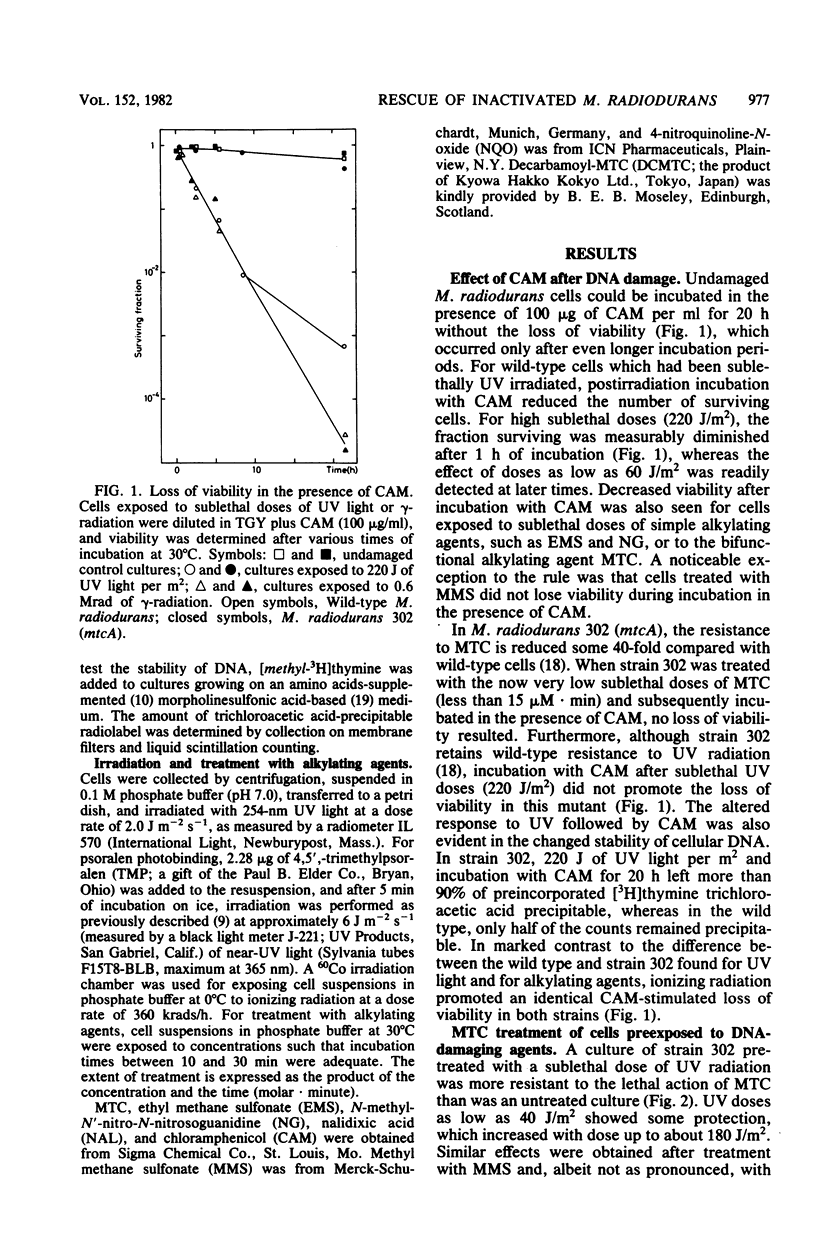
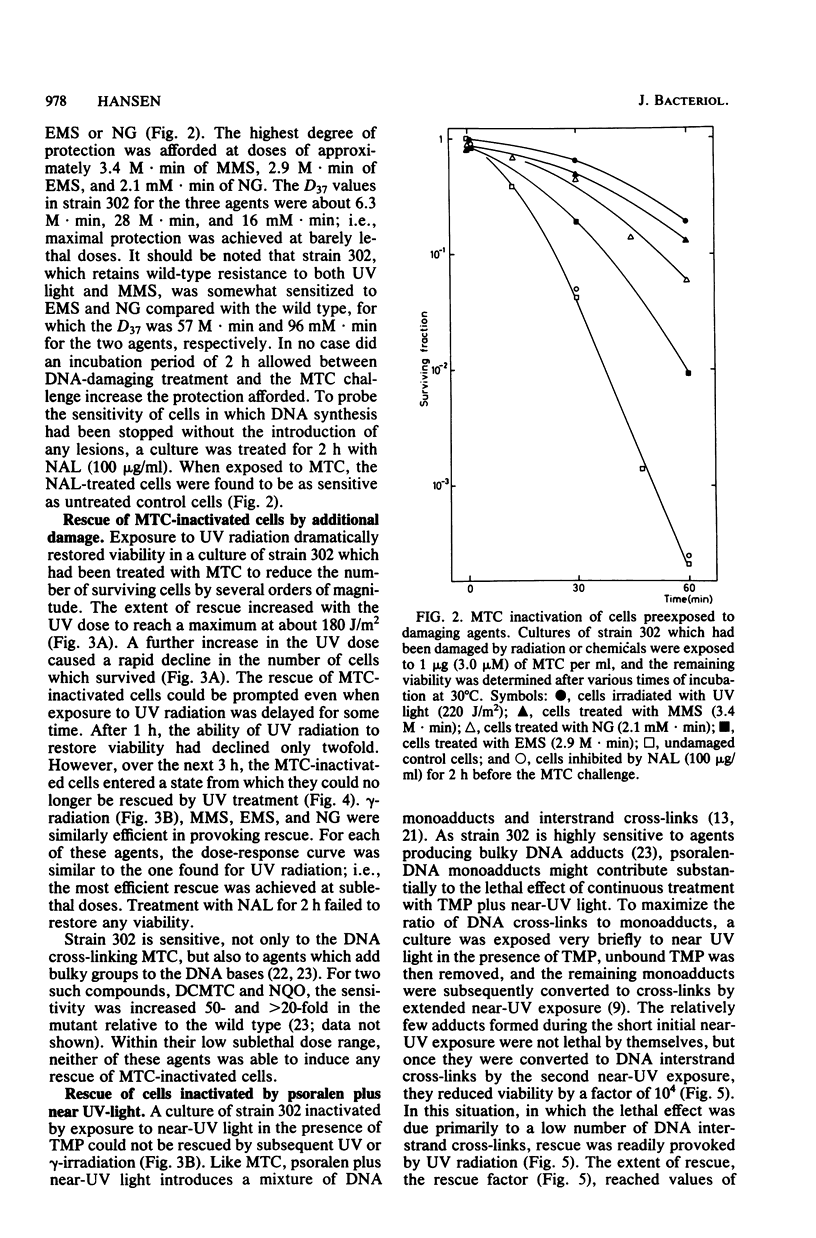
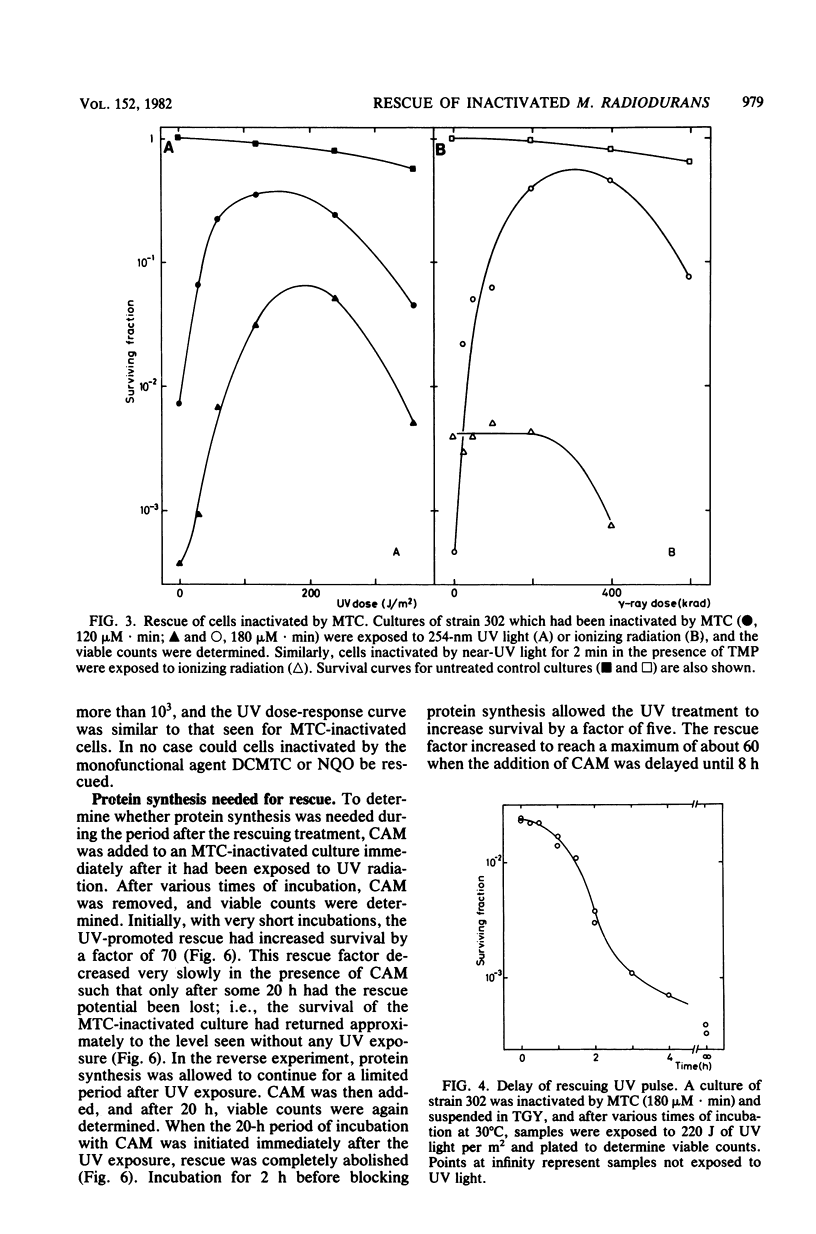
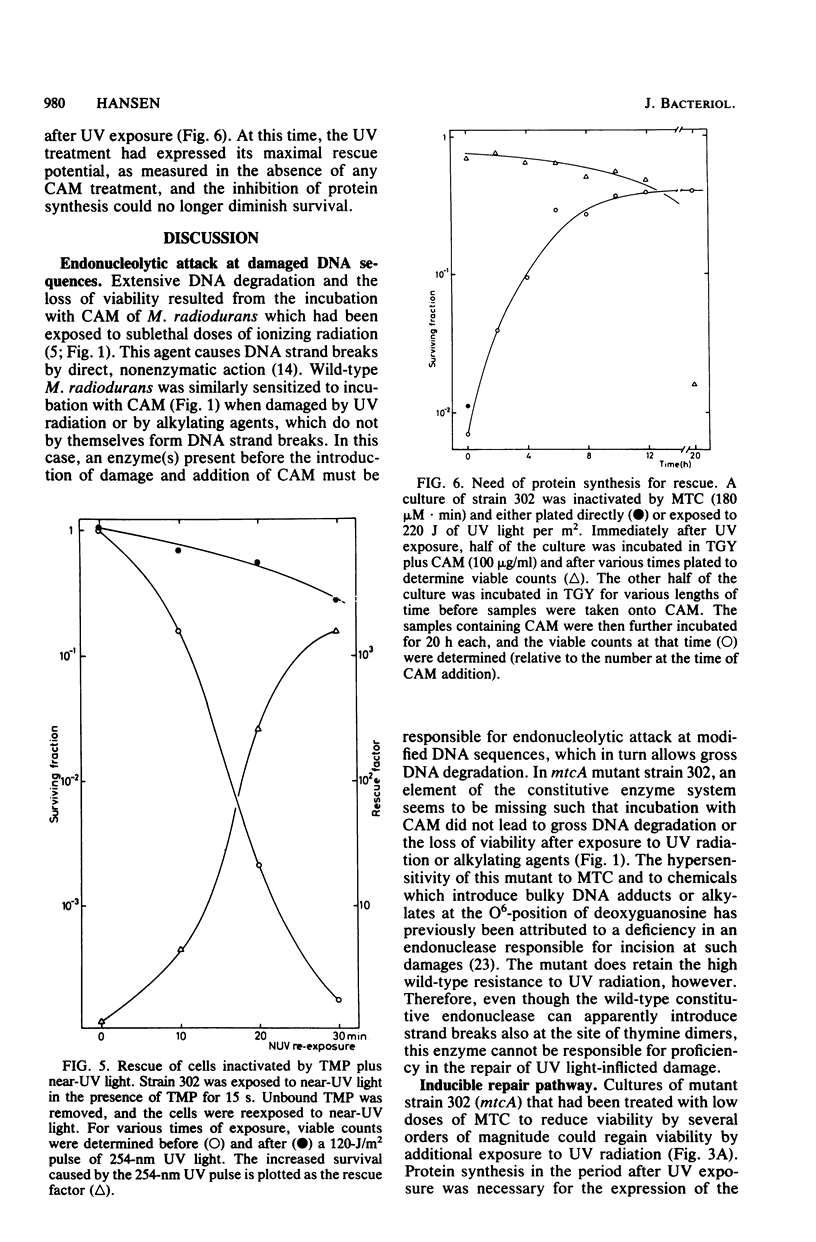
Abstract
The processing of damaged DNA was altered in a mitomycin C-sensitive mutant (mtcA) of Micrococcus radiodurans. Even though the mutant retained resistance to 254-nm UV radiation, it did not, in contrast to the wild-type strain, show any excessive DNA degradation or cell death when incubated with chloramphenicol after sublethal doses of either UV light or mitomycin C. The results suggest the constitutive synthesis of an enzyme system responsible for wild-type proficiency in the repair of mitomycin C-induced damage. An alternative system able to repair damage caused by mitomycin C was demonstrated in the mtcA background. In this strain, additional damage inflicted upon the cellular DNA effected a massive rescue of cells previously inactivated by mitomycin C. Rescue was provoked by ionizing radiation, by UV light, or by simple alkylating agents. Cells treated with psoralen plus near-UV radiation could be rescued only when inactivation was due primarily to psoralen-DNA interstrand cross-links rather than to monoadducts. The rescue of inactivated cells was prevented in the presence of chloramphenicol. These results can be interpreted most readily in terms of an alternative repair system able to overcome DNA interstrand cross-links produced by mitomycin C or psoralen plus near-UV light, but induced only by the more abundant number of damages produced by radiation or simple alkylating agents.