Abstract
Decay-accelerating factor (Daf) dissociates C3/C5 convertases that assemble on host cells and thereby prevents complement activation on their surfaces. We demonstrate that during primary T cell activation, the absence of Daf on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and on T cells enhances T cell proliferation and augments the induced frequency of effector cells. The effect is factor D- and, at least in part, C5-dependent, indicating that local alternative pathway activation is essential. We show that cognate T cell–APC interactions are accompanied by rapid production of alternative pathway components and down-regulation of Daf expression. The findings argue that local alternative pathway activation and surface Daf protein function respectively as a costimulator and a negative modulator of T cell immunity and explain previously reported observations linking complement to T cell function. The results could have broad therapeutic implications for disorders in which T cell immunity is important.
Complement directly destroys invading pathogens and is a source of anaphylatoxins that attract phagocytic cells to sites of insult (1). In adaptive immune responses, it is the effector system for antibody-mediated immunity. Previous studies have indicated that complement influences alloimmune, autoimmune, antiviral, and antitumor T cell responses (2–5), but these observations remain largely unexplained. Because protective antiviral and antitumor T cell reactivity as well as T cell memory are highly dependent on the size of the induced effector T cell repertoire (6–8), clarifying how complement shapes the effector T cell repertoire has broad biological and clinical implications.
Decay-accelerating factor (Daf) is a ubiquitously expressed intrinsic complement-regulatory protein whose function is to dissociate C3/C5 convertases on host-cell surfaces (9), thereby limiting local C3a/C5a anaphylatoxin production and C3b/C5b-initiated progression of the cascade. Daf also has been identified as a ligand for CD97, a leukocyte- and endothelial cell-associated member of the epidermal growth factor family of proteins, which has been identified as a Daf adhesin for attracting leukocytes (10, 11). Although it is known that Daf, a glycophosphatidylinositol-anchored protein (12, 13), is expressed in lipid rafts on T lymphocytes and can be found in the general proximity of the TCR complex (14, 15), no direct or indirect role for Daf in controlling T cell immunity has previously been described. Here we report the unanticipated findings that Daf modulates T cell immunity by controlling T cell– and APC-induced alternative pathway C3 activation during cognate interactions.
Results And Discussion
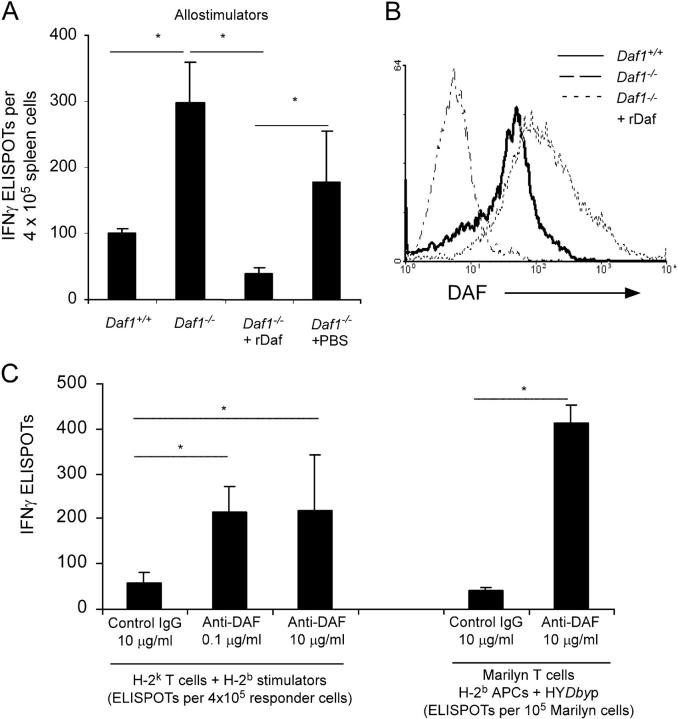
To address whether Daf influences cellular immune responses, we studied splenocytes obtained from mice made genetically deficient in the Daf1 gene (Daf1 −/−, H-2 b) and from Daf1 + / + littermates. Initial studies, using mixed lymphocyte cultures in which H-2 b Daf1−/− or control Daf1 + / + spleen cells were stimulated with allogeneic H-2 k spleen cells in vitro, revealed that Daf1 − / − cells responded more vigorously than did control Daf1 + / + cells (Fig. 1 A). Reconstitution of Daf1 − / − spleen cells with lipid-tailed mouse Daf protein attenuated the increased responsiveness (Fig. 1, A and B), verifying that the effects were specific to Daf deficiency. Substantiating this interpretation, the addition of anti-Daf mAb 2C6 specifically increased the number of induced alloreactive, WT effector T cells (Fig. 1 C).
