Abstract
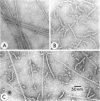
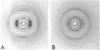
Pili isolated from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAK were solubilized in the detergent octyl-glucoside. Subsequent removal of the detergent by dialysis resulted in the formation of short rods of about 9 nm in diameter and various lengths. The aggregation process was followed by ultracentrifugation, viscometry, and electron microscopy to show that the aggregates produced in this way are distinct from pili produced by the bacteria, both in diameter, as measured by electron micrographs, and in their inability to compete in a biological assay for pili.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron C., Thompson T. E. Solubilization of bacterial membrane proteins using alkyl glucosides and dioctanoyl phosphatidylcholine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;382(3):276–285. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90270-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. A function of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO polar pili: twitching motility. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Feb;26(2):146–154. doi: 10.1139/m80-022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Basic characterization of a Pseudomonas aeruginosa pilus-dependent bacteriophage with a long noncontractile tail. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):1139–1148. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.1139-1148.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E., Pitt T. L. Pilus-dependence of four Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteriophages with non-contractile tails. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. The adsorption of Pseudomonas aeruginosa pilus-dependent bacteriophages to a host mutant with nonretractile pili. Virology. 1974 Mar;58(1):149–163. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90150-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Yang J. T., Martinez H. M. Determination of the secondary structures of proteins by circular dichroism and optical rotatory dispersion. Biochemistry. 1972 Oct 24;11(22):4120–4131. doi: 10.1021/bi00772a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshdat Y., Silverblatt F. J., Sharon N. Dissociation and reassembly of Escherichia coli type 1 pili. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):308–314. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.308-314.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkhard W., Marvin D. A., Watts T. H., Paranchych W. Structure of polar pili from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains K and O. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 15;149(1):79–93. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90261-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost L. S., Paranchych W. Composition and molecular weight of pili purified from Pseudomonas aeruginosa K. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jul;131(1):259–269. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.1.259-269.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay C. M. The presence of beta-structure in concanavalin A. FEBS Lett. 1970 Jul 29;9(2):78–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80317-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D., Sowa B. A., Ippen-Ihler K. Location of an F-pilin pool in the inner membrane. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):251–259. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.251-259.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng Y. C., Dunker A. K. Effects of metabolic inhibitors on the assembly of fd phage. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1981;64:467–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oikawa K., Kay C. M., McCubbin W. D. The ultraviolet circular dichroism of muscle proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 10;168(1):164–167. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90248-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paranchych W., Sastry P. A., Frost L. S., Carpenter M., Armstrong G. D., Watts T. H. Biochemical studies on pili isolated from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Oct;25(10):1175–1181. doi: 10.1139/m79-182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smilowitz H., Carson J., Robbins P. W. Association of newly synthesized major f1 coat protein with infected host cell inner membrane. J Supramol Struct. 1972;1(1):8–18. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts T. H., Kay C. M., Paranchych W. Dissociation and characterization of pilin isolated from Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains PAK and PAO. Can J Biochem. 1982 Sep;60(9):867–872. doi: 10.1139/o82-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willetts N., Skurray R. The conjugation system of F-like plasmids. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:41–76. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.000353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Straus D. C., Johanson W. G., Jr, Berry V. K., Bass J. A. Role of pili in adherence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to mammalian buccal epithelial cells. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):1146–1151. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.1146-1151.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]