Abstract
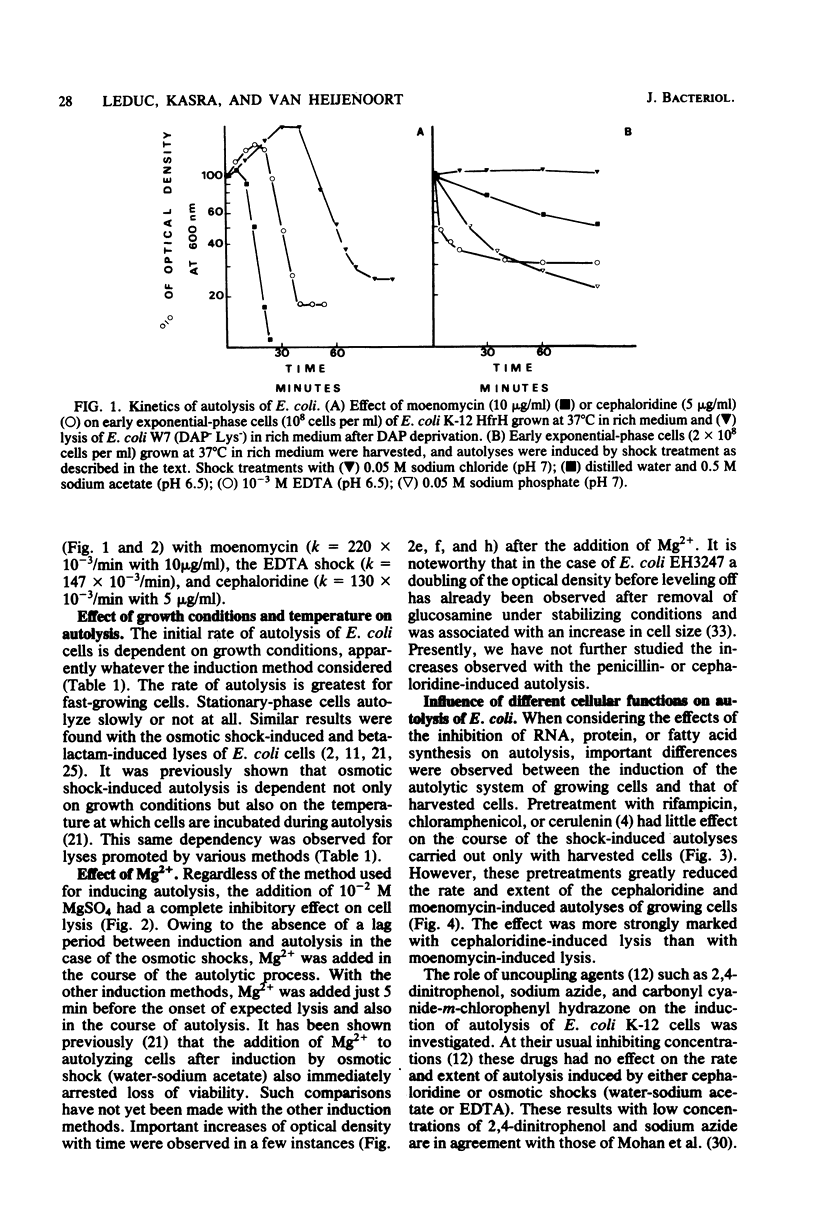
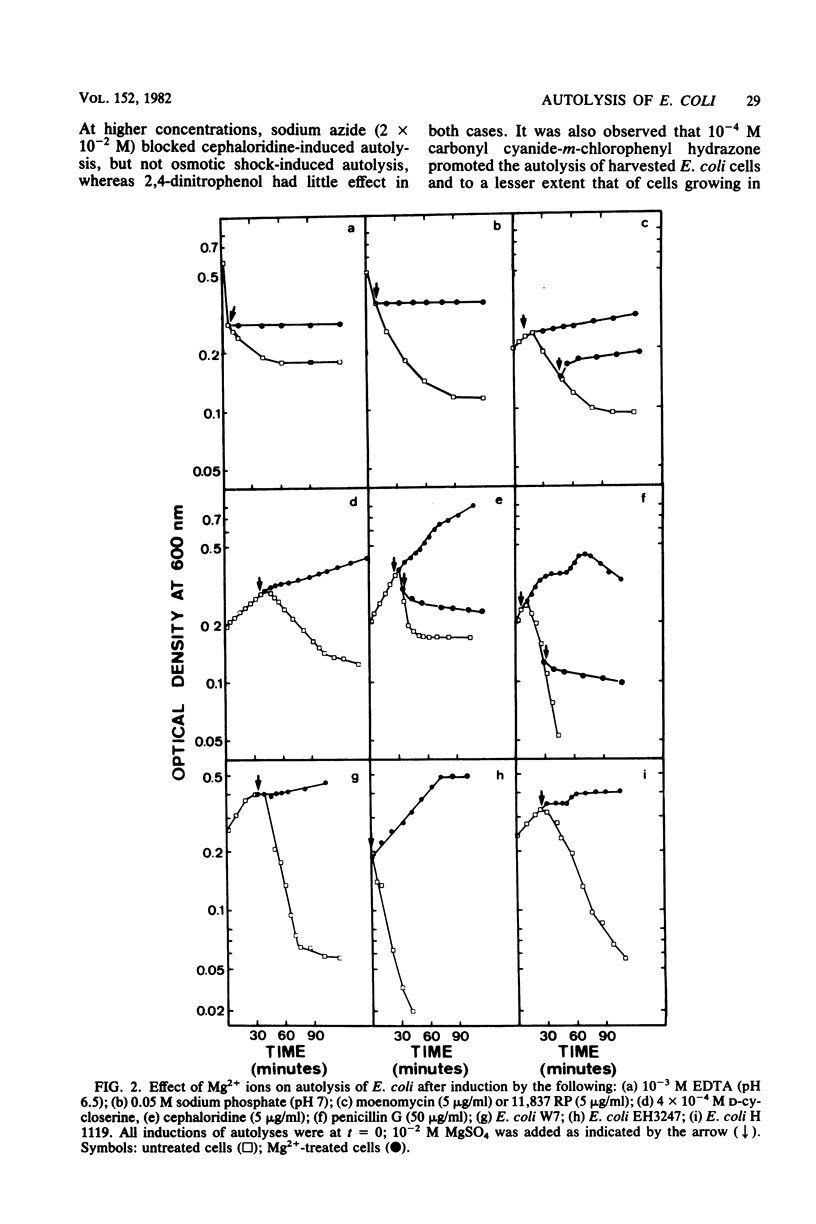
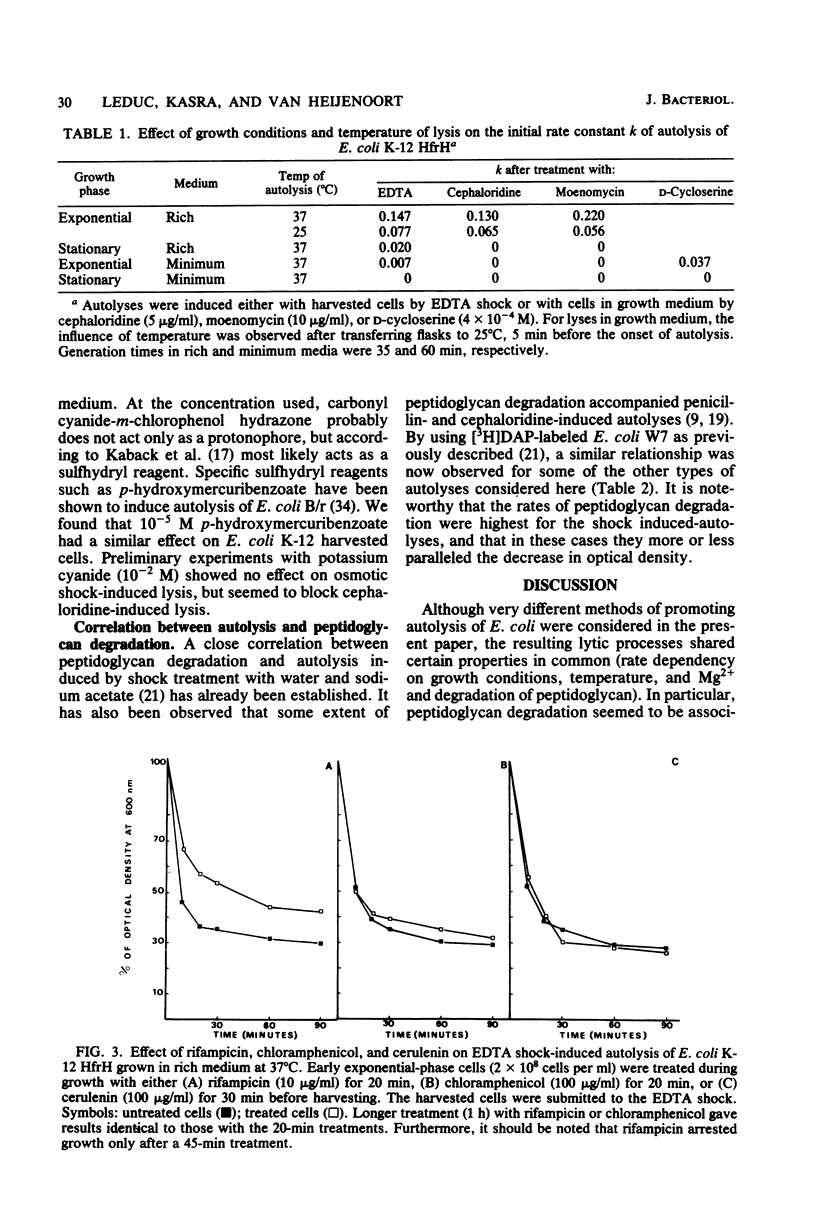
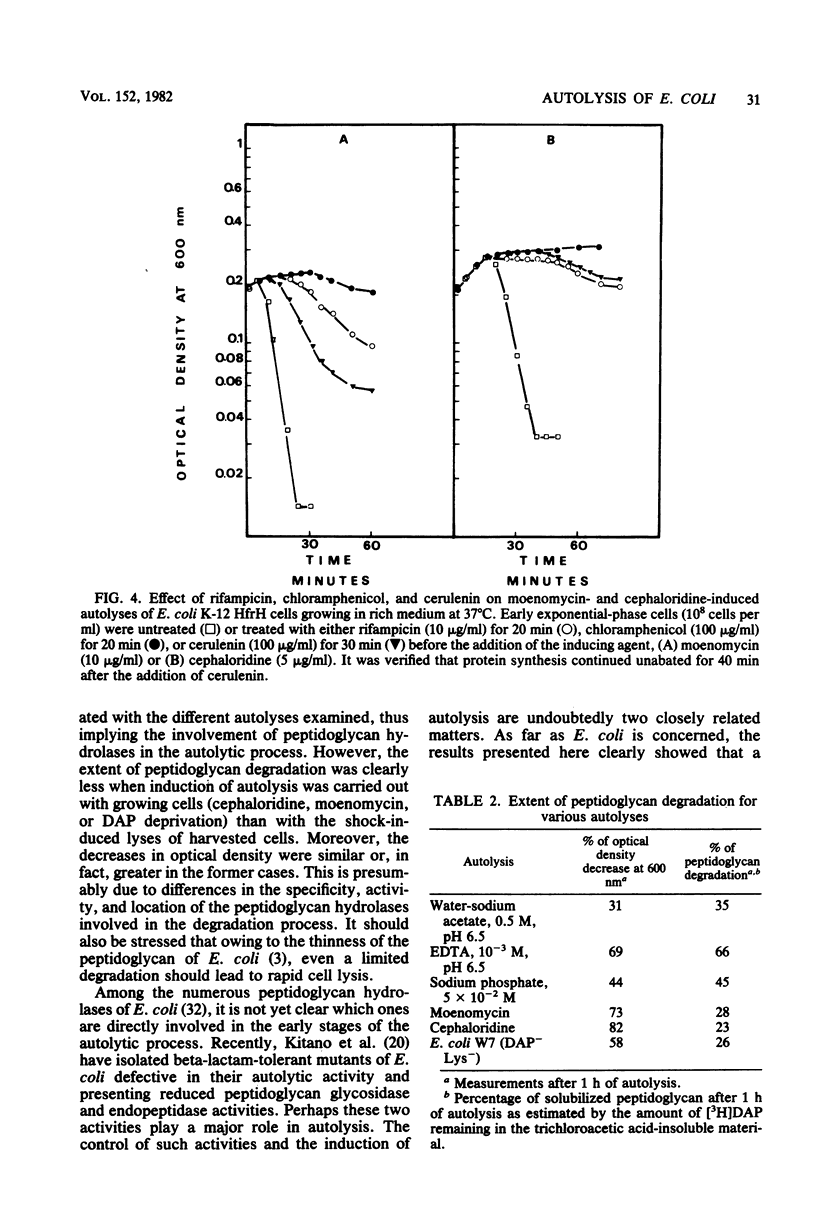
Various methods of inducing autolysis of Escherichia coli cells were investigated, some being described here for the first time. For the autolysis of growing cells only induction methods interfering with the biosynthesis of peptidoglycan were taken into consideration, whereas with harvested cells autolysis was induced by rapid osmotic or EDTA shock treatments. The highest rates of autolysis were observed after induction by moenomycin, EDTA, or cephaloridine. The different autolyses examined shared certain common properties. In particular, regardless of the induction method used, more or less extensive peptidoglycan degradation was observed, and 10(-2) M Mg2+ efficiently inhibited the autolytic process. However, for other properties a distinction was made between methods used for growing cells and those used for harvested cells. Autolysis of growing cells required RNA, protein, and fatty acid synthesis. No such requirements were observed with shock-induced autolysis performed with harvested cells. Thus, the effects of Mg2+, rifampicin, chloramphenicol, and cerulenin clearly suggest that distinct factors are involved in the control of the autolytic system of E. Coli. Uncoupling agents such as sodium azide, 2,4-dinitrophenol, and carbonyl-cyanide-m-chlorophenyl hydrazone used at their usual inhibiting concentration had no effect on the cephaloridine or shock-induced autolysis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. K. Lysis of Escherichia coli mutants by lactose. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):643–648. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.643-648.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V., Gnirke H., Henning U., Rehn K. Model for the structure of the shape-maintaining layer of the Escherichia coli cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1264–1270. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1264-1270.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttke T. M., Ingram L. O. Inhibition of unsaturated fatty acid synthesis in escherichia coli by the antibiotic cerulenin. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 28;17(24):5282–5286. doi: 10.1021/bi00617a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CIAK J., HAHN F. E. Penicillin-induced lysis of Escherichia coli. Science. 1957 Jan 18;125(3238):119–120. doi: 10.1126/science.125.3238.