Figure 1.
Daf deficiency/blockade augments cellular immunity in vitro. (A) IFNγ ELISPOT assays for Daf1 − / − splenocytes (± reconstitution using lipid-tailed murine rDaf) or Daf1 +/+ splenocytes versus allogeneic H-2 k spleen cells. (B) Flow cytometry of Daf expression levels on cells in A. (C) WT H-2 k T cells stimulated with allogeneic H-2 b spleen cells (left) or Mar TCR transgenic T cells stimulated with HYDby peptide-loaded H-2bAPCs (right) with or without anti-Daf mAb 2C6 or control IgG in IFNγ ELISPOT assays. Means and SD (n = 3–5/group) shown are representative of 2–4 independent experiments; *, P < 0.05.
To differentiate antigen-induced versus bystander effects of Daf inhibition on T cell activation, we performed studies using TCR transgenic T cells. The frequency of peptide-activated TCR transgenic Mar T cells (C57BL/6, H-2 b, RAG2 − / − , specific for male antigen HYDby) was similarly increased in the presence of anti-Daf mAb but not of control mAb (Fig. 1 C).
We next evaluated in vivo T cell responses induced to the male antigen, HY. H-2 b female mice reject H-2 b male skin grafts using T cells specific for class II MHC–restricted HYDby and class I MHC–restricted HYUty (16). As shown in Fig. 2 A, transplantation of Daf1 − / − females with Daf1 − / − male skin grafts resulted in a 1.5- and threefold increased frequency of anti-HY CD4 and CD8 T cells, respectively, when compared with control Daf1 +/+ females engrafted with Daf1 +/+ male skin. For the CD4 response, the absence of Daf on either the donor or the recipient similarly enhanced T cell immunity; for the CD8 response, a greater effect was noted when the recipient was Daf1 − / − (Fig. 2 A). The increased frequency of anti-HY T cells was associated with a 2-d acceleration of graft destruction (median survival, 14 d for Daf1 +/+ to Daf1 +/+ vs. 12 d for Daf1 −/− to Daf1 −/−, Daf1 +/+ to Daf1 −/−, or Daf1 −/− to Daf1 +/+; n = 4–8/group; P < 0.05). Similarly, alloreactive T cells in recipient C3H mice (H-2 k) primed at >10-fold higher frequencies to allogeneic Daf1 −/− (8500 / 106 anti-H-2 b IFNγ-producers) versus Daf1 +/+ (520/106 anti-H-2 b IFNγ producers; n = 3/group; P < 0.05) heart grafts.
Figure 2.

Deficiency of Daf protein augments cellular immunity in vivo. (A) IFNγ ELISPOT assays were performed at rejection of male to female skin grafts (+/+, Daf1 + / +; −/−, Daf1 − / −) to assess reactivity to male peptides HYDby (left) and HYUty (right). Each symbol represents an individual animal (mean of triplicate wells, SD < 15%). –, means for all animals per group (n = 4–8); *, P < 0.05 versus Daf1 +/+ to Daf1 +/+. No response (<10 IFNγ producers/500,000 cells) was detected in any animal to control antigens OVA323-339 and β-gal96-103, and no responses were detected in naive mice (not depicted). (B) Spleen cell responses by IFNγ ELISPOT 12 d (top) or 30 d (bottom) after immunization of Daf1 − / − or Daf1 +/+ mice with HYDby peptide plus CFA. No response was detected to control antigens (not depicted). Means plus SD for three to five animals/group are shown. The results are fully representative of two to four independent experiments. *, P < 0.05.
