Abstract
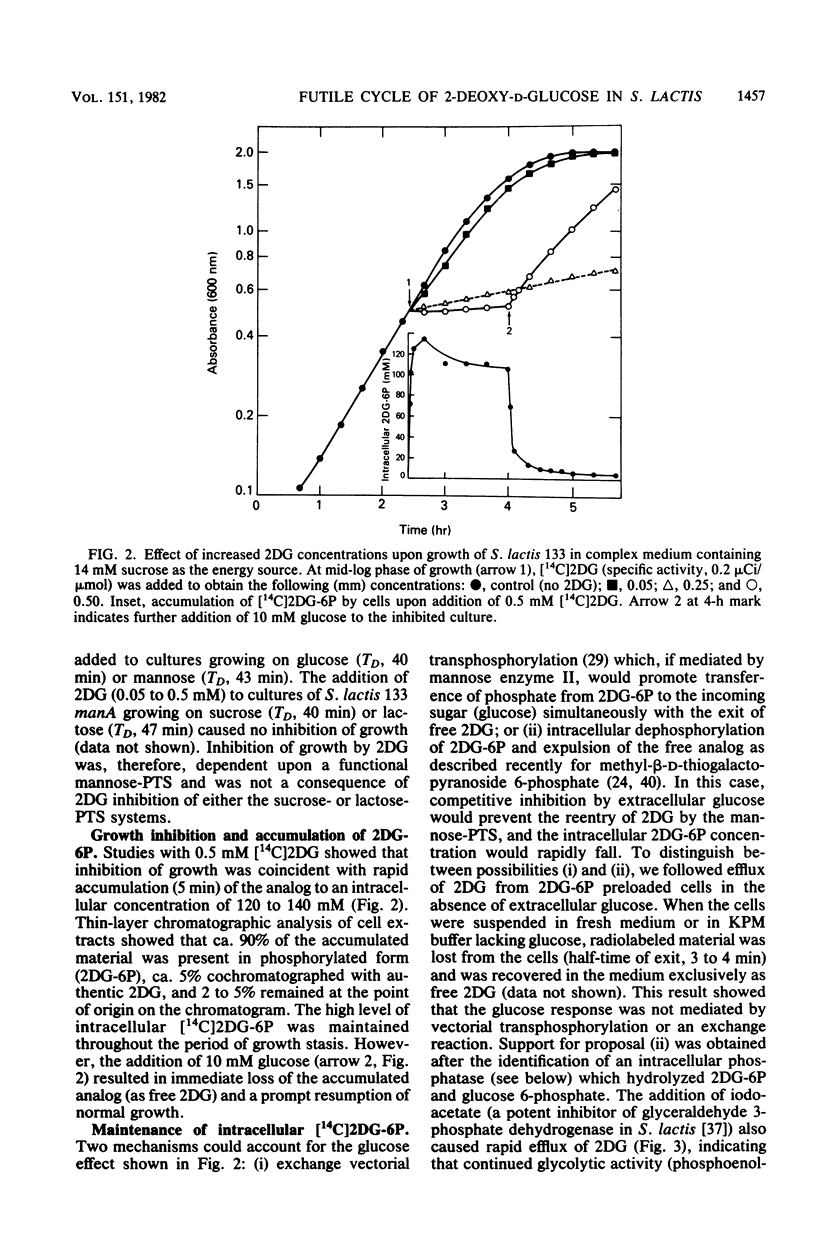
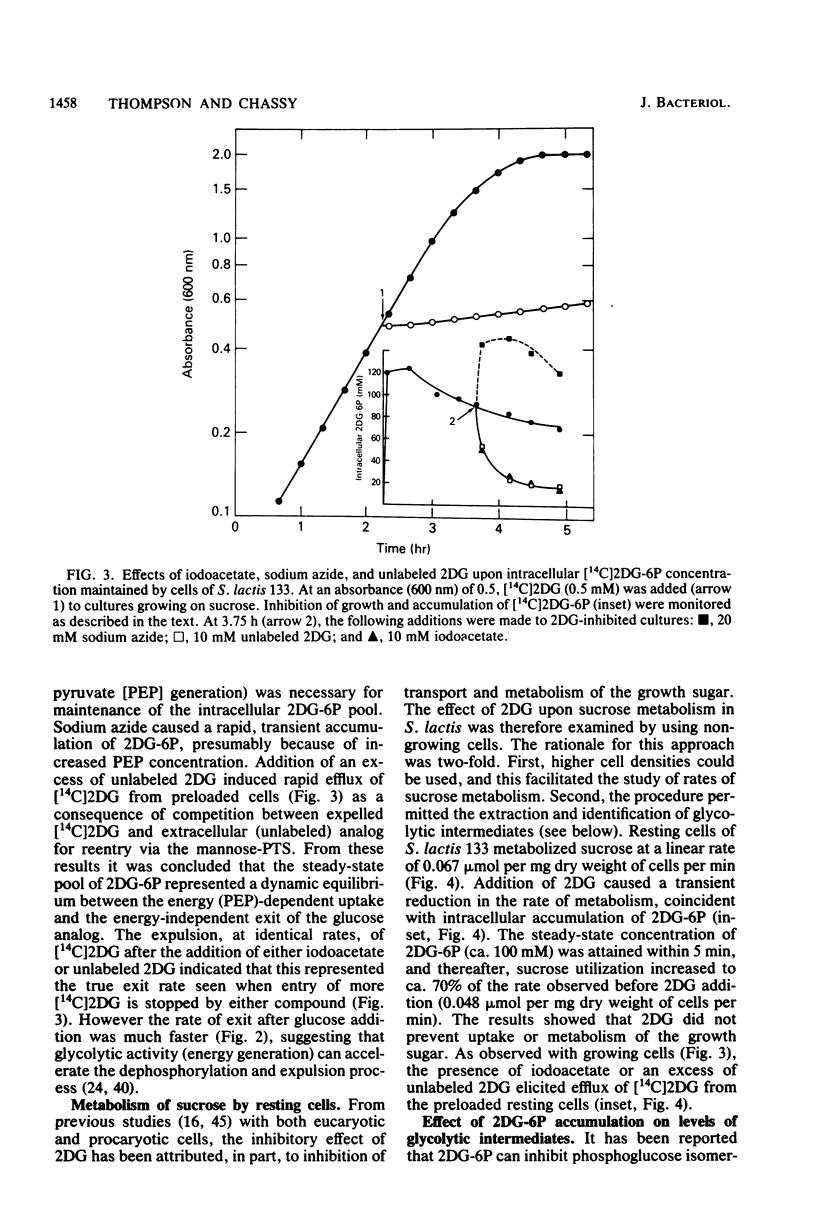
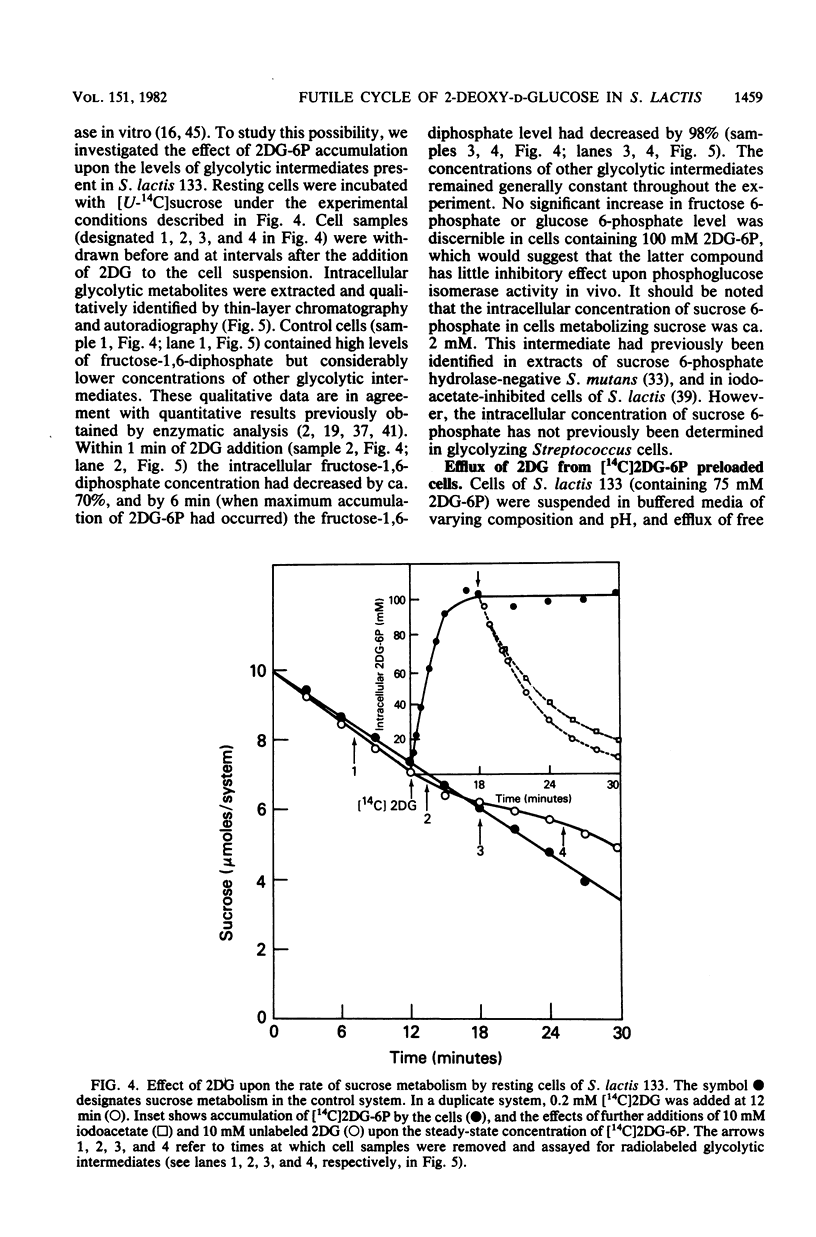
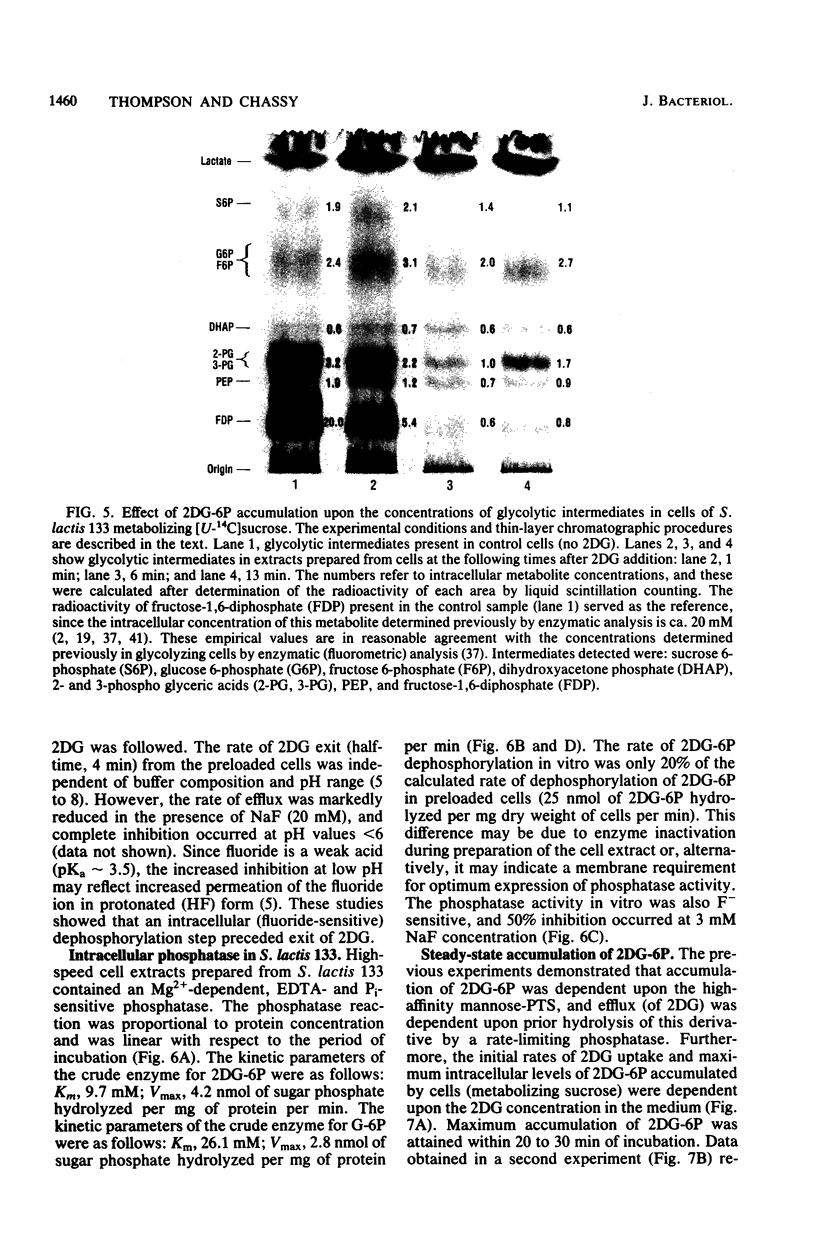
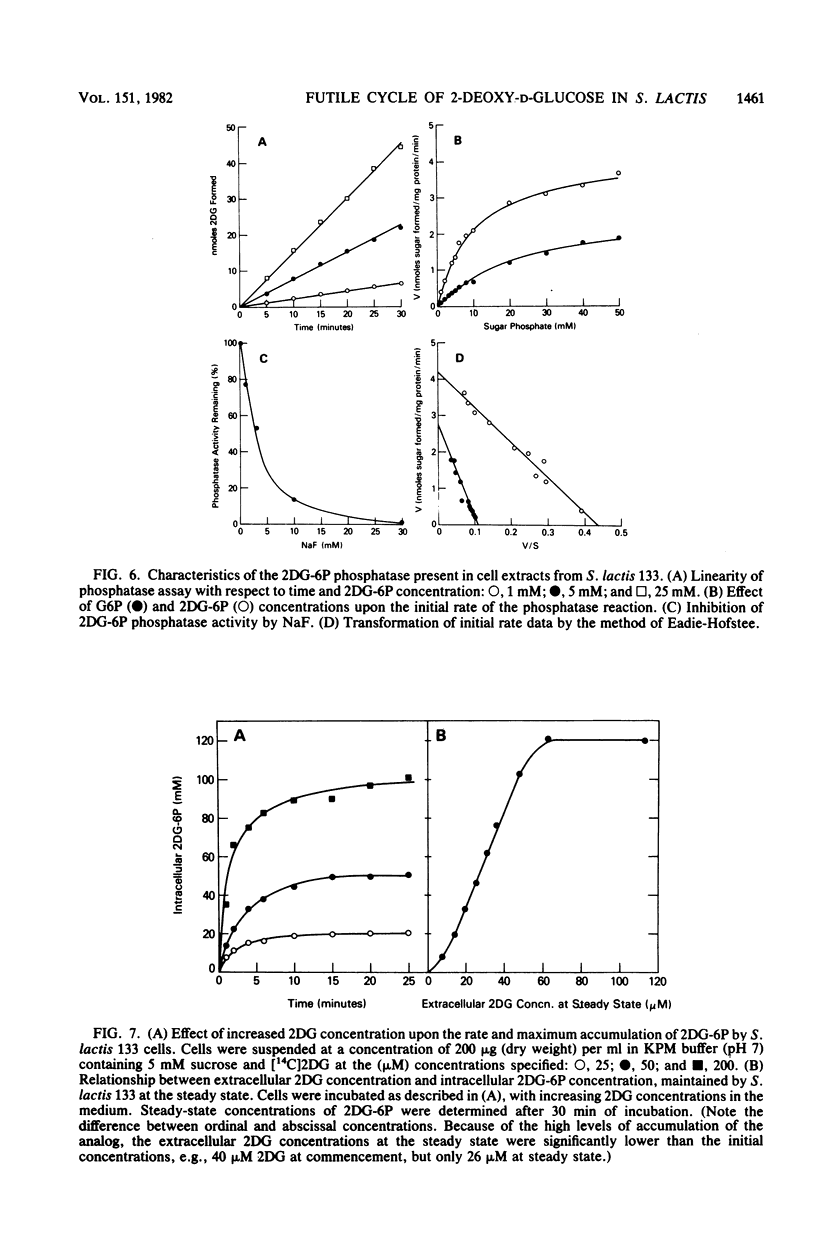
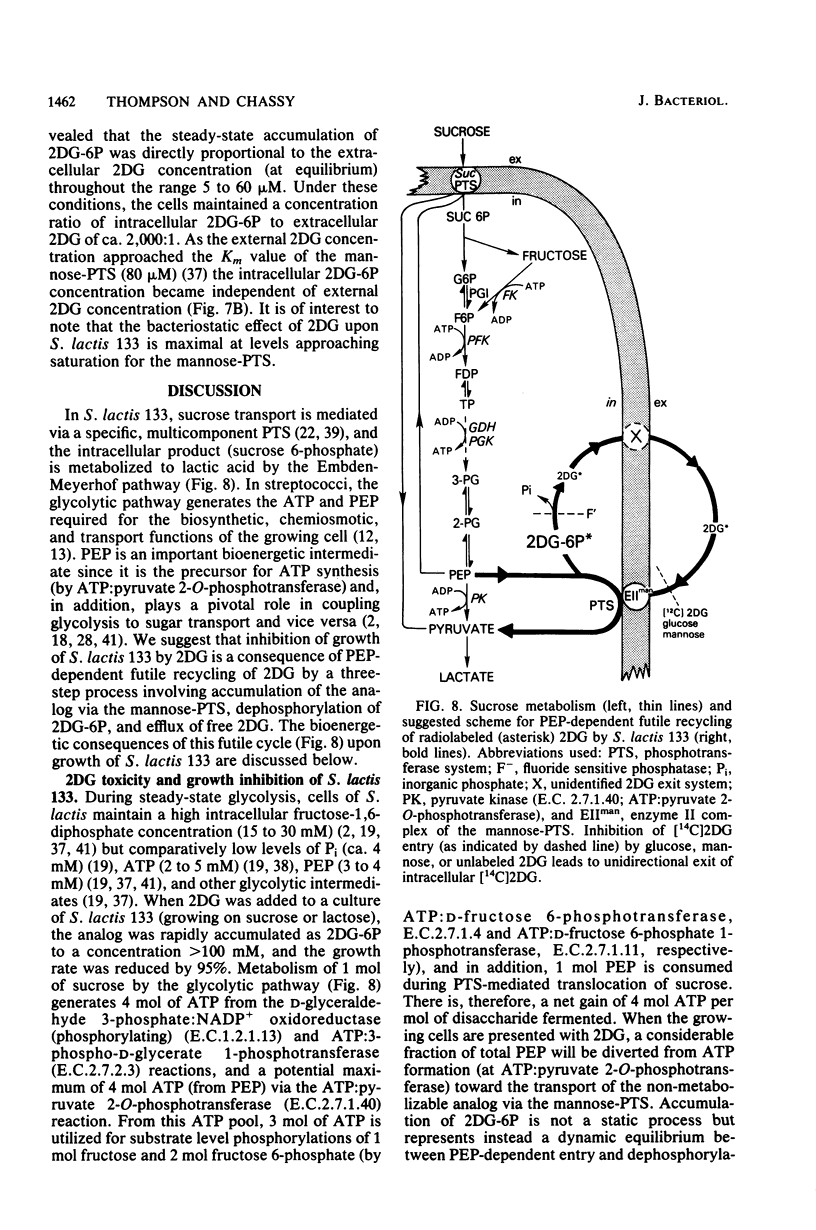
The addition of 2-deoxy-D-glucose to cultures of Streptococcus lactis 133 that were growing exponentially on sucrose or lactose reduced the growth rate by ca. 95%. Inhibition did not occur with glucose or mannose as the growth sugar. The reduction in growth rate was concomitant with rapid accumulation of the analog in phosphorylated form (2-deoxy-D-glucose 6-phosphate) via the phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent mannose:phosphotransferase system. Within 5 min the intracellular 2-deoxy-D-glucose 6-phosphate concentration reached a steady-state level of greater than 100 mM. After maximum accumulation of the sugar phosphate, the rate of sucrose metabolism (glycolysis) decreased by only 30%, but the cells were depleted of fructose-1,6-diphosphate. The addition of glucose to 2-deoxy-D-glucose 6-phosphate preloaded cells caused expulsion of 2-deoxy-D-glucose and a resumption of normal growth. S. lactis 133 contained an intracellular Mg2+-dependent, fluoride-sensitive phosphatase which hydrolyzed 2-deoxy-D-glucose 6-phosphate (and glucose 6-phosphate) to free sugar and inorganic phosphate. Because of continued dephosphorylation and efflux of the non-metabolizable analog, the maintenance of the intracellular 2-deoxy-D-glucose 6-phosphate pool during growth stasis was dependent upon continued glycolysis. This steady-state condition represented a dynamic equilibrium of: (i) phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent accumulation of 2-deoxy-D-glucose 