Abstract
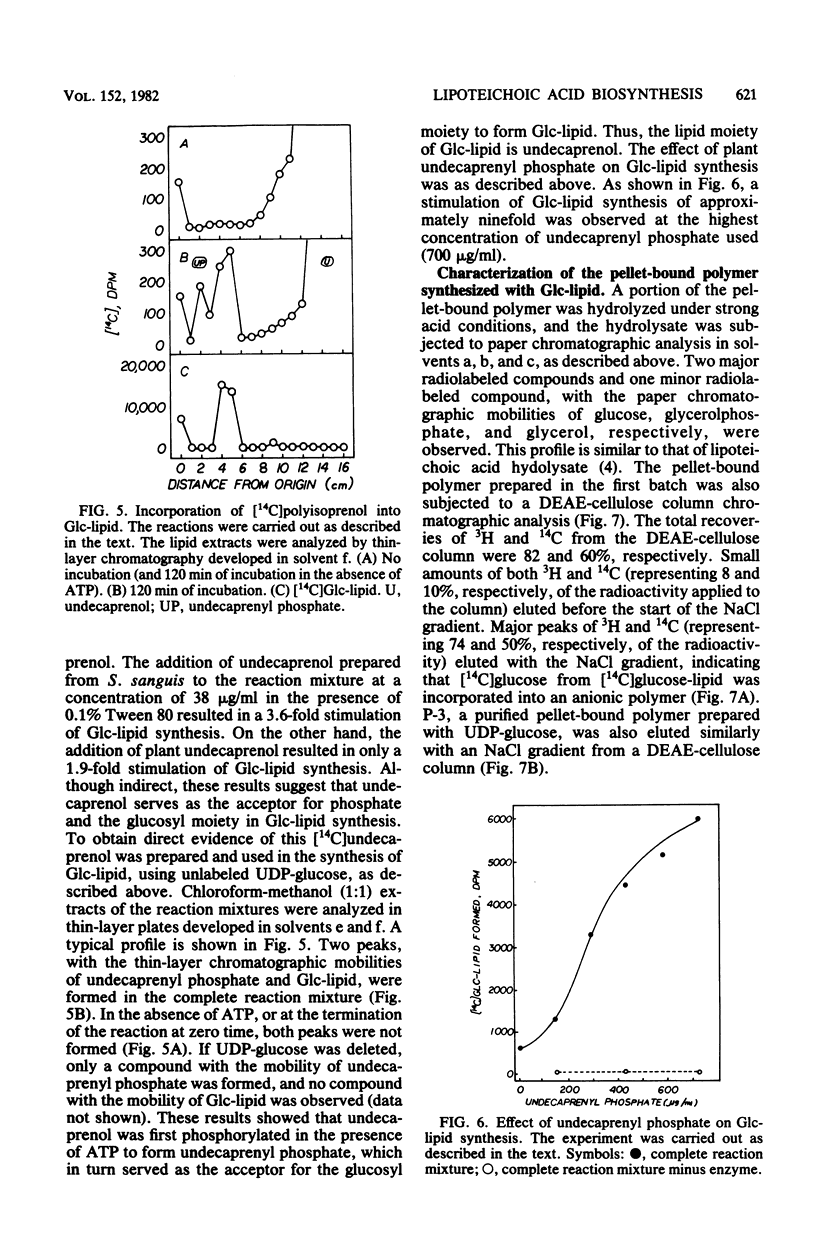
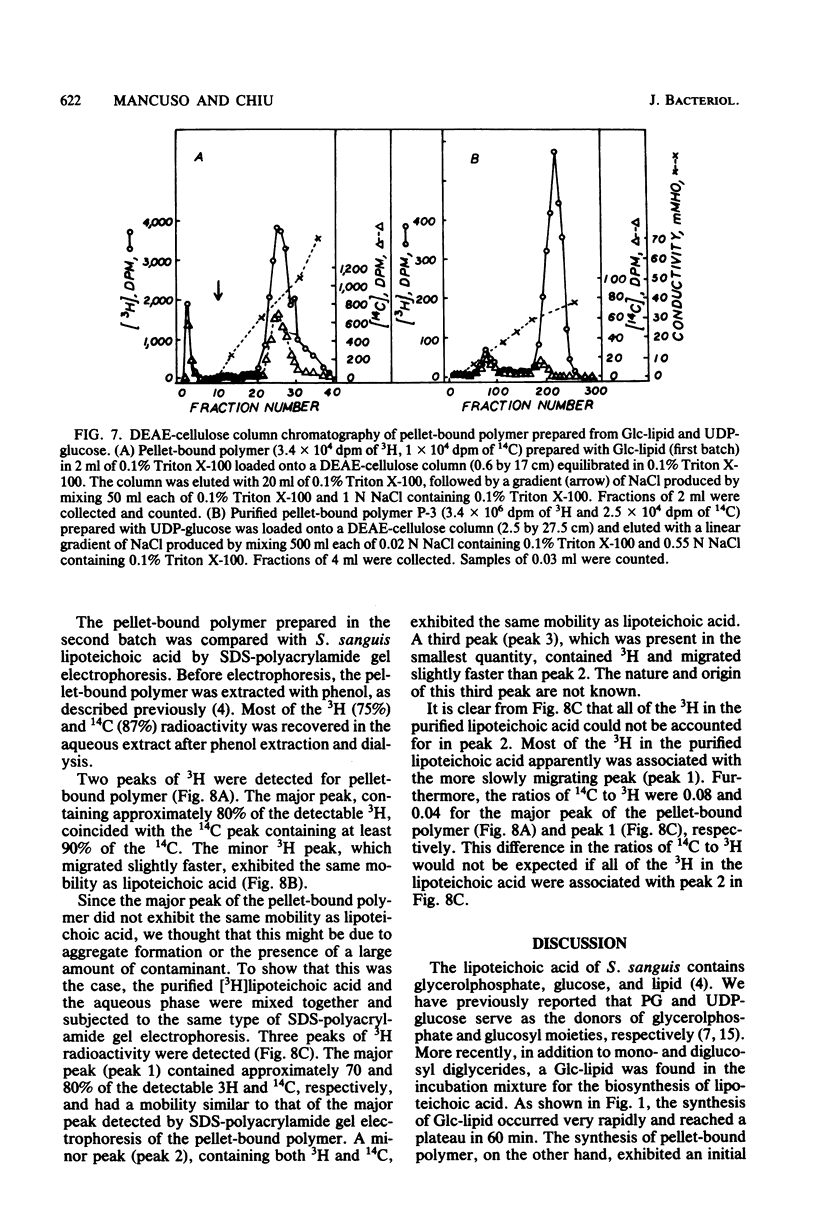
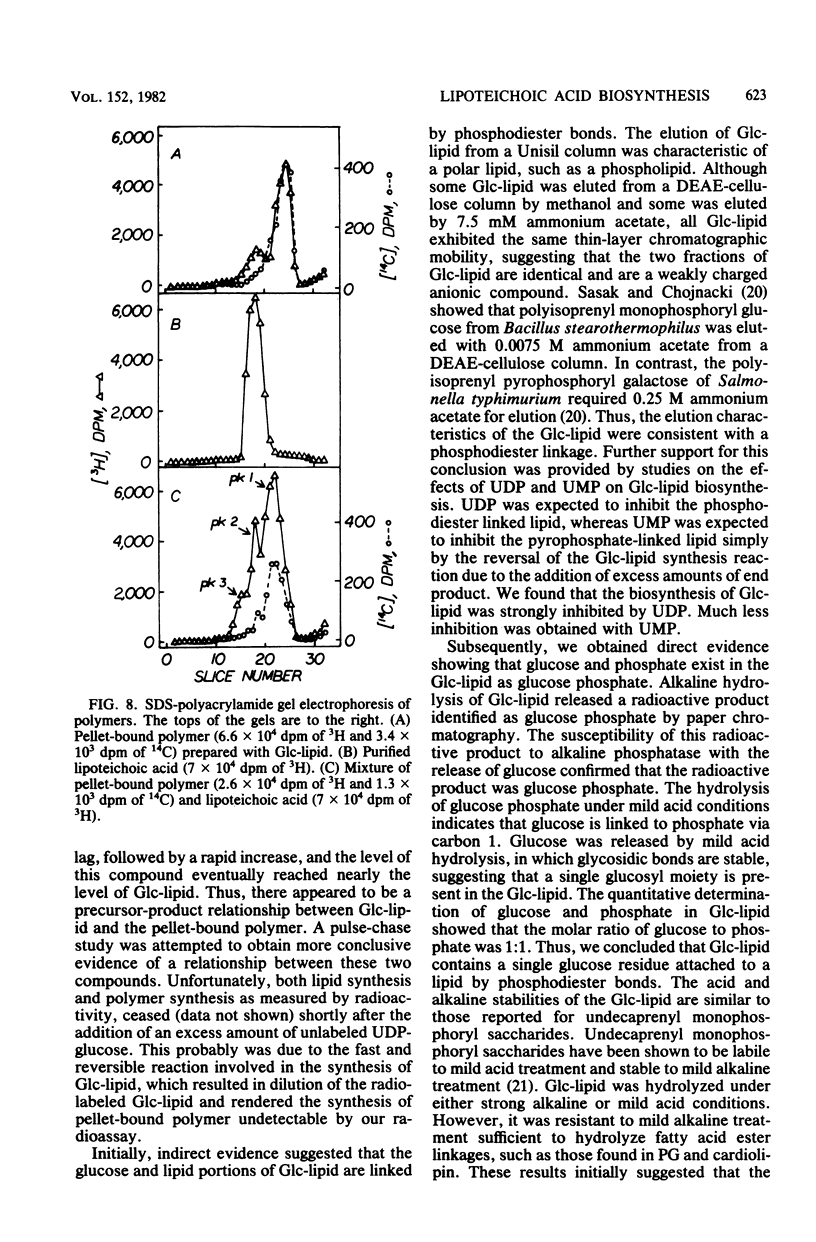
A glucophospholipid was detected in an incubation mixture containing UDP-glucose, MgCl2, ATP, and a particulate enzyme prepared from Streptococcus sanguis. The synthesis of this lipid was inhibited strongly by UDP and moderately by UMP. The molar ratio of glucose to phosphate in the purified lipid was found to be 1:1. Glucose and glucose 1-phosphate were released by mild alkaline hydrolysis of the glucophospholipid. The lipid produced by mild acid degradation of the purified lipid yielded a thin-layer chromatographic profile similar to that of acid-treated undecaprenol. One of the minor components exhibited the same mobility as untreated undecaprenol. To characterize further the lipid moiety of the glucophospholipid, a polyisoprenol was purified from the neutral lipid of S. sanguis. The polyisoprenol was converted in the presence of ATP, UDP-glucose, and the particulate enzyme into a lipid which exhibited the same thin-layer chromatographic mobility as the glucophospholipid. The structure of the polyisoprenol was determined by nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry to be an undecaprenol with an internal cis-trans ratio of 7:2. These results indicate that the glucophospholipid is glucosyl monophosphoryl undecaprenol. The glucosyl moiety of the glucophospholipid was shown to be incorporated in the presence of the particulate enzyme into a macromolecule which was characterized as a lipoteichoic acid by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and DEAE-cellulose column chromatography. This result indicates that glucosyl monophosphoryl undecaprenol is the direct glucosyl donor in the synthesis of lipoteichoic acid.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brautigan V. M., Childs W. C., 3rd, Neuhaus F. C. Biosynthesis of D-alanyl-lipoteichoic acid in Lactobacillus casei: D-alanyl-lipophilic compounds as intermediates. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):239–250. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.239-250.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Childs W. C., 3rd, Neuhaus F. C. Biosynthesis of D-alanyl-lipoteichoic acid: characterization of ester-linked D-alanine in the in vitro-synthesized product. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):293–301. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.293-301.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu T. H., Emdur L. I., Platt D. Lipoteichoic acids from Streptococcus sanguis. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):471–479. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.471-479.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu T. H., Saralkar C. Biosynthesis of oligosaccharide-lipid in Streptococcus sanguis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):185–195. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.185-195.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emdur L. I., Chiu T. H. Turnover of phosphatidylglycerol in Streptococcus sanguis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 5;59(3):1137–1144. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emdur L. I., Saralkar C., McHugh J. G., Chiu T. H. Glycerolphosphate-containing cell wall polysaccharides from Streptococcus sanguis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):724–732. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.724-732.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emdur L., Chiu T. The role of phosphatidylglycerol in the in vitro biosynthesis of teichoic acid and lipoteichoic acid. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jul 15;55(1):216–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80995-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeney J., Hemming F. W. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry of naturally occurring polyprenols. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90258-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser L., Lindsay B. The synthesis of lipoteichoic acid carrier. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Aug 5;59(3):1131–1136. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80096-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi Y., Strominger J. L., Sweeley C. C. Structure of a lipid intermediate in cell wall peptidoglycan synthesis: a derivative of a C55 isoprenoid alcohol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1878–1884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennarz W. J., Scher M. G. Metabolism and function of polyisoprenol sugar intermediates in membrane-associated reactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 4;265(3):417–441. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(72)90015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancuso D. J., Junker D. D., Hsu S. C., Chiu T. H. Biosynthesis of glycosylated glycerolphosphate polymers in Streptococcus sanguis. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):547–554. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.547-554.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mańkowski T., Sasak W., Janczura E., Chojnacki T. Specificity of polyprenyl phosphates in the in vitro formation of lipid-linked sugars. