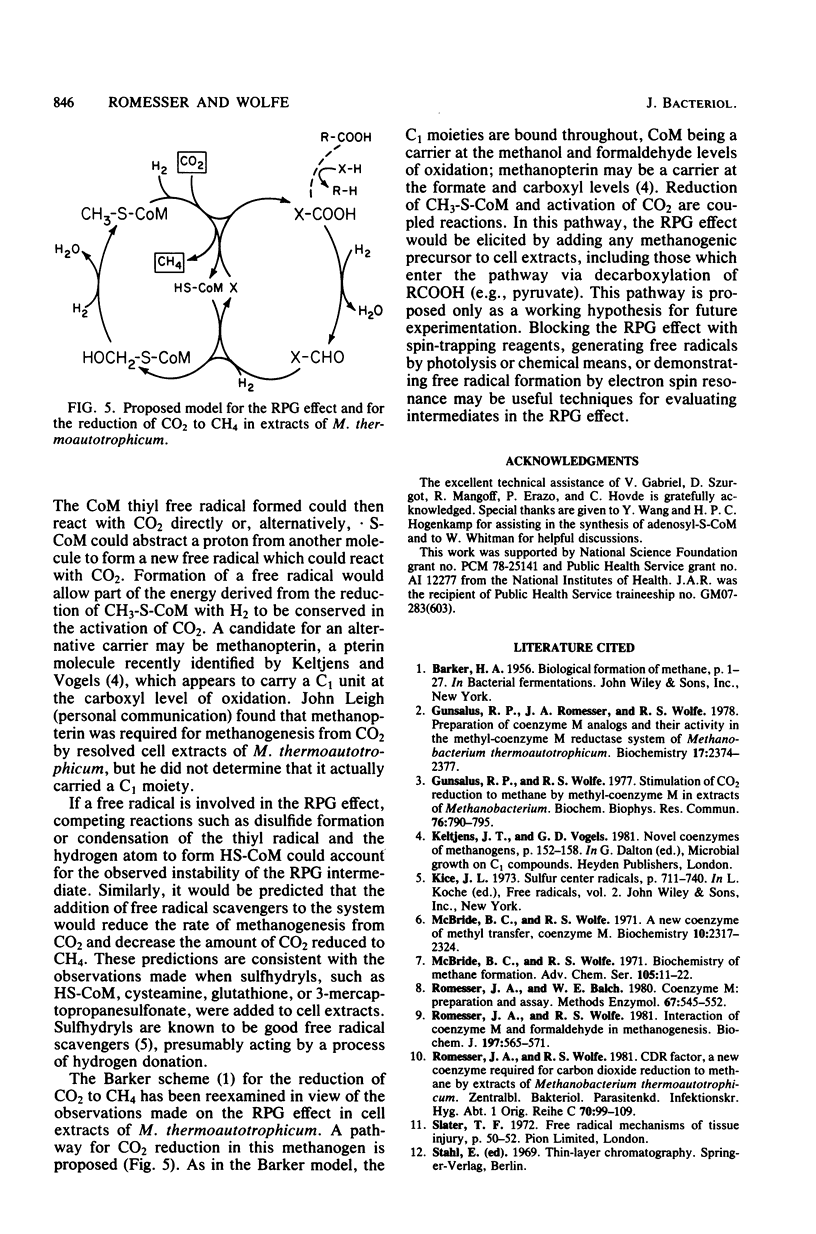
Abstract
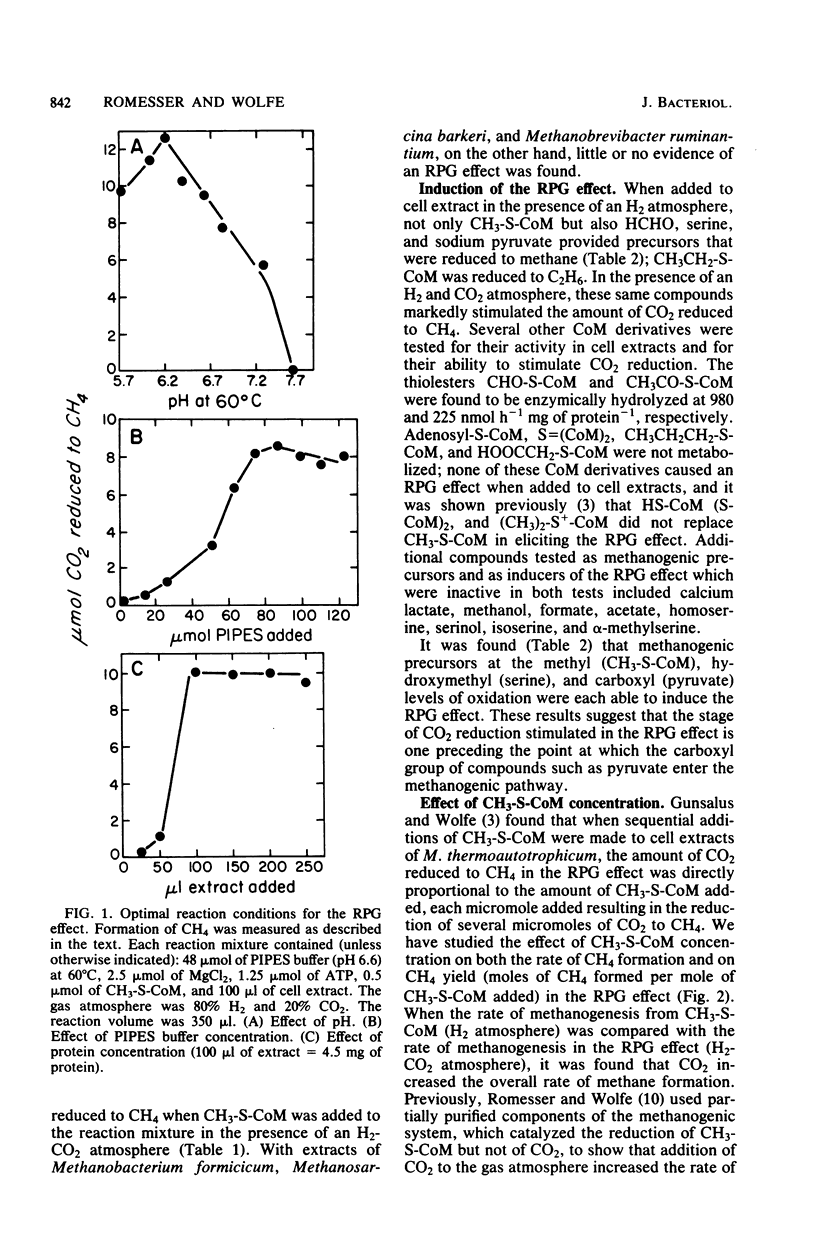
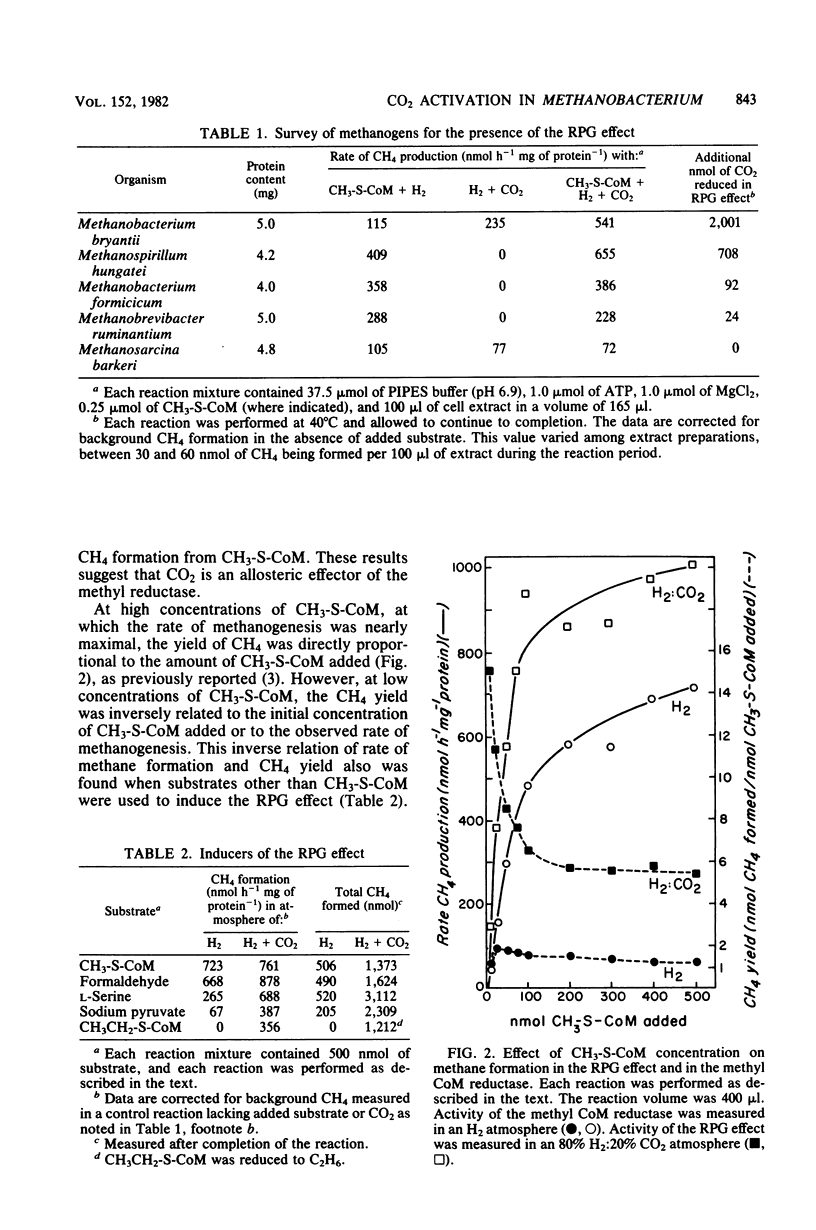
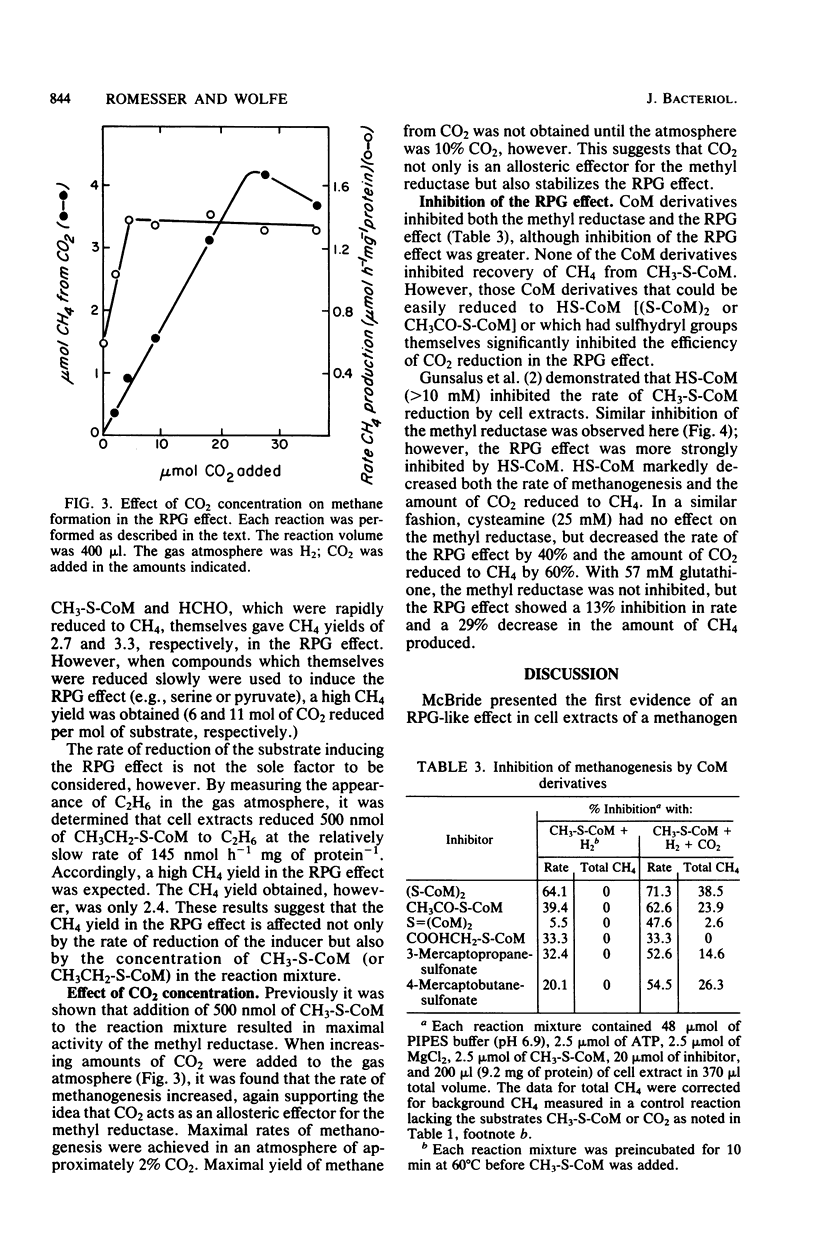
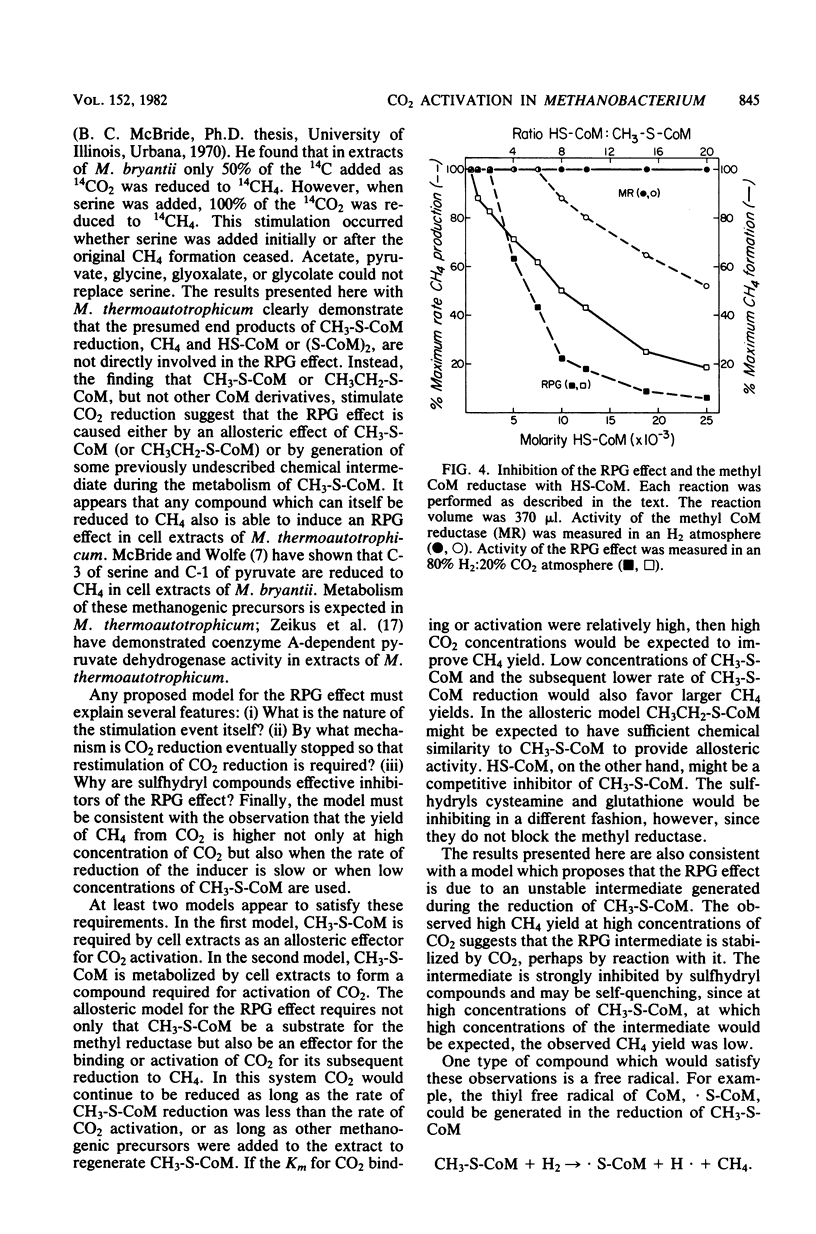
The stimulation of carbon dioxide reduction to methane by addition of 2-(methylthio)ethanesulfonate (CH3-S-CoM) to cell extracts of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum was investigated. Similar stimulation of CO2 reduction by CH3-S-CoM was found for cell extracts of Methanobacterium bryantii and Methanospirillum hungatei. The CH3-S-CoM requirement could be met by the methanogenic precursors formaldehyde, serine, or pyruvate, or by 2-(ethylthio)ethanesulfonate (CH3CH2-S-CoM), but not by other coenzyme M derivatives. Efficient reduction of CO2 to CH4 was favored by low concentrations of CH3-S-CoM and high concentrations of CO2. Sulfhydryl compounds were identified as effective inhibitors of CO2 reduction. Both an allosteric model and a free-radical model for the mechanism of CO2 activation and reduction are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gunsalus R. P., Romesser J. A., Wolfe R. S. Preparation of coenzyme M analogues and their activity in the methyl coenzyme M reductase system of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. Biochemistry. 1978 Jun 13;17(12):2374–2377. doi: 10.1021/bi00605a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunsalus R. P., Wolfe R. S. Stimulation of CO2 reduction to methane by methylcoenzyme M in extracts Methanobacterium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jun 6;76(3):790–795. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91570-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride B. C., Wolfe R. S. A new coenzyme of methyl transfer, coenzyme M. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 8;10(12):2317–2324. doi: 10.1021/bi00788a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romesser J. A., Balch W. E. Coenzyme M: preparation and assay. Methods Enzymol. 1980;67:545–552. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)67067-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romesser J. A., Wolfe R. S. Interaction of coenzyme M and formaldehyde in methanogenesis. Biochem J. 1981 Sep 1;197(3):565–571. doi: 10.1042/bj1970565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. D., Wolfe R. S. Structure and methylation of coenzyme M(HSCH2CH2SO3). J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 10;249(15):4879–4885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G., Fuchs G., Kenealy W., Thauer R. K. Oxidoreductases involved in cell carbon synthesis of Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):604–613. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.604-613.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