6-phosphate, (ii) intracellular dephosphorylation, and (iii) efflux of free 2-deoxy-D-glucose. This sequence of events constitutes a futile cycle which promotes the dissipation of phosphoenolpyruvate. We conclude that 2-deoxy-D-glucose functions as an uncoupler by dissociating energy production from growth in S. lactis 133.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chassy B. M., Porter E. V. Initial characterization of sucrose-6-phosphate hydrolase from Streptococcus mutans and its apparent identity with intracellular invertase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Jul 12;89(1):307–314. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)90979-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins L. B., Thomas T. D. Pyruvate kinase of Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.52-58.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietz G. W., Heppel L. A. Studies on the uptake of hexose phosphates. I. 2-Deoxyglucose and 2-deoxyglucose 6-phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2881–2884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dills S. S., Apperson A., Schmidt M. R., Saier M. H., Jr Carbohydrate transport in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Sep;44(3):385–418. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.3.385-418.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg A. D., Marquis R. E. Enhanced transmembrane proton conductance in Streptococcus mutans GS-5 due to ionophores and fluoride. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 May;19(5):807–812. doi: 10.1128/aac.19.5.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald R. J., Fitzgerald D. B. Inhibition of caries in hamsters by 2-deoxy-D-glucose. J Dent Res. 1977 Nov;56(11):1431–1431. doi: 10.1177/00220345770560113501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel D. G. The accumulation of glucose 6-phosphate from glucose and its effect in an Escherichia coli mutant lacking phosphoglucose isomerase and glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 25;243(24):6451–6457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gachelin G. Studies on the alpha-methylglucoside permease of Escherichia coli. A two-step mechanism for the accumulation of alpha-methylglucoside 6-phosphate. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Oct;16(2):342–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haguenauer R., Kepes A. NaF inhibition of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation involved in -methyl-D glucoside transport in E. coli K 12. A pH dependant phenomenon sensitive to uncoupling agents. Biochimie. 1972;54(4):505–512. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(72)80235-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada S., Slade H. D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Jun;44(2):331–384. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.2.331-384.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Conservation and transformation of energy by bacterial membranes. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Jun;36(2):172–230. doi: 10.1128/br.36.2.172-230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez-Asensio M., Del Campo F. F. Enhancement of alpha-methylglucoside efflux by respiration in respiratory mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1980 Apr 1;200(2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(80)90360-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J., Rognstad R. Futile cycles in the metabolism of glucose. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1976;10:237–289. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152810-2.50013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg H. L. Formation and utilization of PEP in microbial carbohydrate transport. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;18:313–327. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152818-8.50024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason P. W., Carbone D. P., Cushman R. A., Waggoner A. S. The importance of inorganic phosphate in regulation of energy metabolism of Streptococcus lactis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1861–1866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meredith S. A., Romano A. H. Uptake and phosphorylation of 2-deoxy-D-glucose by wild type and respiration-deficient bakers' yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 26;497(3):745–759. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(77)90295-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postma P. W., Roseman S. The bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Dec 14;457(3-4):213–257. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racker E. Energy cycles in health and disease. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1981;18:361–376. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152818-8.50027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reizer J., Panos C. Regulation of beta-galactoside phosphate accumulation in Streptococcus pyogenes by an expulsion mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5497–5501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rephaeli A. W., Saier M. H., Jr Substrate specificity and kinetic characterization of sugar uptake and phosphorylation, catalyzed by the mannose enzyme II of the phosphotransferase system in Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8585–8591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts K. R., Hayes M. L. Effects of 2-deoxy D-glucose and other sugar analogues on acid production from sugars by human dental plaque bacteria. Scand J Dent Res. 1980 Jun;88(3):201–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1980.tb01215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romano A. H., Trifone J. D., Brustolon M. Distribution of the phosphoenolpyruvate:glucose phosphotransferase system in fermentative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):93–97. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.93-97.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saier M. H., Jr, Feucht B. U., Mora W. K. Sugar phosphate: sugar transphosphorylation and exchange group translocation catalyzed by the enzyme 11 complexes of the bacterial phosphoenolpyruvate: sugar phosphotransferase system. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 25;252(24):8899–8907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele C. F. Glucose transport in Streptococcus mutans: preparation of cytoplasmic membranes and characteristics of phosphotransferase activity. J Dent Res. 1975 Mar-Apr;54(2):330–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachtele D. F., Leung W. L. Effect of sugar analogues on growth, sugar utilization, and acid production by Streptococcus mutans. J Dent Res. 1975 May-Jun;54(3):433–440. doi: 10.1177/00220345750540030301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slee A. M., Tanzer J. M. Phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase activity in Streptococcus mutans NCTC 10449. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):821–828. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.821-828.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Martin E. J., Wittenberger C. L. Characterization of a phosphoenolpyruvate-dependent sucrose phosphotransferase system in Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):865–868. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.865-868.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Martin E. J., Wittenberger C. L. Regulation and function of sucrose 6-phosphate hydrolase in Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1979 Nov;26(2):487–491. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.2.487-491.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. D. Activator specificity of pyruvate kinase from lactic streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1240–1242. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1240-1242.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. Characteristics and energy requirements of an alpha-aminoisobutyric acid transport system in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):719–730. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.719-730.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Chassy B. M. Uptake and metabolism of sucrose by Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):543–551. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.543-551.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. In vivo regulation of glycolysis and characterization of sugar: phosphotransferase systems in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Nov;136(2):465–476. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.2.465-476.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. Lactose metabolism in Streptococcus lactis: phosphorylation of galactose and glucose moieties in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):774–785. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.774-785.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Saier M. H., Jr Regulation of methyl-beta-d-thiogalactopyranoside-6-phosphate accumulation in Streptococcus lactis by exclusion and expulsion mechanisms. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):885–894. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.885-894.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Thomas T. D. Phosphoenolpyruvate and 2-phosphoglycerate: endogenous energy source(s) for sugar accumulation by starved cells of Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1977 May;130(2):583–595. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.2.583-595.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Turner K. W., Thomas T. D. Catabolite inhibition and sequential metabolism of sugars by Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1163–1174. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1163-1174.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Handel E. Determination of fructose and fructose-yielding carbohydrates with cold anthrone. Anal Biochem. 1967 Apr;19(1):193–194. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Steveninck J. Transport-associated phosphorylation of 2-deoxy-D-glucose in yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Nov 5;163(3):386–394. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(68)90123-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]