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jun;181(2):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90244-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido K., Nikaido H. Glucosylation of lipopolysaccharide in Salmonella: biosynthesis nof O antigen factor n12 2 . II. Structure of the lipid intermediate. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jun 25;246(12):3912–3919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Weiner I. M. Biosynthesis of a bacterial lipopolysaccharide. VI. Mechanism of incorporation of abequose into the O-antigen of Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 25;243(10):2631–2639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RADIN N. S., BROWN J. R., LAVIN F. B. The preparative isolation of cerebrosides. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):977–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasak W., Chojnacki T. The identification of lipid acceptor and the biosynthesis of lipid-linked glucose in Bacillus stearothermophilus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Jun;181(2):402–410. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90245-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher M., Lennarz W. J., Sweeley C. C. The biosynthesis of mannosyl-1-phosphoryl-polyisoprenol in Micrococcus lysodeikticus and its role in mannan synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Apr;59(4):1313–1320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.4.1313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone K. J., Wellburn A. R., Hemming F. W., Pennock J. F. The characterization of ficaprenol-10, -11 and 12 from the leaves of Ficus elastica (decorative rubber plant). Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):325–330. doi: 10.1042/bj1020325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbreit J. N., Stone K. J., Strominger J. L. Isolation of polyisoprenyl alcohols from Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1972 Dec;112(3):1302–1305. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.3.1302-1305.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Lipoteichoic acids: a new class of bacterial antigen. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1161–1167. doi: 10.1126/science.46620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright A. Mechanism of conversion of the salmonella O antigen by bacteriophageepsilon 34. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):927–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.927-936.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]