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burrell A. D., Feldschreiber P., Dean C. J. DNA-membrane association and the repair of double breaks in x-irradiated Micrococcus radiodurans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 30;247(1):38–53. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90805-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole R. S. Inactivation of Escherichia coli, F' episomes at transfer, and bacteriophage lambda by psoralen plus 360-nm light: significance of deoxyribonucleic acid cross-links. J Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;107(3):846–852. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.3.846-852.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole R. S., Levitan D., Sinden R. R. Removal of psoralen interstrand cross-links from DNA of Escherichia coli: mechanism and genetic control. J Mol Biol. 1976 May 5;103(1):39–59. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90051-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean C. J., Little J. G., Serianni R. W. The control of post irradiation DNA breakdown in Micrococcus radiodurans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Apr 8;39(1):126–134. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90767-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driedger A. A., Grayston M. J. The effects of nalidixic acid on X-ray-induced DNA degradation and repair in Micrococcus radiodurans. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Apr;17(4):501–505. doi: 10.1139/m71-083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogliano M., Schendel P. F. Evidence for the inducibility of the uvrB operon. Nature. 1981 Jan 15;289(5794):196–198. doi: 10.1038/289196a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S. Genetic control of the SOS system in E. coli. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):1–2. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90261-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover N. B., Margalit A., Zaritsky A., Ben-Hur E., Hansen M. T. Sensitivity of exponentially growing populations of Escherichia coli to photo-induced psoralen-DNA interstrand crosslinks. Biophys J. 1981 Jan;33(1):93–106. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84874-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M. T. Multiplicity of genome equivalents in the radiation-resistant bacterium Micrococcus radiodurans. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):71–75. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.71-75.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearst J. E. Psoralen photochemistry. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1981;10:69–86. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.10.060181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapp D. S., Smith K. C. Chemical nature of chain breaks produced in DNA by x-irradiation in vitro. Radiat Res. 1970 Apr;42(1):34–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenyon C. J., Walker G. C. Expression of the E. coli uvrA gene is inducible. Nature. 1981 Feb 26;289(5800):808–810. doi: 10.1038/289808a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman R., Weaver J., Tomasz M. Electrostatic complexes of mitomycin C with nucleic acids and polyanions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 21;521(2):779–791. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90317-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley B. E., Copland H. F. Four mutants of Micrococcus radiodurans defective in the ability to repair DNA damaged by mitomycin-C, two of which have wild-type resistance to ultraviolet radiation. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Apr 17;160(3):331–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00332977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley B. E., Copland H. J. The rate of recombination repair and its relationship to the radiation-induced delay in DNA synthesis in Micrococcus radiodurans. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Apr;93(2):251–258. doi: 10.1099/00221287-93-2-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott B. R., Pathak M. A., Mohn G. R. Molecular and genetic basis of furocoumarin reactions. Mutat Res. 1976;39(1):29–74. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(76)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest P. R., Moseley B. E. Defective excision repair in a mutant of Micrococcus radiodurans hypermutable by some monofunctional alkylating agents. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(1):191–199. doi: 10.1007/BF00268463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz M., Mercado C. M., Olson J., Chatterjie N. The mode of interaction of mitomycin C with deoxyribonucleic acid and other polynucleotides in vitro. Biochemistry. 1974 Nov 19;13(24):4878–4887. doi: 10.1021/bi00721a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Ultraviolet mutagenesis and inducible DNA repair in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):869–907. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.869-907.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



