradative enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Oct 6;66(3):889–892. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90723-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossinger J., Lawther R. P., Cooper T. G. Nitrogen repression of the allantoin degradative enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):821–829. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.821-829.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandriss M. C., Magasanik B. Genetics and physiology of proline utilization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: enzyme induction by proline. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):498–503. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.498-503.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandriss M. C., Magasanik B. Genetics and physiology of proline utilization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: mutation causing constitutive enzyme expression. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):504–507. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.504-507.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisholm G., Cooper T. G. Isolation and characterization of mutants that produce the allantoin-degrading enzymes constitutively in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1088–1095. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. G., Gorski M., Turoscy V. A cluster of three genes responsible for allantoin degradation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1979 Jun;92(2):383–396. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
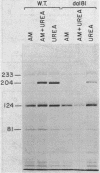
- Cooper T. G., Lawther R. P. Induction of the allantoin degradative enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by the last intermediate of the pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2340–2344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. G., McKelvey J., Sumrada R. Oxalurate transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):917–923. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.917-923.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. G., Sumrada R. Urea transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):571–576. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.571-576.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drillien R., Lacroute F. Ureidosuccinic acid uptake in yeast and some aspects of its regulation. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):203–208. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.203-208.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlop P. C., Meyer G. M., Roon R. J. Nitrogen catabolite repression of asparaginase II in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):422–426. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.422-426.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenson M., Hou C., Crabeel M. Multiplicity of the amino acid permeases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. IV. Evidence for a general amino acid permease. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):770–777. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.770-777.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. P., Holland M. J. The primary structure of a glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9839–9845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Hansen J. N., Konkel D., Leder A., Nishioka Y., Talkington C. Mouse globin system: a functional and evolutionary analysis. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1336–1342. doi: 10.1126/science.7414319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Shander M. H., Manley J. L., Gefter M. L., Maniatis T. Structure and in vitro transcription of human globin genes. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1329–1336. doi: 10.1126/science.6158093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roon R. J., Larimore F., Levy J. S. Inhibition of amino acid transport by ammonium ion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):325–331. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.325-331.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M., Leung D. W., Gillam S., Astell C. R., Montgomery D. L., Hall B. D. Sequence of the gene for iso-1-cytochrome c in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John T. P., Davis R. W. The organization and transcription of the galactose gene cluster of Saccharomyces. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 25;152(2):285–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90244-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiles J. I., Szostak J. W., Young A. T., Wu R., Consaul S., Sherman F. DNA sequence of a mutation in the leader region of the yeast iso-1-cytochrome c mRNA. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90253-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumrada R., Cooper T. G. Oxaluric acid: a non-metabolizable inducer of the allantoin degradative enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1240–1247. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1240-1247.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschumper G., Carbon J. Sequence of a yeast DNA fragment containing a chromosomal replicator and the TRP1 gene. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turoscy V., Cooper T. G. Allantoate transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):971–979. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.971-979.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney P. A., Cooper T. G., Magasanik B. The induction of urea carboxylase and allophanate hydrolase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6203–6209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney P. A., Cooper T. G. Urea carboxylase and allophanate hydrolase. Two components of adenosine triphosphate:urea amido-lyase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1972 Mar 10;247(5):1349–1353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney P. A., Magasanik B. The induction of arginase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6197–6202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickerham L. J. A Critical Evaluation of the Nitrogen Assimilation Tests Commonly Used in the Classification of Yeasts. J Bacteriol. 1946 Sep;52(3):293–301. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Poll K. W. Ammonium repression in a mutant of Saccharomyces carlsbergensis lacking NADP dependent glutamate dehydrogenase activity. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jun 1;32(2):265–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80848-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]