We next immunized Daf1 −/− and control females with the HYDby peptide and tested for recall responses at d 12 and d 30 (Fig. 2 B). At both time points, the frequency of splenic HYDby-specific IFNγ producers was significantly higher in the Daf1 −/− mice. Immunization also induced stronger responses to OVA323-339 and to MOG35-55 in Daf1 −/− mice compared with controls (3–5-fold at 12 and 30 d after immunization; unpublished data). In combination, these experiments argued that T cell immunity induced by proinflammatory stimuli is augmented in the absence of Daf.
We next asked how APC-expressed (as opposed to T cell-expressed) Daf affects T cell reactivity. H-2 b Daf1−/− splenic stimulators primed approximately sixfold higher frequencies of alloreactive IFNγ-secreting C3H (H-2 k) effector T cells than control Daf1 + / + H-2 b spleen cells (Fig. 3 A). This effect was abrogated by incorporation of recombinant lipid-tailed mouse Daf onto the surface of the Daf1 −/− spleen cells (Fig. 3 A). Although these data were obtained using APCs from mice backcrossed four generations to C57BL/6, similar results were obtained using splenic APCs from ninth-generation backcross Daf1 − / − (101 ± 18/105 C3H T cells) and Daf1 + / + littermates (45 ± 11/105 C3H T cells; P < 0.05). Responder C3H T cells also proliferated more vigorously both in vitro and in vivo (Fig. 3, B and C) when stimulated with allogeneic Daf1 − / − APCs versus Daf1 + / + APCs. Female Mar T cells responded up to fivefold more vigorously, both in vitro (Fig. 3 D) and in vivo (Fig. 3 E), when stimulated with male H-2 b stimulator cells from Daf1 − / − mice than from Daf1 + / + controls, confirming an antigen-specific effect. Mar cells also responded at higher frequency in vitro to splenic APCs from ninth-generation backcross by 5,6-carboxy-2,7-dechlorofluorescein (CFSE) proliferation (3.01% vs. 0.49% of Mar cells divided >2 times in Daf1 − / − vs. Daf1 + / +, respectively) and ELISPOT (127 ± 12 IFNγ producers/104 cells with Daf1 − / − APCs vs. 46 ± 5 with Daf1 + / +APCs. P < 0.05).
Figure 3.
Daf1 −/− APCs augment T cell immunity in vitro and in vivo via alternative complement activation. (A) H-2 k T cells mixed with allogeneic H-2 b splenic stimulators with or without rDaf were tested in IFNγ ELISPOT assays (means plus SD; n = 3 replicates/group). (B) Proliferation of CFSE-labeled WT H-2 k T cells versus allogeneic Daf1 − / − or Daf1 +/+ macrophages on d 5. The precursor frequencies of responding T cells were 1.01% (4.1% underwent more than three divisions) against Daf1 − / − cells versus 0.07% against Daf1 +/+ cells (1.1% underwent more than three divisions). (C) Proliferation of splenic CFSE-labeled H-2 k T cells on day 5 after injection into allogeneic hosts. The mean numbers of transferred cells that underwent more than three cell divisions (n = 3 animals/group) are shown. (D) IFNγ ELISPOT production by Mar T cells stimulated with 10 μM HYDby plus spleen cells. (E) Proliferation of CFSE-labeled Vβ6+ Mar T cells 3 d after adoptive transfer into indicated mice (3 × 106 cells/mouse). (Left) representative plots gated on CFSE+ Vβ6+ cells (inset: % Mar cells/spleen). (Right) quantified means (n = 3 animals/group). (F, left) Daf1 +/+ or Daf1 −/− mice were immunized with OVA323-339 plus anti-C5 mAb or control (1 mg i.p. every other day), and recall assays to OVA323-339 (0.1 μM) were performed by ELISPOT on d 16. *, P < 0.05 versus the response in Daf1 − / − mice. Right: 3-d in vitro IFNγ ELISPOT assays of H-2 k T cells versus Daf1 +/+ or Daf1 − / − APCs plus 100 μg/ml anti-C5 mAb or control (top) or H-2 k T cells versus Daf1 +/+ spleen cells plus recombinant C5a (bottom). *, P < 0.05 versus control. Each result is representative of three individual experiments.
