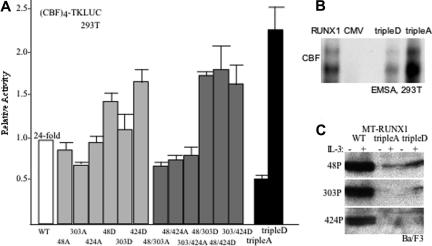
Figure 3.
Cdk phosphorylation of RUNX1 increases transactivation potency. (A) 293T cells were transiently transfected with (CBF)4TKLUC and either CMV, CMV-RUNX1 (WT), or the indicated RUNX1 mutant variants expressed from the CMV promoter. CMV-βGal was also included in each transfection as an internal control. TripleA and tripleD represent S48/303/424A or S48/303/424D, respectively. Induction by RUNX1 compared with empty CMV vector was set to 1 in each experiment. Relative activation by each mutant compared with RUNX1 is shown (mean and SE from 4 experiments). (B) Nuclear extracts from 293T cells transiently transfected on 100-mM dishes with 3 μg CMV-CBFβ together with 3 μg of either CMV-RUNX1, CMV, CMV-RUNX1(tripleD), or CMV-RUNX1(tripleA) were subjected to gel shift assay using a radiolabeled CBF-binding site from the MPO promoter. Input of RUNX1 or mutant RUNX1 proteins was normalized based on Western blot analysis. Data shown are representative of 2 assessments. (C) Ba/F3 cells stably transduced with MT-RUNX1, MT-RUNX1(tripleA), or MT-RUNX1(tripleD) were cultured for 24 hours with or without IL-3 and with zinc chloride. Total cell extracts corresponding to 106 cells were then subjected to Western blotting with anti-S48, anti-S303, or anti-S424 phospho-specific antiserum.