Abstract
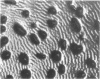
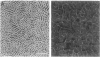
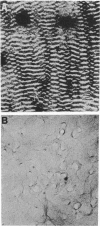
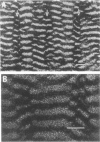
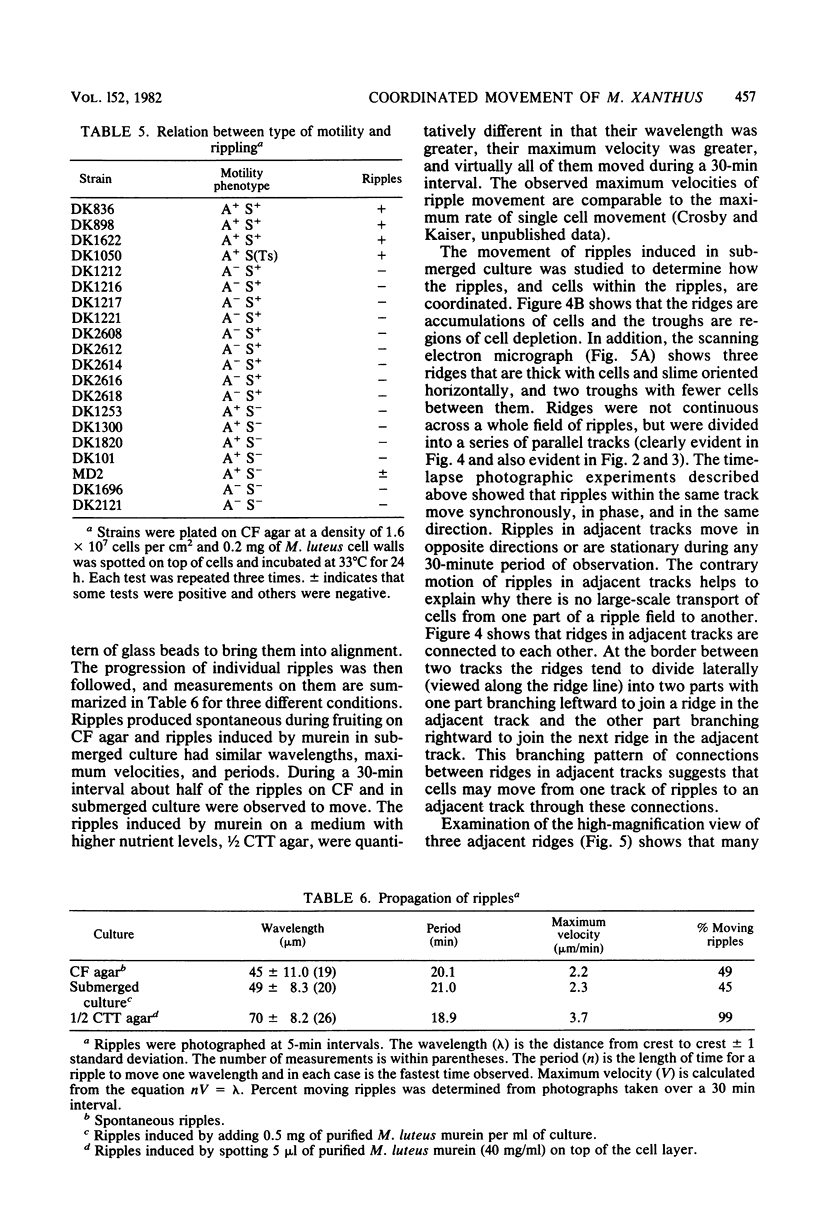
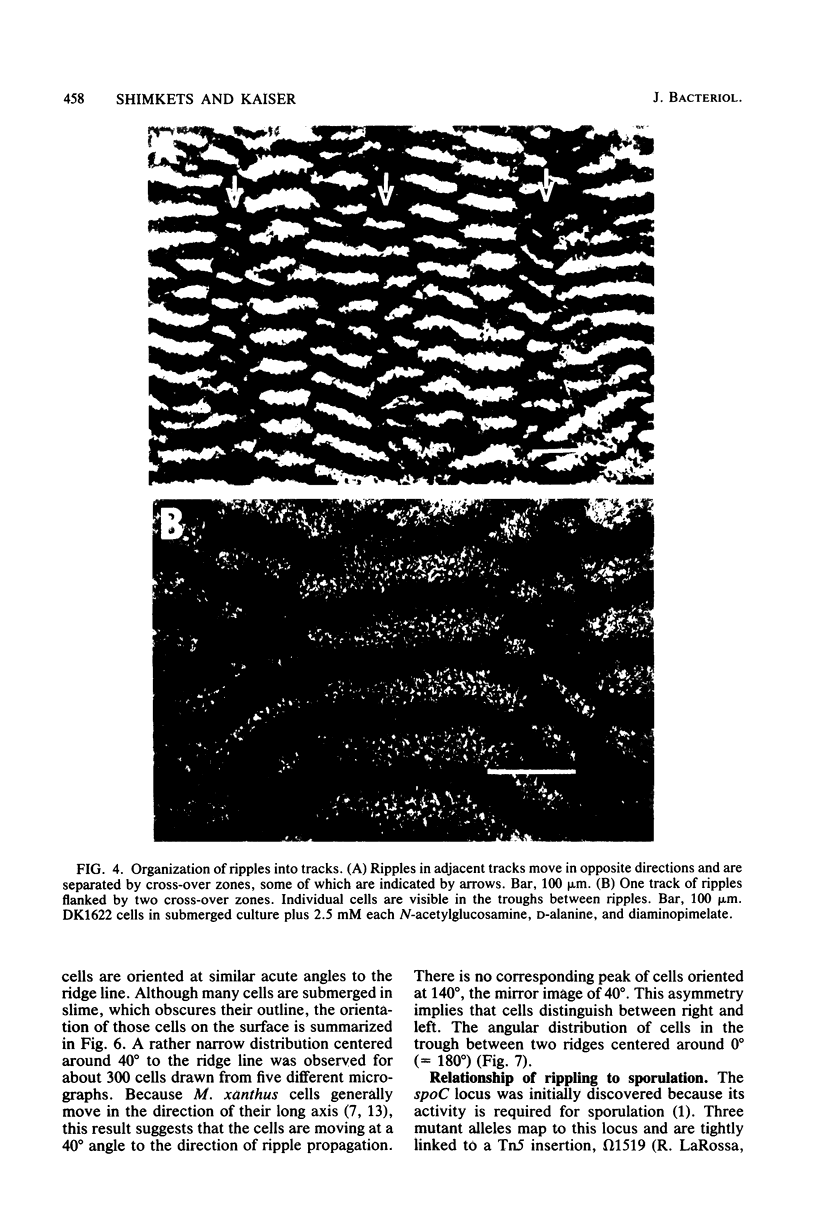
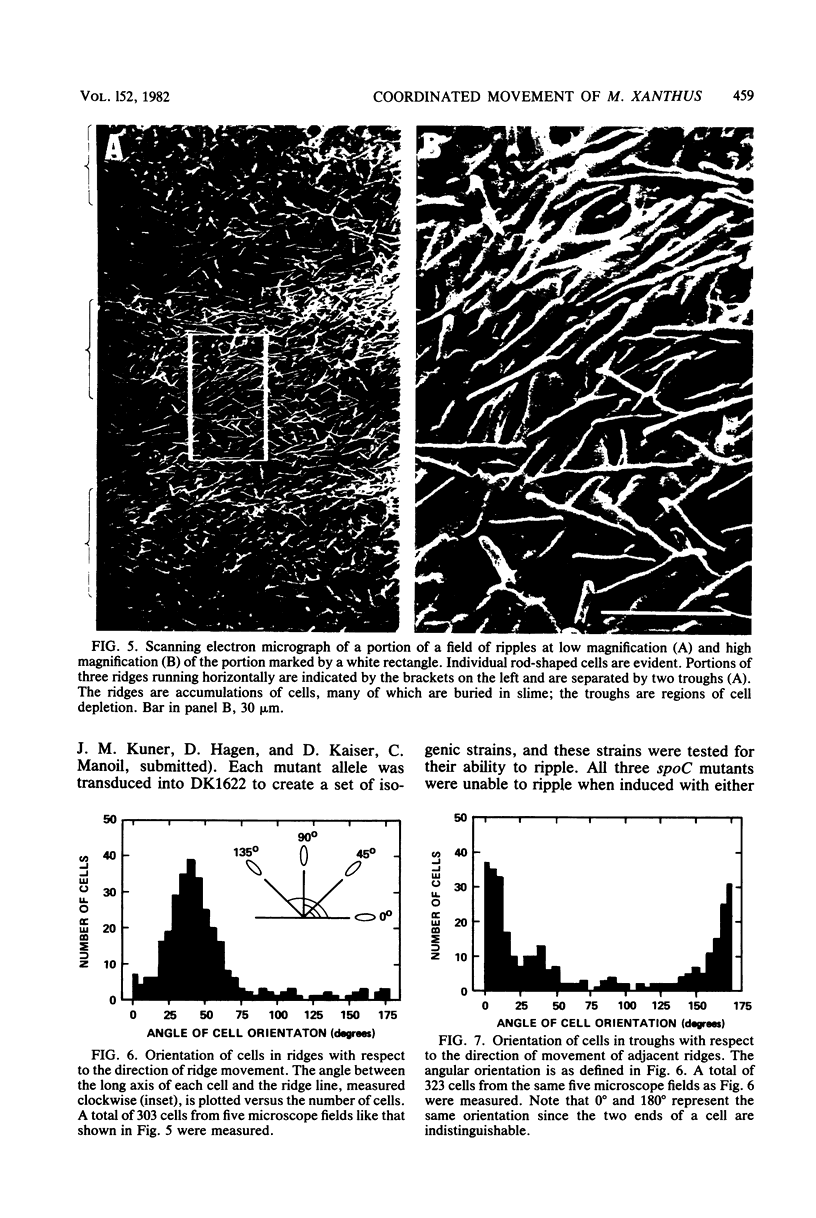
Rhythmically advancing waves of cells, called ripples, arise spontaneously during the aggregation of Myxococcus xanthus into fruiting bodies. Extracts prepared by washing rippling cells contain a substance that will induce quiescent cells to ripple. Three lines of evidence indicate that murein (peptidoglycan) is the ripple-inducing substance in the extracts. First, ripple-inducing activity is associated with the cell envelope of sonically disrupted M. xanthus cells. Second, whole cells, cell extracts, or purified murein from a variety of different bacteria are capable of inducing ripples. In contrast, extracts prepared from Methanobacterium spp. which contain pseudomurein instead of typical bacterial murein fail to induce ripples. Third, four components of M. xanthus murein, N-acetylglucosamine, N-acetylmuramic acid, diaminopimelate, and D-alanine, are able to induce ripples. Ripples produced by aggregating cells have a wavelength of 45 micrometers and a maximum velocity of 2 micrometers/min. Both of the multigene systems that control gliding motility appear to be required for rippling, and all known mutations at the spoC locus eliminate both rippling and sporulation.