We next asked if the absence of Daf on T cells affects the induced T cell immune response. As assessed by IFNγ ELISPOT (Fig. 4 A) or CFSE dilution (not depicted), Daf1 − / − T cells responded more vigorously than Daf1 + / + T cells to Daf1 + / + allogeneic stimulator cells. Moreover, Thy1.2+ Daf1 − / − T cells responded to in vivo immunization more vigorously than Thy1.2+ Daf1 + / + T cells when the T cells were transferred into congenic Thy1.1+ Daf1 + / + recipients (the Thy1.1 and Thy1.2 antigens allowed differentiation of the transferred T cells from the endogenous T cells; Fig. 4 B). The effect was similar but smaller in magnitude than when Daf protein was deficient on the APCs (Fig. 3).
Figure 4.

Daf deficiency on T cells enhances T cell responsiveness. (A) Purified T cells were mixed with WT allogeneic H-2 k splenic stimulator cells in IFNγ ELISPOT assays. (B) T cell–depleted WT Thy1.1 (H-2 b) females were given adoptive transfers of 7.5 × 106 unfractionated, purified splenic T cells isolated from Thy1.2+ Daf1 +/+ or Daf1 − / − mice. The reconstituted hosts were immunized with HYDby plus CFA, and recall IFNγ ELISPOT assays (means plus SD; n = 3/group) were performed 21 d later. Flow cytometry confirmed that all IFNγ derived from the Thy1.2+ cells (not depicted). *, P < 0.05.
To determine if the augmenting effect of Daf deficiency relates to work published in the 1980s that Daf cross-linking transmits a proliferative signal (17), we tested in vitro female responses to HYDby. 5 d of in vitro culture with HYDby peptide induced a significantly higher frequency of effector IFNγ producers from Daf1 − / − splenocytes compared with Daf1 + / + spleen cells (52 ± 9 vs. 13.8 ± 4/200,000 spleen cells; mean of n = 4/group; P < 0.05). Frequencies of HYDby-reactive IFNγ and IL-2 producers were identical (<1 in 300,000) in naive Daf1 − / − and Daf1 + / + spleens at the start of the culture. Thus, the enhanced T cell immunity must be attributed to the absence of Daf and not to a Daf-transmitted proliferative signal.
Because C3 deficiency has been found to limit T cell reactivity in vivo (3, 5, 18), and because Daf's known function is to circumvent C3 deposition on host cells (1, 9), we investigated whether the enhanced T cell responsiveness generated in the absence of Daf could at least in part be mediated via a C3-dependent process. Factor D is essential for assembly of the alternative pathway C3 convertase (C3bBb; reference 1), which is dissociated by Daf (9). Splenocytes genetically deficient in factor D or doubly deficient in factor D and Daf primed allogeneic IFNγ producers at frequencies lower or comparable to spleen cells obtained from Daf1 + / + mice (Fig. 3 A). The enhanced expansion either of polyclonal allogeneic T cells (Fig. 3 C) or Mar TCR transgenic T cells (Fig. 3 E) in Daf1 − / − male mice did not occur in vivo in male mice doubly deficient in Daf and factor D. Mar cells responded similarly in factor D–deficient and WT males (Fig. 3 D). In contrast, although CD97 is a ligand for Daf, addition of blocking anti-CD97 mAb (11) had essentially no effect on the induced frequency of effector T cells in an in vitro assay (140–160 alloreactive IFNγ-producing T cells/400,000 responders ± 0–10 μg/ml anti-CD97 mAb 1B2 or control; unpublished data).
Because the absence of Daf disables cell-surface C3 and C5 convertase regulatory activity, and because there is a report that C5a can influence T cell immunity (19), we tested whether C5 is involved in the enhanced T cell responsiveness. As shown in Fig. 3 F, anti-C5 mAb partially abrogated the enhanced in vivo T cell responsiveness in Daf1 − / − mice after immunization and partially blocked the augmented T cell alloimmunity primed in vitro by Daf1 − / − APCs. Addition of C5a to in vitro cultures enhanced T cell responsiveness (Fig. 3 F).
