Abstract
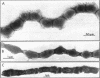
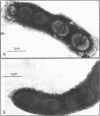
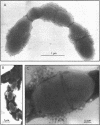
Choline-containing teichoic acid seems to be essential for the adsorption of bacteriophage Dp-1 to pneumococci. This conclusion is based on the following observations: In contrast to pneumococci grown in choline-containing medium, cells grown in medium containing ethanolamine or other submethylated aminoalcohols instead of choline were found to be resistant to infection by Dp-1. Live choline-grown bacteria and heat- or UV-inactivated cells and purified cell walls prepared from these cells were capable of adsorbing phage Dp-1; ethanolamine-grown pneumococci or cell wall preparations were unable to do so. Adsorption of Dp-1 to choline-containing cell walls was competitively inhibited by phosphorylcholine and by several choline-containing soluble cell surface components, such as the Forssman antigen and the teichoic acid-glycan complexes formed by autolytic cell wall degradation. Cell walls prepared from pneumococci grown in ethanolamine or phosphorylethanolamine were inactive. Electron microscopic studies with pneumococci that had segments of choline-containing cell wall material amid ethanolamine-containing regions indicated that the Dp-1 phage particles adsorbed exclusively to the choline-containing surface areas. We suggest that the choline residues of the pneumococcal teichoic acid are essential components of the Dp-1 phage receptors in this bacterium.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archibald A. R. Cell wall assembly in Bacillus subtilis: development of bacteriophage-binding properties as a result of the pulsed incorporation of teichoic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):956–960. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.956-960.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald A. R., Coapes H. E. Bacteriophage SP50 as a marker for cell wall growth in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1195–1206. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1195-1206.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles E. B., Tomasz A. Pneumococcal Forssman antigen. A choline-containing lipoteichoic acid. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 25;248(18):6394–6397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles E. B., Tomasz A. Radioautographic evidence for equatorial wall growth in a gram-positive bacterium. Segregation of choline-3H-labeled teichoic acid. J Cell Biol. 1970 Dec;47(3):786–790. doi: 10.1083/jcb.47.3.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee A. N. Use of bacteriophage-resistant mutants to study the nature of the bacteriophage receptor site of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):519–527. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.519-527.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemphill H. E., Whiteley H. R. Bacteriophages of Bacillus subtilis. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Sep;39(3):257–315. doi: 10.1128/br.39.3.257-315.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Tomasz A. Purification of the pneumococcal N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase to biochemical homogeneity. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4199–4207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Tomasz A. Specific recognition of choline residues in the cell wall teichoic acid by the N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase of Pneumococcus. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6072–6076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel V., Rosen H., Levine M. Binding of bacteriophage P22 tail parts to cells. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1152–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1152-1158.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez R., Ronda C., Tomasz A., Portoles A. Properties of "diplophage": a lipid-containing bacteriophage. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):201–210. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.201-210.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mcdonnell M., Lain R., Tomasz A. "Diplophage": a bacteriophage of Diplococcus pneumoniae. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):577–582. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90329-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser J. L., Tomasz A. Choline-containing teichoic acid as a structural component of pneumococcal cell wall and its role in sensitivity to lysis by an autolytic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jan 25;245(2):287–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rane L., Subbarow Y. Nutritional Requirements of the Pneumococcus: I. Growth Factors for Types I, II, V, VII, VIII. J Bacteriol. 1940 Nov;40(5):695–704. doi: 10.1128/jb.40.5.695-704.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Cellular metabolism in genetic transformation of pneumococci: requirement for protein synthesis during induction of competence. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):860–871. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.860-871.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Choline in the cell wall of a bacterium: novel type of polymer-linked choline in Pneumococcus. Science. 1967 Aug 11;157(3789):694–697. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3789.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Model for the mechanism controlling the expression of competent state in Pneumococcus cultures. J Bacteriol. 1966 Mar;91(3):1050–1061. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.3.1050-1061.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Westphal M., Briles E. B., Fletcher P. On the physiological functions of teichoic acids. J Supramol Struct. 1975;3(1):1–16. doi: 10.1002/jss.400030102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young F. E. Requirement of glucosylated teichoic acid for adsorption of phage in Bacillus subtilis 168. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2377–2384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzopulos J., DeLong S., Chapman V., Kozloff L. M. Bacteriophage T4D receptor and the Escherichia coli cell wall structure: binding of endotoxin-like particles to the cell wall. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):982–991. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.982-991.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzopulos J., Kozloff L. M., Chapman V., DeLong S. Bacteriophage T4D receptors and the Escherichia coli cell wall structure: role of spherical particles and protein b of the cell wall in bacteriophage infection. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):545–555. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.545-555.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]