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hagen D. C., Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Synergism between morphogenetic mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. Dev Biol. 1978 Jun;64(2):284–296. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgkin J., Kaiser D. Cell-to-cell stimulation of movement in nonmotile mutants of Myxococcus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2938–2942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuner J. M., Kaiser D. Fruiting body morphogenesis in submerged cultures of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):458–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.458-461.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuner J. M., Kaiser D. Introduction of transposon Tn5 into Myxococcus for analysis of developmental and other nonselectable mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):425–429. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König H., Kandler O. The amino acid sequence of the peptide moiety of the pseudomurein from Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Arch Microbiol. 1979 Jun;121(3):271–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00425067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S., Sodergren E., Masuda T., Kaiser D. Systematic isolation of transducing phages for Myxococcus xanthus. Virology. 1978 Jul 1;88(1):44–53. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARK J. T., HANCOCK R. A fractionation procedure for studies of the synthesis of cell-wall mucopeptide and of other polymers in cells of Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Feb;22:249–258. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-1-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Kaiser D. Murein components rescue developmental sporulation of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):462–470. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.462-470.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudo S., Dworkin M. Bacteriolytic enzymes produced by Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):236–245. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.236-245.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D., Dworkin M., Tipper D. J. Peptidoglycan of Myxococcus xanthus: structure and relation to morphogenesis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jun;95(6):2186–2197. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.6.2186-2197.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wireman J. W., Dworkin M. Developmentally induced autolysis during fruiting body formation by Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):798–802. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.798-802.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]