Because of the previously described findings implicating complement, we next evaluated synthesis of alternative pathway complement components by T cells and APCs during cognate interactions. We established an MLR in serum-free medium, separated the T cells and APCs by flow sorting at different time points, and performed quantitative RT-PCR for C3, factor B, and factor D on each population. These studies showed that both T cells and APCs markedly up-regulated synthesis of all three components within 1 h of interaction (Fig. 5 A). Similar results were detected when Mar TCR transgenic T cells were stimulated with syngeneic macrophages plus HYDby peptide (but not OVA323-339; unpublished data). In accordance with the increased gene expression, stimulation of Mar T cells with HYDby-peptide–loaded macrophages induced C3 protein as detected by immunoelectron microscopy (Fig. 5 B). Antigen-specific T cell/APC mixing, as well as anti-CD3 stimulation of polyclonal T cells, generated C3, factor B, and factor D proteins in serum-free culture supernatants as assessed by zymosan C3b uptake assays (Fig. 5 C). Western blotting with specific antibodies further verified the complement component production by T cells as well as by APCs (Fig. 5 D).
Figure 5.
T cells and APCs produce complement components during cognate interactions. (A) H-2 k T cells were mixed with allogeneic peritoneal macrophages, flow sorted at predetermined time points, tested for complement expression by quantitative RT-PCR, and compared with unstimulated controls. (B) Electron micrograph of immunostaining using gold–anti-C3 of Mar T cells mixed with female H-2 b peritoneal macrophages plus HYDby peptide (top) or OVA323-339 (bottom). Note gold particles (arrowheads) only in the HYDby peptide-stimulated sample. T, T cell; M, macrophage. Bar, 200 μm. (C) C3, factor B, and factor D in serum-free culture supernates of Mar T cells mixed with HYDby-loaded APCs overnight before (top) and after (middle) cell sorting and reculturing for an additional 3 h. Data are plotted as relative increase over OVA323-339-stimulated controls. C3, factor B, and factor D in serum-free culture supernates of H-2 k T cells stimulated overnight with anti-CD3 (bottom panel), expressed as fold increase over controls. (D) Western blots for factor B (fB, top) and C3 (bottom) in culture supernatants of Mar T cells stimulated with WT or C3 − / − splenic APCs and HYDby peptide or OVA323-339. Densitometry revealed 20% increase in C3 and 175% increase in factor B with HYDby peptide versus OVA323-339. +, positive control (normal mouse serum); —, negative control (serum from fB − / − /Crry − / − or C3−/− mice). E. Plots of Daf expression on macrophages at 0, 24, and 48 h after mixing with Mar T cells plus HYDby peptide or OVA323-339. All results are representative of experiments performed at least two or three times.
Overall, our findings that (a) T cells proliferate into an expanded number of effector cells in the absence of Daf, (b) the effects of Daf deficiency are abrogated in the absence of factor D, (c) the augmented responsiveness is reduced by anti-C5 mAb, and (d) T cell responsiveness is increased by C5a uncover an important role for complement and Daf as modulators of T cell immunity.
The precise mechanisms by which APC- and/or T cell–produced complement activation fragments participate in costimulation remains to be characterized fully. Although our data demonstrate a role for C5 (see Fig. 3 F) potentially through C5a, a finding consistent with previous reports that C5aR inhibition diminishes antiviral immunity (19), the molecular basis of complement–T cell interactions may be multifactorial. There are reports that CR1 blockade inhibits in vitro T cell activation (20–22), and there are reports that the absence of C3a receptor on APCs decreases Th1 immunity (23). Deposited C3b or other complement split products during T cell–APC interactions also could stimulate T cells during antigen-induced activation (21). Control experiments have shown Daf deficiency does not affect surface expression of costimulatory molecules on CpG-activated macrophages or DCs (unpublished data).
Enhanced T cell responsiveness in the absence of Daf potentially has several implications. In addition to the accelerated kinetics of rejection (Fig. 2), other studies have shown that MOG35-55-induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis is more severe in Daf1 − / − mice, indicating that Daf may be important in T cell autoimmunity (unpublished data). Our data reveal that the augmented immunity persists for at least 30 d (Fig. 2), but we have not yet fully addressed the longevity of the memory response.
