Abstract
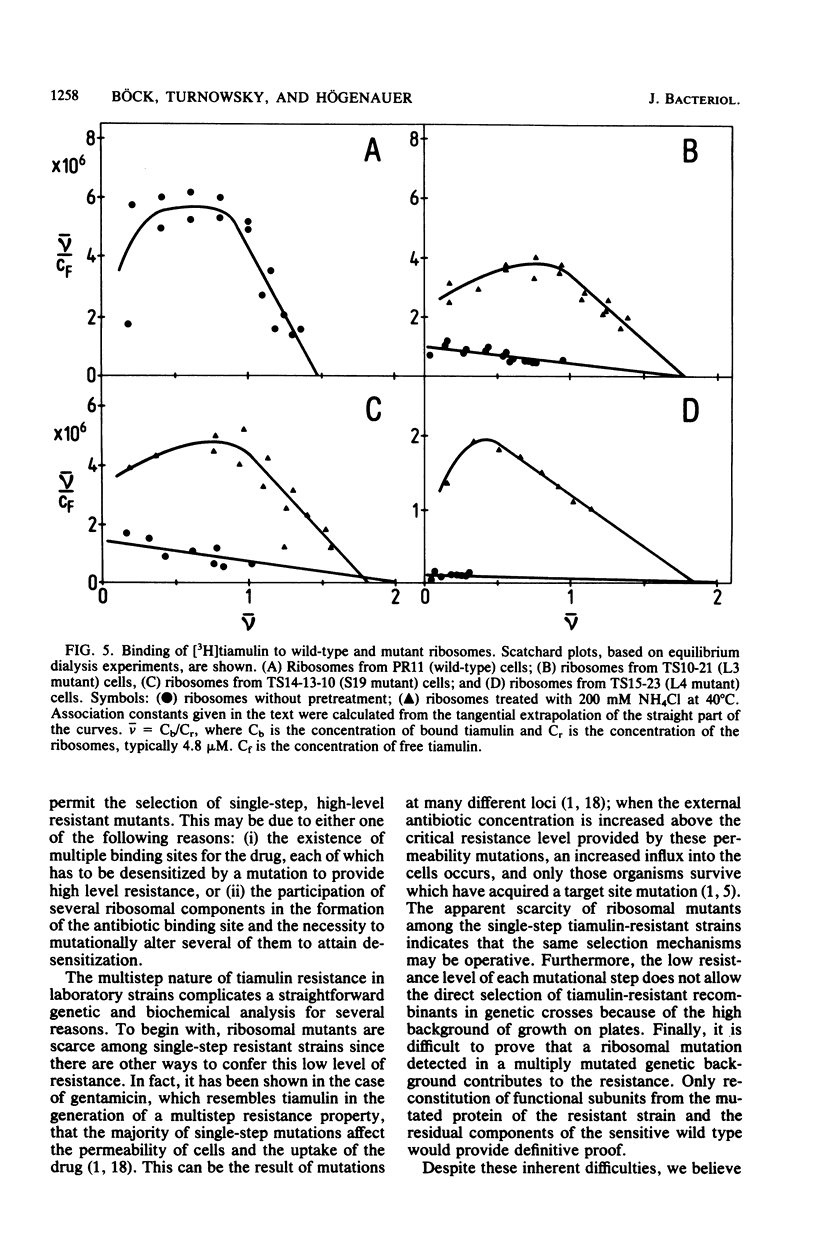
Forty "two-step" and 13 "three-step" tiamulin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli PR11 were isolated and tested for alteration of ribosomal proteins. Mutants with altered ribosomal proteins S10, S19, L3, and L4 were detected. The S19, L3, and L4 mutants were studied in detail. The L3 and L4 mutations did not segregate from the resistance character in transductional crosses and therefore seem to be responsible for the resistance. Extracts of these mutants also exhibited an increased in vitro resistance to tiamulin in the polyuridylic acid and phage R17 RNA-dependent polypeptide synthesis systems, and it was demonstrated that this was a property of the 50S subunit. In the case of the S19 mutant, genetic analysis showed segregation between resistance and the S19 alteration and therefore indicated that mutation of a protein other than S19 was responsible for the resistance phenotype. The isolated ribosomes of the S19, L3, and L4 mutants bound radioactive tiamulin with a considerably reduced strength when compared with those of wild-type cells. The association constants were lower by factors ranging from approximately 20 to 200. When heated in the presence of ammonium chloride, these ribosomes partially regained their avidity for tiamulin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad M. H., Rechenmacher A., Böck A. Interaction between aminoglycoside uptake and ribosomal resistance mutations. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1980 Nov;18(5):798–806. doi: 10.1128/aac.18.5.798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apirion D., Saltzman L. Functional interdependence of 50S and 30S ribosomal subunits. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;135(1):11–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00433896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J., Low K. B. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 6. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Mar;44(1):1–56. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.1.1-56.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckel P., Buchberger A., Böck A., Wittmann H. G. Alteration of ribosomal protein L6 in mutants of Escherichia coli resistant to gentamicin. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Dec 14;158(1):47–54. doi: 10.1007/BF00455118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornhelm P., Högenauer G. The effects of tiamulin, a semisynthetic pleuromutilin derivative, on bacterial polypeptide chain initiation. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Nov 15;91(2):465–473. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12699.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drews J., Georgopoulos A., Laber G., Schütze E., Unger J. Antimicrobial activities of 81.723 hfu, a new pleuromutilin derivative. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 May;7(5):507–516. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.5.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesteland R. F. Isolation and characterization of ribonuclease I mutants of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):67–84. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyl D., Böck A., Wittmann H. G. Cold-sensitive growth of a mutant of Escherichia coli with an altered ribosomal protein S8: analysis of revertants. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Apr 29;152(3):331–336. doi: 10.1007/BF00693088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgin L. A., Högenauer G. The mode of action of pleuromutilin derivatives. Effect on cell-free polypeptide synthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Sep 16;47(3):527–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Högenauer G., Ruf C. Ribosomal binding region for the antibiotic tiamulin: stoichiometry, subunit location, and affinity for various analogs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Feb;19(2):260–265. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.2.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühberger R., Piepersberg W., Petzet A., Buckel P., Böck A. Alteration of ribosomal protein L6 in gentamicin-resistant strains of Escherichia coli. Effects on fidelity of protein synthesis. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 9;18(1):187–193. doi: 10.1021/bi00568a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piepersberg W., Noseda V., Böck A. Bacterial ribosomes with two ambiguity mutations: effects of translational fidelity, on the response to aminoglycosides and on the rate of protein synthesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Mar 9;171(1):23–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00274011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorbjarnardóttir S. H., Magnúsdóttir R. A., Eggertsson G. Mutations determining generalized resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Apr 25;161(1):89–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00266619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams G., Smith I. Chromosomal mutations causing resistance to tetracycline in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):23–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00267249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann H. G., Stöffler G., Apirion D., Rosen L., Tanaka K., Tamaki M., Takata R., Dekio S., Otaka E. Biochemical and genetic studies on two different types of erythromycin resistant mutants of Escherichia coli with altered ribosomal proteins. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Dec 20;127(2):175–189. doi: 10.1007/BF00333665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]