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis N. A., Orr D., Ross G. W., Boulton M. G. Affinities of penicillins and cephalosporins for the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K-12 and their antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Nov;16(5):533–539. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.5.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daneo-Moore L., Bourbeau P., Weinstein R., Carson D. Effects of cerulenin on antibiotic-induced lysis of streptococcus faecalis (S. faecium). Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Dec;16(6):858–861. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.6.858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W., Lopez R., Tomasz A. Suppression of lytic effect of beta lactams on Escherichia coli and other bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3293–3297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell W., Tomasz A. Alteration of Escherichia coli murein during amino acid starvation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1009–1016. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1009-1016.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gschwender H. H., Hofschneider P. H. Lysis inhibition of phi-X174-, M12-, and Q-beta-infected Escherichia coli bacteria by magnesium ions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 22;190(2):454–459. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Conservation and transformation of energy by bacterial membranes. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Jun;36(2):172–230. doi: 10.1128/br.36.2.172-230.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann R., Bock-Hennig S. B., Schwarz U. Murein hydrolases in the envelope of Escherichia coli. Properties in situ and solubilization from the envelope. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jan 3;41(1):203–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota Y., Suzuki H., Nishimura Y., Yasuda S. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli: a mutant of E. coli lacking a murein-lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1417–1420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram L. O. Mechanism of lysis of Escherichia coli by ethanol and other chaotropic agents. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):331–336. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.331-336.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishino F., Mitsui K., Tamaki S., Matsuhashi M. Dual enzyme activities of cell wall peptidoglycan synthesis, peptidoglycan transglycosylase and penicillin-sensitive transpeptidase, in purified preparations of Escherichia coli penicillin-binding protein 1A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Nov 17;97(1):287–293. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80166-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R., Reeves J. P., Short S. A., Lombardi F. J. Mechanisms of active transport in isolated bacterial membrane vesicles. 18. The mechanism of action of carbonylcyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jan;160(1):215–222. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(74)80028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitano K., Tomasz A. Escherichia coli mutants tolerant to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;140(3):955–963. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.3.955-963.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitano K., Tomasz A. Triggering of autolytic cell wall degradation in Escherichia coli by beta-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Dec;16(6):838–848. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.6.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leduc M., van Heijenoort J. Autolysis of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):52–59. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.52-59.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg E. J., v Schijndel-van Dam A. Temperature-sensitive mutant of Escherichia coli K-12 with an impaired D-alanine:D-alanine ligase. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):96–104. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.96-104.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEADOW P., HOARE D. S., WORK E. Interrelationships between lysine and alpha epsilon-diaminopimelic acid and their derivatives and analogues in mutants of Escherichia coli. Biochem J. 1957 Jun;66(2):270–282. doi: 10.1042/bj0660270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathys E., Van Gool A. Sensitivity of Escherichia coli to cephaloridine at different growth rates. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):642–646. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.642-646.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuhashi M., Maruyama I. N., Takagaki Y., Tamaki S., Nishimura Y., Hirota Y. Isolation of a mutant of Escherichia coli lacking penicillin-sensitive D-alanine carboxypeptidase IA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2631–2635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McQUILLEN K. Lysis resulting from metabolic disturbance. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Apr;18(2):498–512. doi: 10.1099/00221287-18-2-498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mengin-Lecreulx D., Flouret B., van Heijenoort J. Cytoplasmic steps of peptidoglycan synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1109–1117. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1109-1117.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan R. R., Kronish D. P., Pianotti R. S., Epstein R. L., Schwartz B. S. Autolytic mechanism for spheroplast formation in Bacillus cereus and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1355–1364. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1355-1364.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESTIDGE L. S., PARDEE A. B. Induction of bacterial lysis by penicillin. J Bacteriol. 1957 Jul;74(1):48–59. doi: 10.1128/jb.74.1.48-59.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAECHTER M., SANTOMASSINO K. A. Lysis of Escherichia coli by sulfhydryl-binding reagents. J Bacteriol. 1962 Aug;84:318–325. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.2.318-325.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarvas M. Mutant of Escherichia coli K-12 defective in D-glucosamine biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Feb;105(2):467–471. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.2.467-471.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt L. S., Botta G., Park J. T. Effects of furazlocillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic which binds selectively to penicillin-binding protein 3, on Escherichia coli mutants deficient in other penicillin-binding proteins. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jan;145(1):632–637. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.1.632-637.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz U., Leutgeb W. In vivo studies on murein synthesis. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 1967;12(3):279–282. doi: 10.1007/BF02868744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockman G. D. Symposium on the fine structure and replication of bacteria and their parts. IV. Unbalanced cell-wall synthesis: autolysis and cell-wall thickening. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Sep;29(3):345–358. doi: 10.1128/br.29.3.345-358.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slein M. W., Logan G. F., Jr Lysis of Escherichia coli by ethylenediaminetetraacetate and phospholipases as measured by beta-galactosidase activity. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):934–941. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.934-941.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slusarchyk W. A. Chemical and biological aspects of a new family of phosphorus-containing antibiotics. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1971 May;13(3):399–407. doi: 10.1002/bit.260130307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spratt B. G. Properties of the penicillin-binding proteins of Escherichia coli K12,. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):341–352. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11258.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stolp H., Starr M. P. Bacteriolysis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1965;19:79–104. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.19.100165.000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Nishimura Y., Hirota Y. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli: a series of mutants of E. coli altered in the penicillin-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., van Heijenoort Y., Tamura T., Mizoguchi J., Hirota Y., van Heijenoort J. In vitro peptidoglycan polymerization catalysed by penicillin binding protein 1b of Escherichia coli K-12. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 11;110(2):245–249. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80083-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamaki S., Nakajima S., Matsuhashi M. Thermosensitive mutation in Escherichia coli simultaneously causing defects in penicillin-binding protein-1Bs and in enzyme activity for peptidoglycan synthesis in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5472–5476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Suzuki H., Nishimura Y., Mizoguchi J., Hirota Y. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli: isolation and characterization of penicillin-binding proteins 1a, 1b, and 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4499–4503. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. The mechanism of the irreversible antimicrobial effects of penicillins: how the beta-lactam antibiotics kill and lyse bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:113–137. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W., PELZER H. BAGSHAPED MACROMOLECULES--A NEW OUTLOOK ON BACTERIAL CELL WALLS. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1964;26:193–232. doi: 10.1002/9780470122716.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yem D. W., Wu H. C. Physiological characterization of an Escherichia coli mutant altered in the structure of murein lipoprotein. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1419–1426. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1419-1426.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Heijenoort Y., van Heijenoort J. Biosynthesis of the peptidoglycan of Escherichia coli K-12: properties of the in vitro polymerization by transglycosylation. FEBS Lett. 1980 Feb 11;110(2):241–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