Although our data generated in Daf1 − / − mice implicate that Daf is important in T cell responsiveness via effects on complement activation, the physiological mechanism is not established. Flow cytometric analysis showed down-regulated surface expression of Daf on APCs during antigen-specific, cognate interactions between Marilyn (Mar) T cells and macrophages (see Fig. 5 E). These findings are consistent with previously reported analyses (24) that, after superantigen administration, isolated splenic T cell mRNAs for common T cell–signaling molecules were markedly increased at 8 h, but mRNA for Daf was decreased 10-fold.
In summary, in addition to providing a possible explanation for previous reports (2–4, 6, 21, 23, 25), our data raise the possibility that Daf expression could be genetically or pharmacologically manipulated for therapeutic purposes.
Materials and Methods
Mice.
Daf1 −/− (H-2 b) mice and littermate controls backcrossed to C57BL/6 four or nine generations were produced as described previously (25). Factor D − / − mice were intercrossed with the Daf1 −/− mice. Female Mar-Rag2 − / − mice (H-2 b; reference 26) were a gift from P. Matzinger (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD). Remaining mice were purchased from Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories. Animals were used under approved animal protocols. Skin graft transplantation was performed as described previously (27, 28).
IFNγ ELISPOT assays.
Cytokine-secreting spleen or purified T cells (>93% CD3+; columns obtained from R&D Systems) were quantified by IFNγ or IL-2 ELISPOT as described previously (27, 28) with or without anti-C5 mAb (clone BB5.1; Alexion), anti-Daf mAb (25) (2C6; B.P. Morgan, Cardiff University, Cardiff, Wales, UK), isotype control, or recombinant mouse C5a (Cell Sciences). Daf expression was reconstituted on Daf1 −/− cells using a lipid-tailed Daf molecule (N-(myristoyl)GSSKSPSKKKKKKPGDC-(S-2-thiopyridyl) C-amide (R.A.G. Smith, Inflazyme Pharmaceuticals, Richmond, BC, Canada) added to the free carboxyl-terminal Cys of mouse Daf CCP1-4 (supplemental text is available at http://www.jem.org/cgi/content/full/jem.20041967/DC1). Peptides were synthesized by Research Genetics. In vitro experiments were performed in serum-free HL-1 medium (Cambrex Bioproducts).
Proliferation assays.
CFSE-stained T cells (27) were mixed with spleen cells or thioglycollate-induced peritoneal macrophages. For in vivo stimulation, 3 × 106 CFSE-labeled cells were injected into the tail vein of sublethally irradiated (400 rad) mice and analyzed 3 d later. The percentage of responding cells was calculated as described previously (27). All other antibodies were obtained from BD Biosciences. Cells were stained (27, 28) and analyzed on a Becton Dickinson FACScan.
In vivo T cell transfer and immunization.
Female C57BL/6 Thy1.1 (Daf1 + / +) mice CD4- and CD8-depleted with GK1.5/YTS 191 plus TIB 105/YTS 169.4 on days −3, −2, and −1. 7.5 × 106 Daf1 + / + or Daf1 − / − (both Thy 1.2) T cells were adoptively transferred (tail vein) on day 0. Mice were immunized on day 1 using 100 μg of HYDby peptide in CFA.
Immunoelectron microscopy.
Peritoneal macrophages were placed in 0.4-μm tissue culture inserts (Becton Dickinson) in 24-well culture dishes with Mar T cells at a 1:1 ratio, with or without HYDby peptide or control OVA323-339 peptide at 10 μg/ml. After fixation with 1% paraformaldehyde/0.1% glutaraldehyde/PBS/0.05 M sucrose, samples were dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, labeled with goat anti–mouse C3 (MP Biomedicals, Inc.), and gold-labeled donkey anti–goat IgG (Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories). Counterstaining was performed with lead citrate.
Quantitative analysis of complement components in T cells and macrophages.
