Abstract
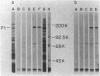
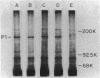
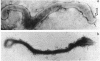
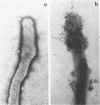
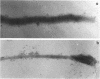
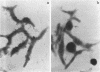
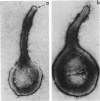
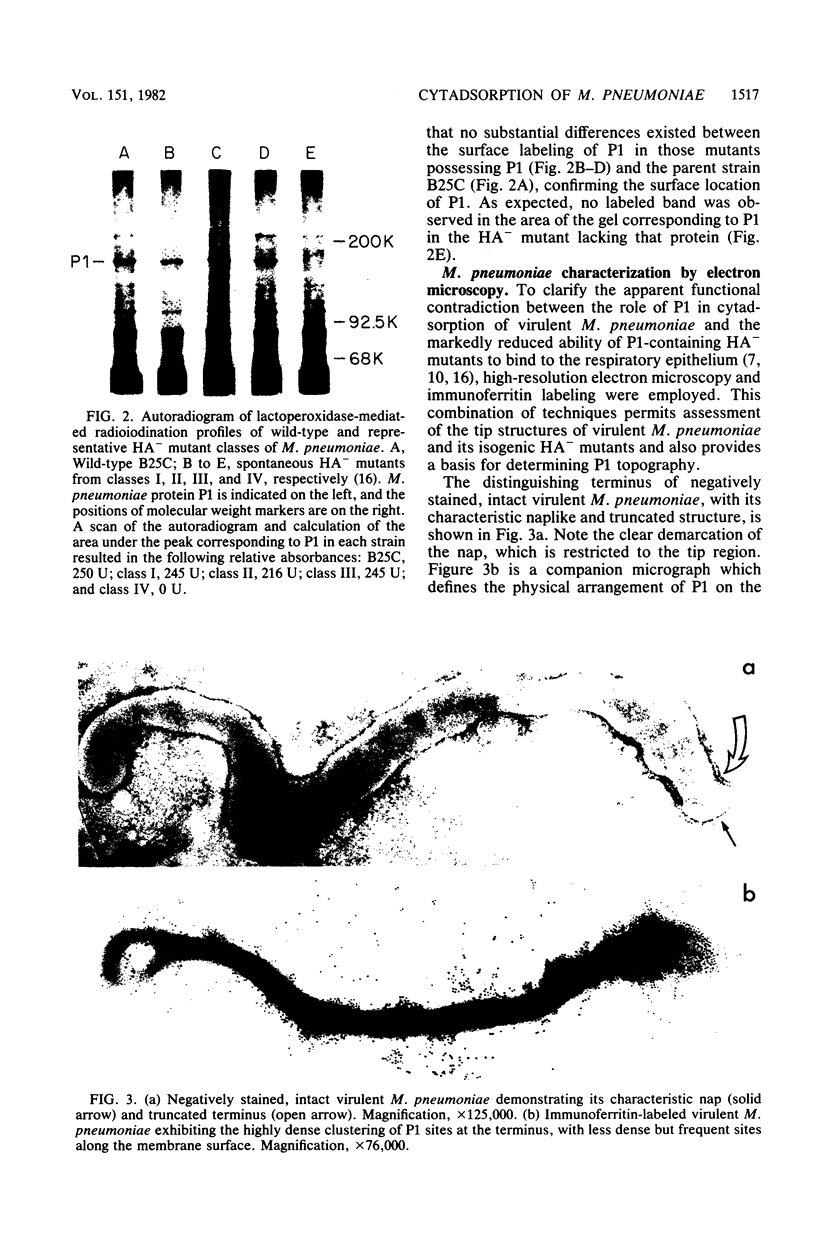
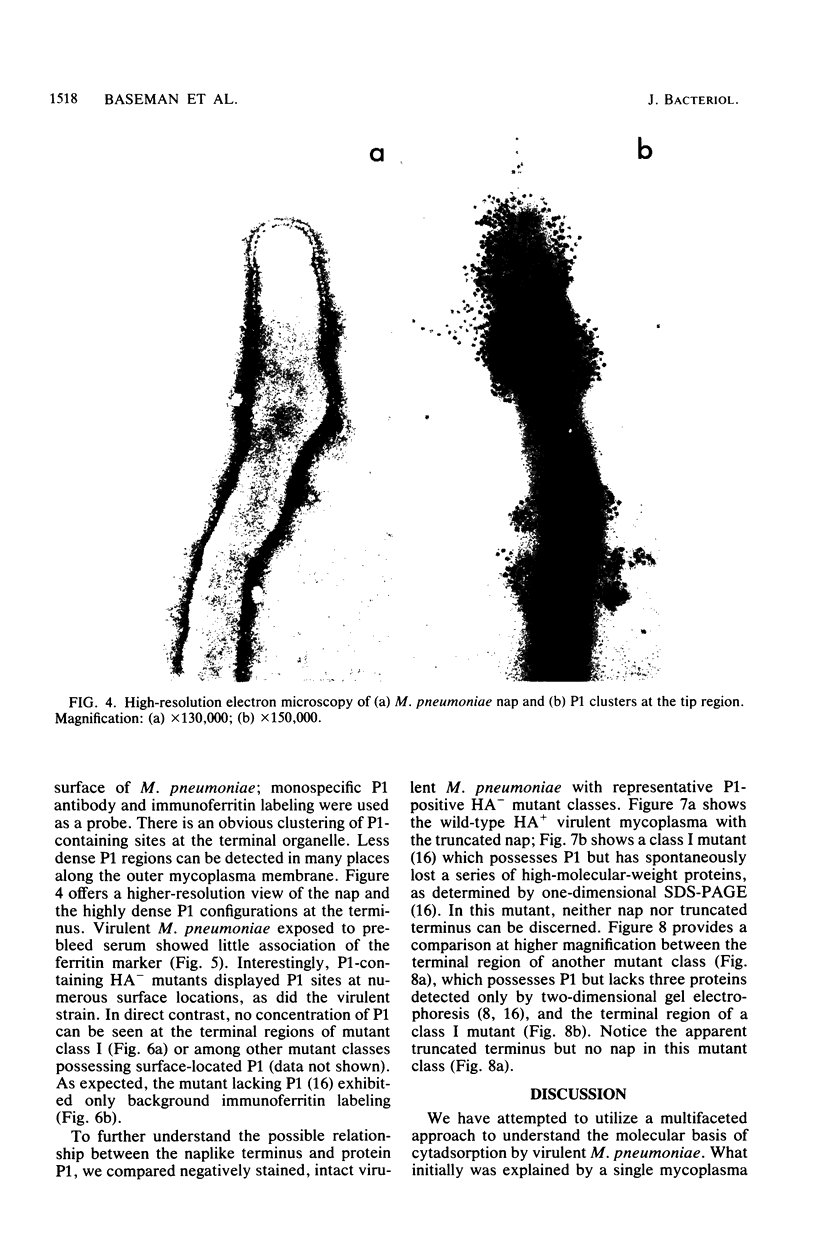
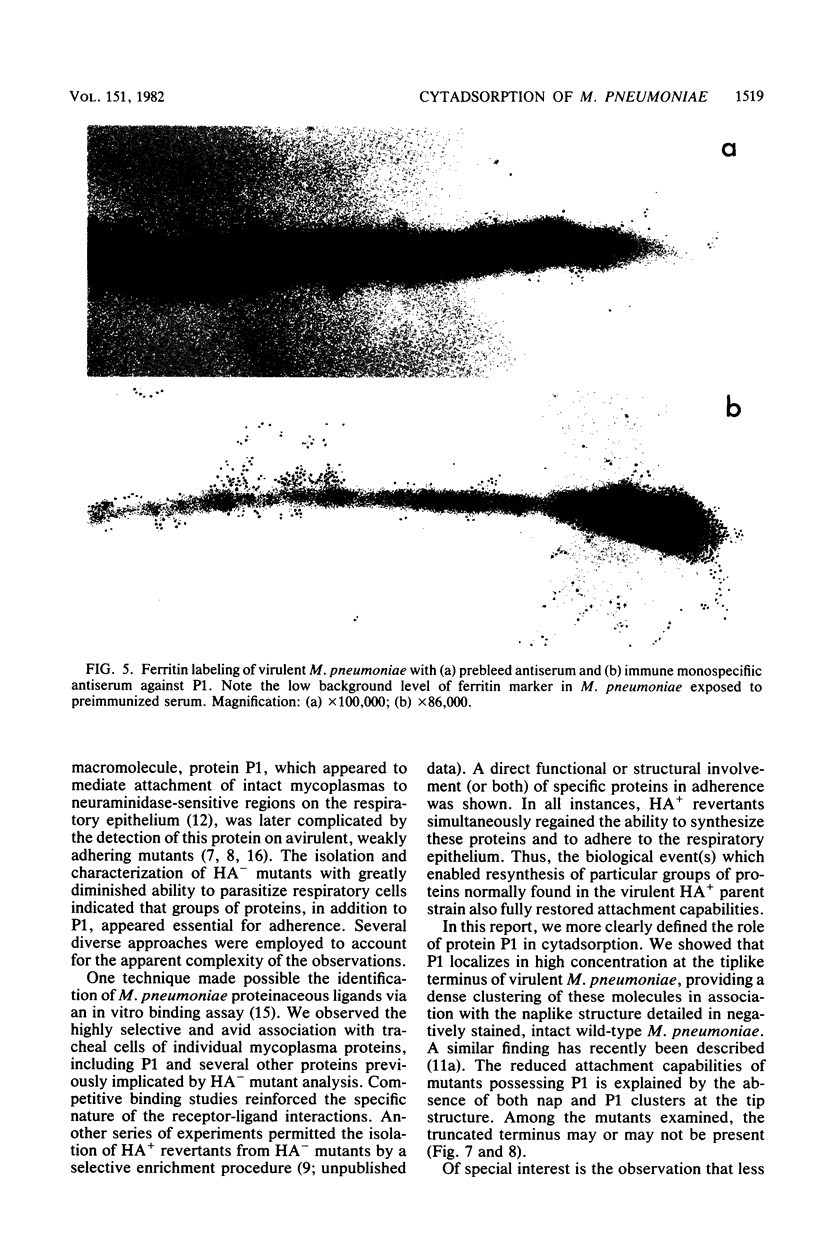
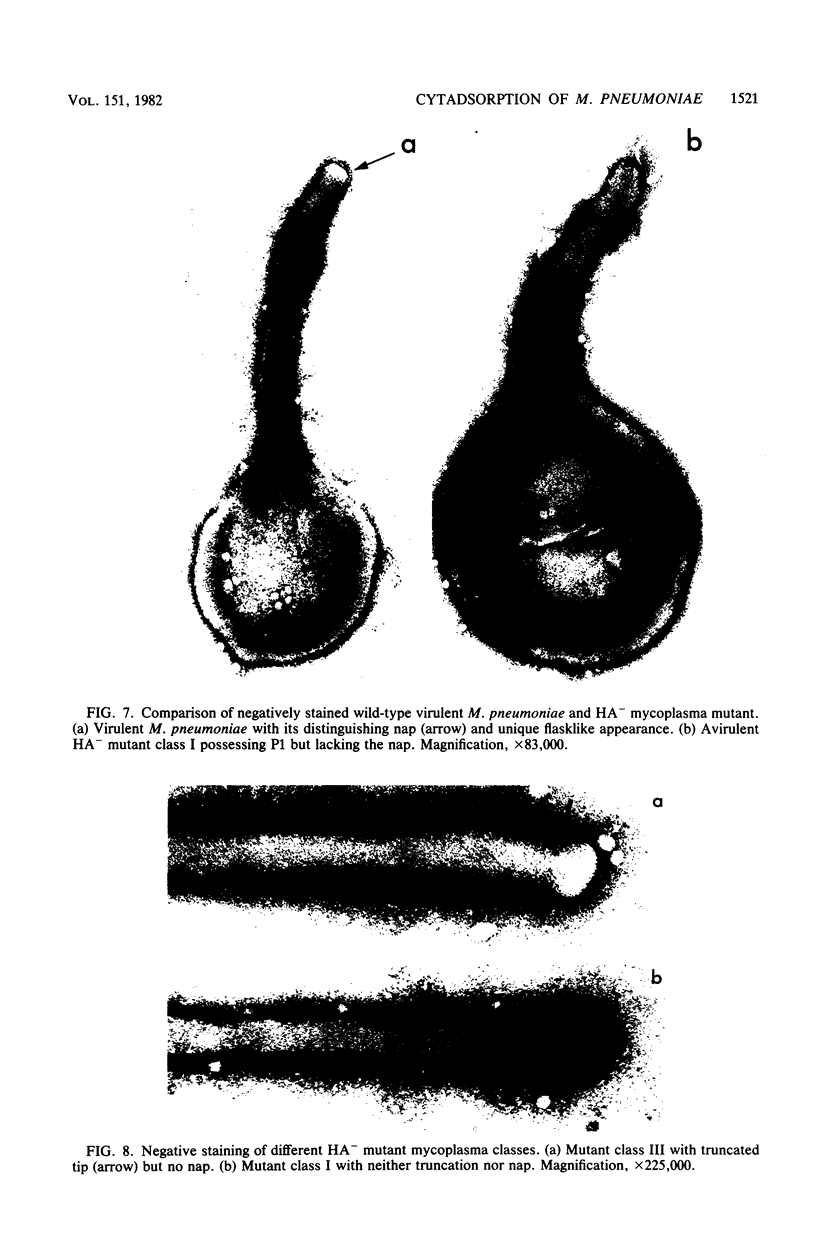
Hemadsorbing (HA+) virulent Mycoplasma pneumoniae and spontaneously derived nonhemadsorbing (HA-) avirulent mutants were compared by biochemical and ultrastructural techniques in an attempt to understand the molecular basis for cytadsorption. Lactoperoxidase-catalyzed iodination of intact mycoplasmas indicated that both virulent and avirulent mycoplasmas displayed similar surface protein patterns. A specific external protein, P1 (molecular weight, 165,000), previously implicated as a major ligand mediating attachment, was readily detected in HA+ and HA- mycoplasma strains. However, immunoferritin electron microscopy, with monospecific antibody against P1, revealed that differences in P1 topography existed among these strains. Only virulent mycoplasmas exhibited high concentrations of P1 at the terminal organelle. Avirulent mycoplasmas which possessed P1 showed no P1 clustering at the terminus. Both virulent M. pneumoniae and avirulent P1-containing mutants possessed numerous less dense P1 regions along the mycoplasma surface. Not surprisingly, an HA- mutant lacking P1 exhibited only background immunoferritin labeling. Negative staining of intact mycoplasmas revealed a well-defined, naplike terminus (associated with P1 clusters) confined at the tip of virulent M. pneumoniae. Previous characterization of HA+ virulent and HA- avirulent strains of M. pneumoniae by one- and two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis suggests that identified groups of mycoplasma proteins, lacking in specific HA- mycoplasmas, regulate the physical arrangement of P1 and the ultrastructure of the terminus, thus influencing adherence to the respiratory epithelium and virulence.