Vol. 201, No. 12, June 20, 2005. Pages 1973–1985.
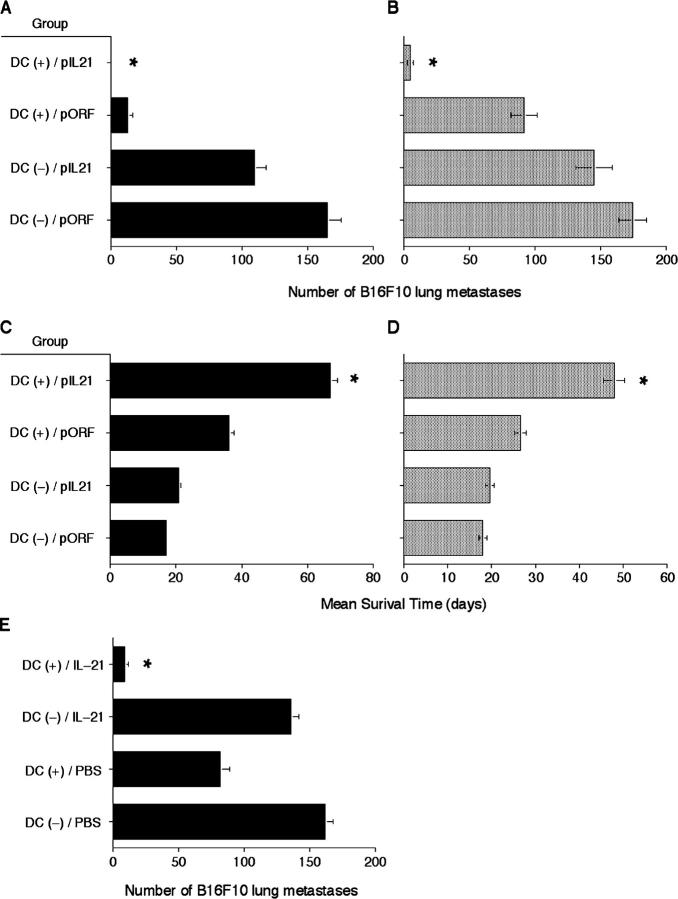
The legend for Fig. 7 contained errors regarding the schedule of treatments administered. Fig. 7 and the corrected legend appear below.
Figure 7.
α-GalCer/DC/IL-21 combination mediates extremely potent suppression of tumor metastases. Groups of five C57BL/6 WT mice were injected i.v. with 5 × 105 B16F10 tumor cells. Mice were treated: (A and C) on day 4 i.v. with 5 × 105 α-GalCer–pulsed DC (+) or vehicle-pulsed DC (−) and on day 7 i.v. with 20 μg of either pORF or pIL21 DNA plasmid as indicated; and (B and D) on day 8 i.v. with 5 × 105 α-GalCer–pulsed DC (+) or vehicle-pulsed DC (−) and on day 11 i.v. with 20 μg of either pORF or pIL21 DNA plasmid; and (E) on day 8 i.v. with 5 × 105 α-GalCer–pulsed DC (+) or vehicle pulsed DC (−) and on day 11, 12, and 13 with 50 μg of recombinant mouse IL-21 or PBS as indicated. In some experiments (A, B, and E) 14 d after tumor inoculation the lungs of these mice were harvested and tumor colonies counted and recorded as the mean number of colonies ± SEM. Asterisks indicate the groups where combined α-GalCer/DC/IL-21 treatment significantly reduced that group's number of lung metastases compared with all other groups (Kruskal-Wallis: *P < 0.05). In other experiments (C and D) the survival of these mice was monitored and recorded as the mean survival time (days) ± SEM. Asterisks indicate the groups where combined α-GalCer/DC/pIL21 treatment significantly increased that group's survival compared with all other groups (Kruskal-Wallis: *P < 0.05). Results are representative of two experiments performed.