Total RNA was extracted from the sorted populations of T cells and macrophages (QIAGEN mini RNeasy kit) and reverse transcribed by oligo dT primer with SuperscriptII reverse transcriptase (Invitrogen). Real-time PCR was performed on an Applied Biosystems Prism 7700 Sequence Detection System with respective primers (available from author by request). The average threshold cycle differences among the samples were normalized against β-actin (control) in the corresponding cDNA preparation.
Complement assays.
Supernates were obtained from overnight cultures of purified T cells with or without anti-CD3 (2C11, 2 μg/ml) or CFSE-labeled Mar T cells plus peptide/APCs in serum-free medium. CFSE-labeled Mar T cells were flow sorted and incubated for an additional 3 h at 37°C. The supernates were added to C3-, factor B-, or factor D-deficient mouse sera, and C3b uptake on zymosan granules was quantified by flow cytometry after staining with FITC-labeled polyclonal anti–mouse C3 (25). Western blots were performed as described previously (22), see supplemental Materials and methods.
Statistical analysis.
Statistical analysis to determine differences between groups for recall immune responses was performed using the Student's t test. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Online supplemental material.
Details of the methods for preparation of lipid-tailed Daf and Western blots for complement components in culture supernatants are available online or from the author by request. Online supplemental material is available at http://www.jem.org/cgi/content/full/jem.20041967/DC1.
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by National Institutes of Health grant nos. R01 AI43578 (to P.S. Heeger) and AI23598 (to M.E. Medof). P.N. Lalli received a fellowship grant from the Ohio Affiliate of the American Heart Association. A. Valujskikh is a recipient of a Scientist Development Award from the American Heart Association.
The authors have no conflicting financial interests.
References
- 1.Janeway, C., Jr., P. Travers, M. Walport, and M.J. Shlomchik. 2004. Innate immunity. In Immunobiology. Garland Publishing, New York. 37–100.
- 2.Suresh, M., H. Molina, M.S. Salvato, D. Mastellos, J.D. Lambris, and M. Sandor. 2003. Complement component 3 is required for optimal expansion of CD8 T cells during a systemic viral infection. J. Immunol. 170:788–794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pratt, J.R., S.A. Basheer, and S.H. Sacks. 2002. Local synthesis of complement component C3 regulates acute renal transplant rejection. Nat. Med. 8:582–587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nataf, S., S.L. Carroll, R.A. Wetsel, A.J. Szalai, and S.R. Barnum. 2000. Attenuation of experimental autoimmune demyelination in complement-deficient mice. J. Immunol. 165:5867–5873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kopf, M., B. Abel, A. Gallimore, M. Carroll, and M.F. Bachmann. 2002. Complement component C3 promotes T-cell priming and lung migration to control acute influenza virus infection. Nat. Med. 8:373–378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kaech, S.M., E.J. Wherry, and R. Ahmed. 2002. Effector and memory T-cell differentiation: implications for vaccine development. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2:251–262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pien, G.C., K.B. Nguyen, L. Malmgaard, A.R. Satoskar, and C.A. Biron. 2002. A unique mechanism for innate cytokine promotion of T cell responses to viral infections. J. Immunol. 169:5827–5837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Goldberg, J., P. Shrikant, and M.F. Mescher. 2003. In vivo augmentation of tumor-specific CTL responses by class I/peptide antigen complexes on microspheres (large multivalent immunogen). J. Immunol. 170:228–235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Medof, M.E., T. Kinoshita, and V. Nussenzweig. 1984. Inhibition of complement activation on the surface of cells after incorporation of decay-accelerating factor (DAF) into their membranes. J. Exp. Med. 160:1558–1578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hamann, J., B. Vogel, G.M. van Schijndel, and R.A. van Lier. 1996. The seven-span transmembrane receptor CD97 has a cellular ligand (CD55, DAF). J. Exp. Med. 184:1185–1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Leemans, J.C., A.A. te Velde, S. Florquin, R.J. Bennink, K. de Bruin, R.A. van Lier, T. van der Poll, and J. Hamann. 