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baseman J. B., Hayes E. C. Molecular characterization of receptor binding proteins and immunogens of virulent Treponema pallidum. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):573–586. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biberfeld G., Biberfeld P. Ultrastructural features of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):855–861. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.855-861.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner H., Krauss H., Schaar H., Schiefer H. G. Electron microscopic studies on the attachment of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to guinea pig erythrocytes. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):906–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.906-911.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabridge M. G., Taylor-Robinson D., Davies H. A., Dourmashkin R. R. Interaction of Mycoplasma pneumoniae with human lung fibroblasts: characterization of the in vitro model. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):446–454. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.446-454.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Wilson R. M., Baseman J. B. Hemadsorption and virulence of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;134:241–251. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0495-2_23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Wilson R. M., Baseman J. B. Isolation of mutants of Mycoplasma pneumoniae defective in hemadsorption. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):903–906. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.903-906.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Wilson R. M., Baseman J. B. Two-dimensional gel electrophoretic comparison of proteins from virulent and avirulent strains of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):468–475. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.468-475.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Wilson R. M., Clyde W. A., Jr, Baseman J. B. Characterization of hemadsorption-negative mutants of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):127–136. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.127-136.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. Tissue cultures and mycoplasmas. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Jun;23(Suppl):285+–285+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Cole R. M., Huang Y. S., Graham J. A., Gardner D. E., Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection: role of a surface protein in the attachment organelle. Science. 1982 Apr 16;216(4543):313–315. doi: 10.1126/science.6801766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Surface parasitism by Mycoplasma pneumoniae of respiratory epithelium. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1328–1343. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane I., Pnini S., Banai M., Baseman J. B., Cassell G. H., Bredt W. Attachment of mycoplasmas to erythrocytes: a model to study mycoplasma attachment to the epithelium of the host respiratory tract. Isr J Med Sci. 1981 Jul;17(7):589–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Cell membrane antigen isolation with the staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 Pt 1):1482–1490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause D. C., Baseman J. B. Mycoplasma pneumoniae proteins that selectively bind to host cells. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):382–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.382-386.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause D. C., Leith D. K., Wilson R. M., Baseman J. B. Identification of Mycoplasma pneumoniae proteins associated with hemadsorption and virulence. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):809–817. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.809-817.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. A., Hu P. C., Wilson M., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Attachment of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to respiratory epithelium. Infect Immun. 1976 Mar;13(3):959–966. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.3.959-966.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin S. Mycoplasmas: the smallest pathogenic procaryotes. Isr J Med Sci. 1981 Jul;17(7):510–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Stinchcomb D., Losick R. Antibody directed against Bacillus subtilis rho factor purified by sodium dodecyl sulfate slab gel electrophoresis. Effect on transcription by RNA polymerase in crude extracts of vegetative and sporulating cells. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8824–8828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully J. G., Whitcomb R. F., Clark H. F., Williamson D. L. Pathogenic mycoplasmas: cultivation and vertebrate pathogenicity of a new spiroplasma. Science. 1977 Mar 4;195(4281):892–894. doi: 10.1126/science.841314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. H., Collier A. M. Ultrastructural study of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in organ culture. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jan;125(1):332–339. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.1.332-339.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]