Abstract
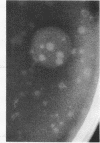
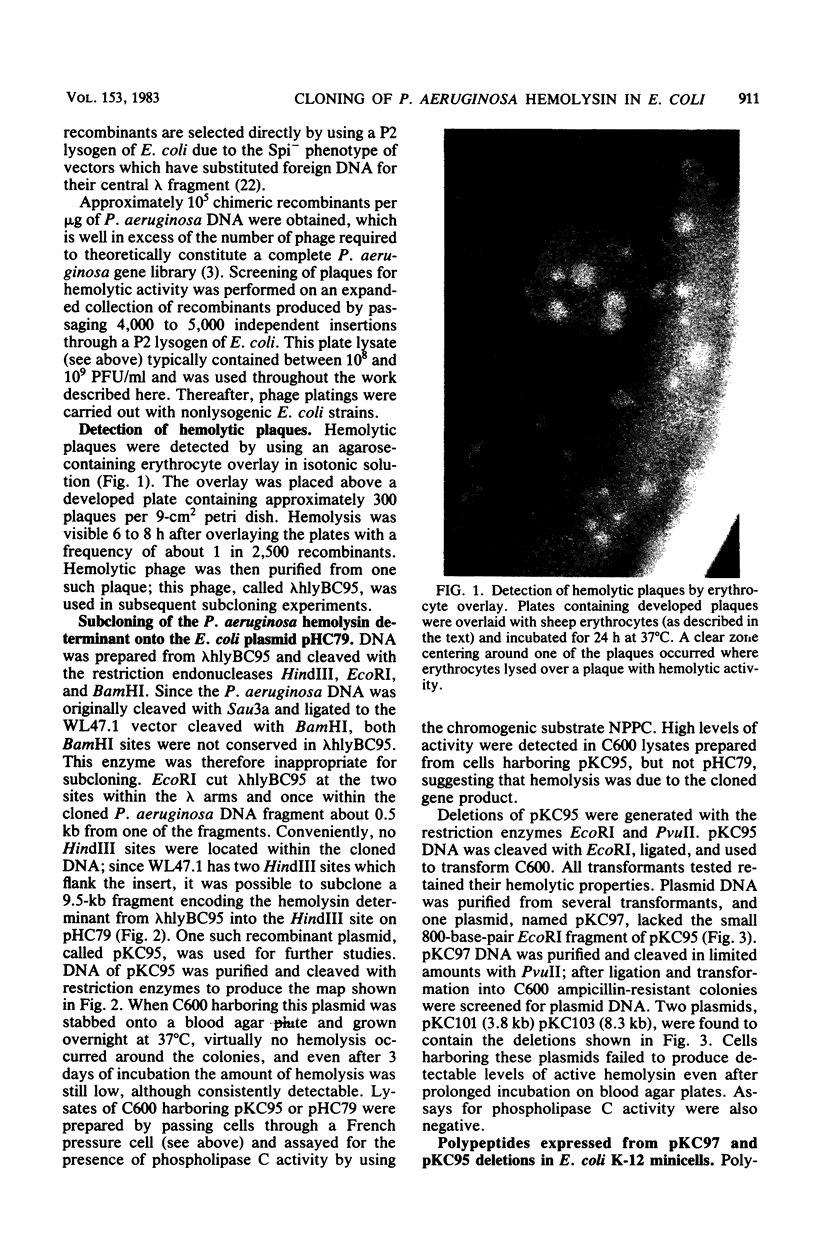
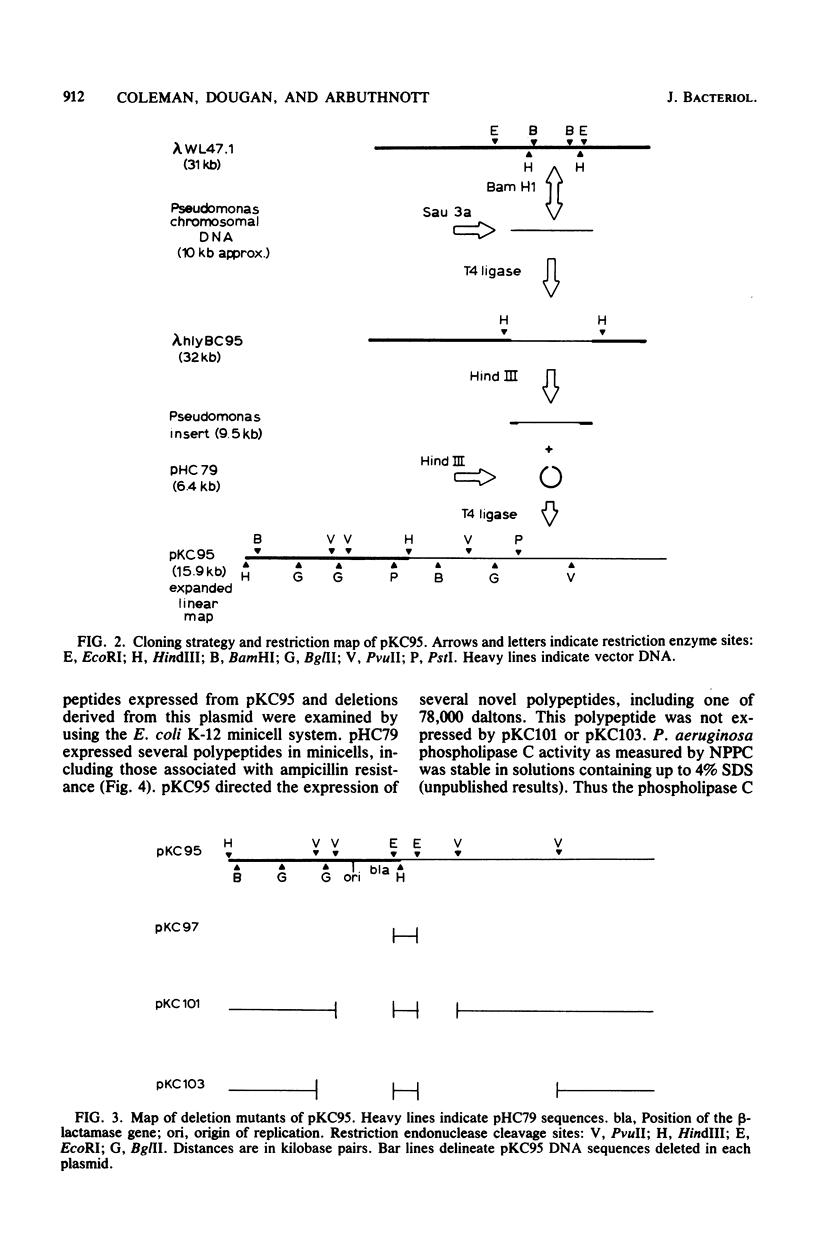
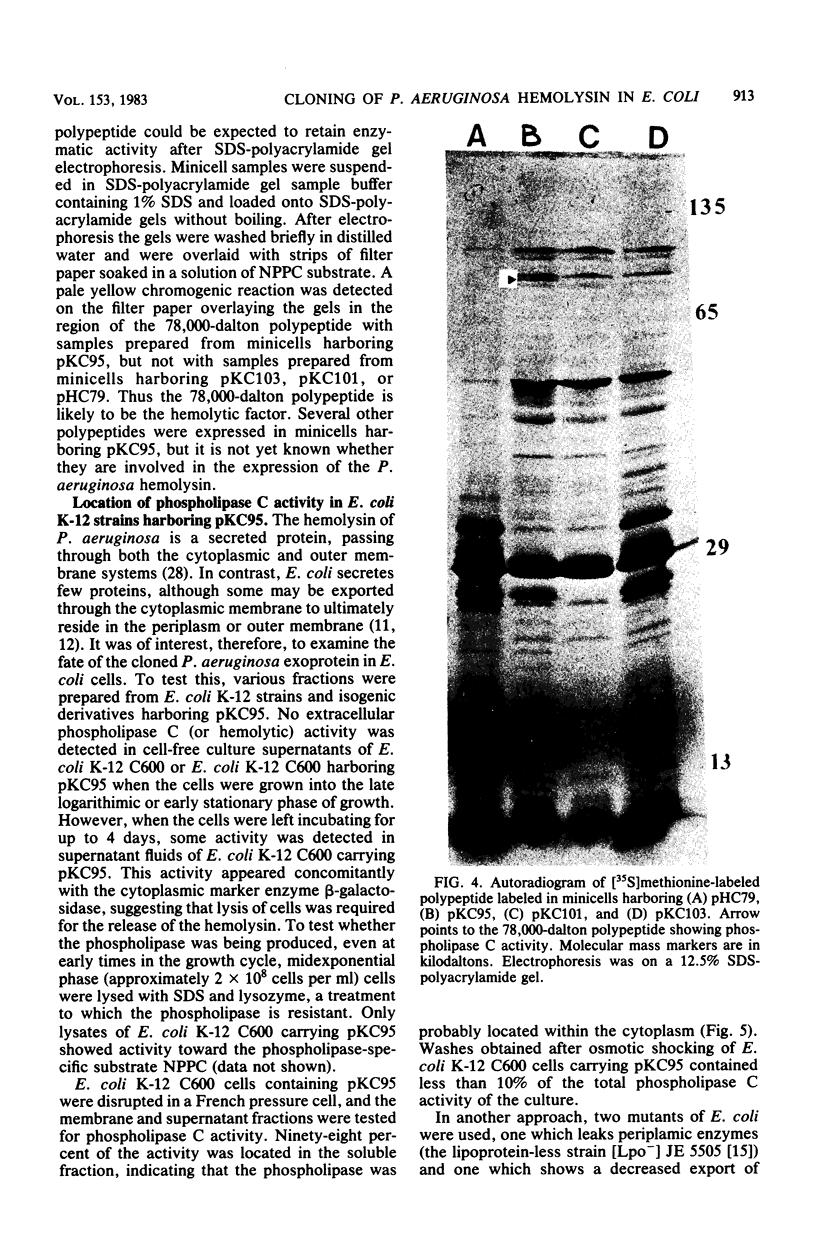
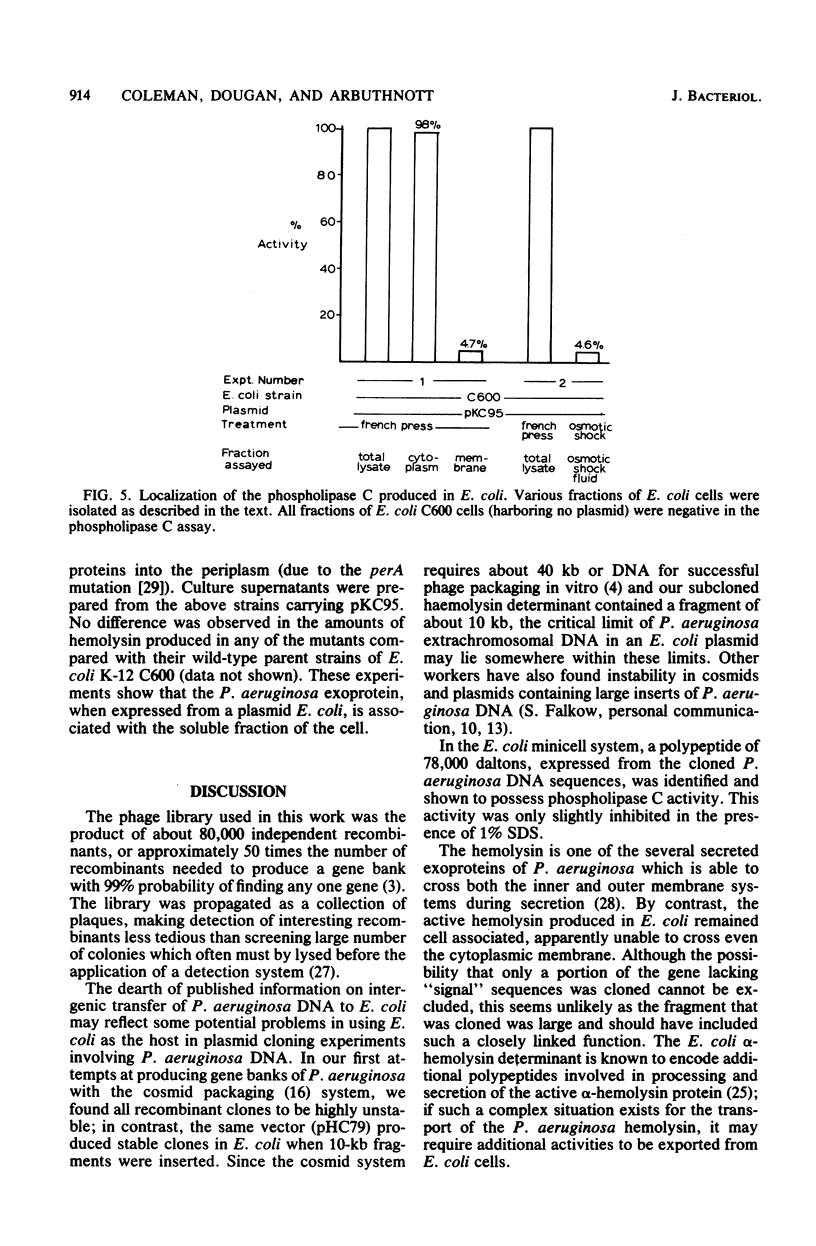
A hemolysin determinant was cloned from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA103 by inserting Sau3a-generated DNA fragments between the BamHI sites of the lambda replacement vector WL47.1. A 9.5-kilobase HindIII fragment encoding the hemolysin was subcloned from this phage and inserted into the plasmid vector pHC79 to generate the recombinant plasmid pKC95. Escherichia coli K-12 strains harboring pKC95 exhibited zones of hemolysis after several days of growth on blood agar plates. Hemolysis was shown to be due to phospholipase C activity by using the chromogenic substrate p-nitrophenylphosphorylcholine. Deletion mutants of pKC95 were isolated, and polypeptides expressed from these plasmids were examined by using the E. coli minicell system. A polypeptide of 78,000 daltons was associated with phospholipase C activity. The hemolytic activity was cell associated when expressed in E. coli.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al-Dujaili A. H., Harris D. M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in hospital: a comparison between 'infective' and 'environmental' strains. J Hyg (Lond) 1975 Oct;75(2):195–201. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400047227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. A colony bank containing synthetic Col El hybrid plasmids representative of the entire E. coli genome. Cell. 1976 Sep;9(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J., Brüning H. J. Plasmids useable as gene-cloning vectors in an in vitro packaging by coliphage lambda: "cosmids". Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):85–107. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougan G., Sherratt D. The transposon Tn1 as a probe for studying ColE1 structure and function. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Mar 7;151(2):151–160. doi: 10.1007/BF00338689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ESSELMANN M. T., LIU P. V. Lecithinase production by gramnegative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1961 Jun;81:939–945. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.6.939-945.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Evans D. G., Höhne C., Noble M. A., Haldane E. V., Lior H., Young L. S. Hemolysin and K antigens in relation to serotype and hemagglutination type of Escherichia coli isolated from extraintestinal infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jan;13(1):171–178. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.1.171-178.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finger J., Krishnapillai V. Host range, entry exclusion, and incompatibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa FP plasmids. Plasmid. 1980 May;3(3):332–342. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(80)90046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Silhavy T. J. Genetic analysis of the major outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:91–142. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.000515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelbauer G. L., Harayama S. Mutants in transmission of chemotactic signals from two independent receptors of E. coli. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):617–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Jacob A. E., Crawford I. P. Wide ranging plasmid bearing the Pseudomonas aeruginosa tryptophan synthase genes. Nature. 1977 May 19;267(5608):283–284. doi: 10.1038/267283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota Y., Suzuki H., Nishimura Y., Yasuda S. On the process of cellular division in Escherichia coli: a mutant of E. coli lacking a murein-lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1417–1420. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Collins J. A small cosmid for efficient cloning of large DNA fragments. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurioka S., Matsuda M. Phospholipase C assay using p-nitrophenylphosphoryl-choline together with sorbitol and its application to studying the metal and detergent requirement of the enzyme. Anal Biochem. 1976 Sep;75(1):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90078-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU P. V., ABE Y., BATES J. L. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. J Infect Dis. 1961 Mar-Apr;108:218–228. doi: 10.1093/infdis/108.2.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. Extracellular toxins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1974 Nov;130 (Suppl)(0):S94–S99. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.supplement.s94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. V. The roles of various fractions of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in its pathogenesis. 3. Identity of the lethal toxins produced in vitro and in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1966 Oct;116(4):481–489. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.4.481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loenen W. A., Brammar W. J. A bacteriophage lambda vector for cloning large DNA fragments made with several restriction enzymes. Gene. 1980 Aug;10(3):249–259. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Brammar W. J., Murray K. Lambdoid phages that simplify the recovery of in vitro recombinants. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Jan 7;150(1):53–61. doi: 10.1007/BF02425325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noegel A., Rdest U., Springer W., Goebel W. Plasmid cistrons controlling synthesis and excretion of the exotoxin alpha-haemolysin of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Oct 1;175(3):343–350. doi: 10.1007/BF00397234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalka A., Shapiro L. In situ immunoassays for gene translation products in phage plaques and bacterial colonies. Gene. 1976;1(1):65–79. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(76)90007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson M. W., Hayden C. Secretion of phospholipase C by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):558–564. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.558-564.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L., Sarthy A., Beckwith J. Escherichia coli pleiotropic mutant that reduces amounts of several periplasmic and outer membrane proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):229–239. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.229-239.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Dellinger E. P., Minshew B., Falkow S. Haemolysin contributes to virulence of extra-intestinal E. coli infections. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):665–667. doi: 10.1038/294665a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]