2004. The epidermal growth factor-seven transmembrane (EGF-TM7) receptor CD97 is required for neutrophil migration and host defense. J. Immunol. 172:1125–1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Walter, E.I., W.D. Ratnoff, K.E. Long, J.W. Kazura, and M.E. Medof. 1992. Effect of glycoinositolphospholipid anchor lipid groups on functional properties of decay-accelerating factor protein in cells. J. Biol. Chem. 267:1245–1252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Medof, M.E., S. Nagarajan, and M.L. Tykocinski. 1996. Cell-surface engineering with GPI-anchored proteins. FASEB J. 10:574–586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cerny, J., H. Stockinger, and V. Horejsi. 1996. Noncovalent associations of T lymphocyte surface proteins. Eur. J. Immunol. 26:2335–2343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Horejsi, V., K. Drbal, M. Cebecauer, J. Cerny, T. Brdicka, P. Angelisova, and H. Stockinger. 1999. GPI-microdomains: a role in signalling via immunoreceptors. Immunol. Today. 20:356–361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Simpson, E., D. Scott, and P. Chandler. 1997. The male-specific histocompatibility antigen, H-Y: a history of transplantation, immune response genes, sex determination and expression cloning. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 15:39–61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Davis, L.S., S.S. Patel, J.P. Atkinson, and P.E. Lipsky. 1988. Decay-accelerating factor functions as a signal transducing molecule for human T cells. J. Immunol. 141:2246–2252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Buono, C., C.E. Come, J.L. Witztum, G.F. Maguire, P.W. Connelly, M. Carroll, and A.H. Lichtman. 2002. Influence of C3 deficiency on atherosclerosis. Circulation. 105:3025–3031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kim, A.H., I.D. Dimitriou, M.C. Holland, D. Mastellos, Y.M. Mueller, J.D. Altman, J.D. Lambris, and P.D. Katsikis. 2004. Complement c5a receptor is essential for the optimal generation of antiviral CD8+ T cell responses. J. Immunol. 173:2524–2529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Arvieux, J., H. Yssel, and M.G. Colomb. 1988. Antigen-bound C3b and C4b enhance antigen-presenting cell function in activation of human T-cell clones. Immunology. 65:229–235. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kerekes, K., J. Prechl, Z. Bajtay, M. Jozsi, and A. Erdei. 1998. A further link between innate and adaptive immunity: C3 deposition on antigen-presenting cells enhances the proliferation of antigen-specific T cells. Int. Immunol. 10:1923–1930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kerekes, K., P.D. Cooper, J. Prechl, M. Jozsi, Z. Bajtay, and A. Erdei. 2001. Adjuvant effect of gamma-inulin is mediated by C3 fragments deposited on antigen-presenting cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 69:69–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kawamoto, S., A. Yalcindag, D. Laouini, S. Brodeur, P. Bryce, B. Lu, A.A. Humbles, H. Oettgen, C. Gerard, and R.S. Geha. 2004. The anaphylatoxin C3a downregulates the Th2 response to epicutaneously introduced antigen. J. Clin. Invest. 114:399–407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Teague, T.K., D. Hildeman, R.M. Kedl, T. Mitchell, W. Rees, B.C. Schaefer, J. Bender, J. Kappler, and P. Marrack. 1999. Activation changes the spectrum but not the diversity of genes expressed by T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 96:12691–12696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lin, F., Y. Fukuoka, A. Spicer, R. Ohta, N. Okada, C.L. Harris, S.N. Emancipator, and M.E. Medof. 2001. Tissue distribution of products of the mouse decay-accelerating factor (DAF) genes. Exploitation of a Daf1 knock-out mouse and site-specific monoclonal antibodies. Immunology. 104:215–225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lantz, O., I. Grandjean, P. Matzinger, and J.P. Di Santo. 2000. Gamma chain required for naive CD4+ T cell survival but not for antigen proliferation. Nat. Immunol. 1:54–58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.He, C., and P.S. Heeger. 2004. CD8 T cells can reject major histocompatibility complex class I-deficient skin allografts. Am. J. Transplant. 4:698–704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.He, C., S. Schenk, Q. Zhang, A. Valujskikh, J. Bayer, R.L. Fairchild, and P.S. Heeger. 2004. Effects of T cell frequency and graft size on transplant outcome in mice. J. Immunol. 172:240–247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]