Abstract
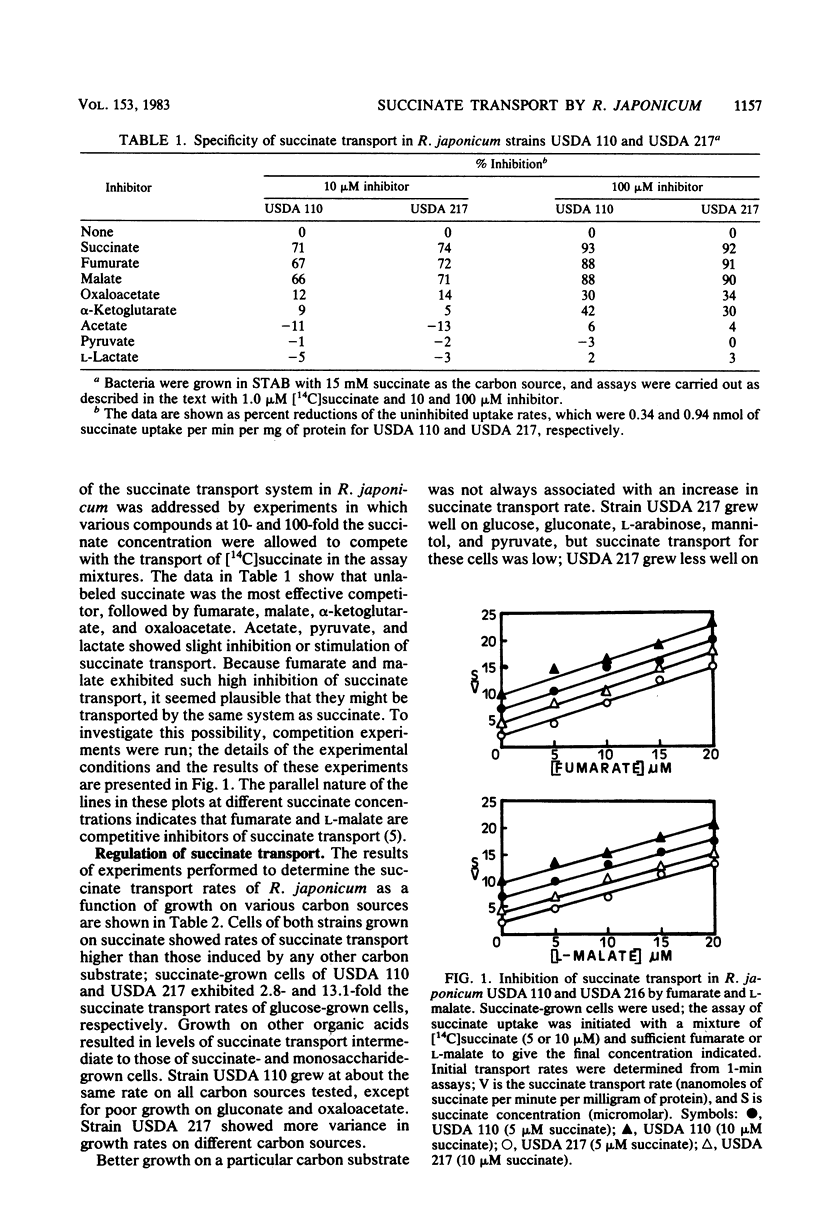
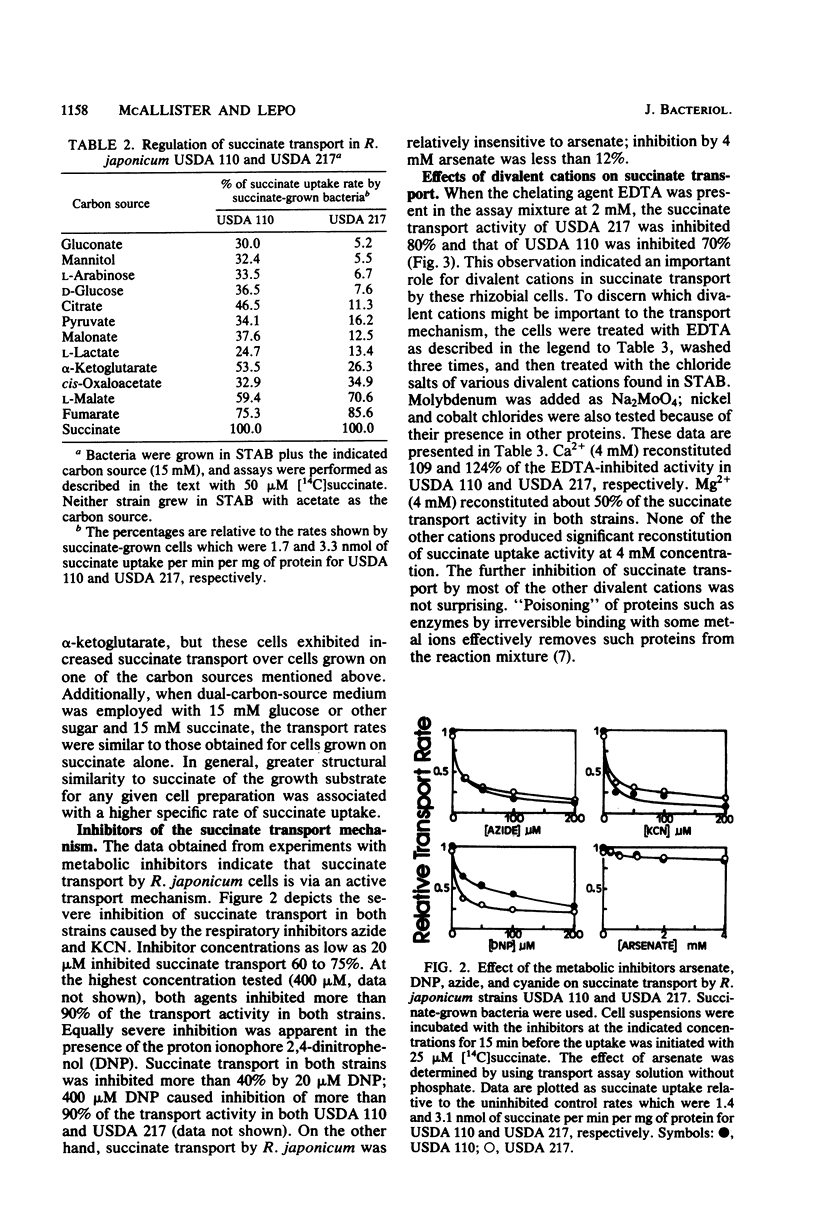
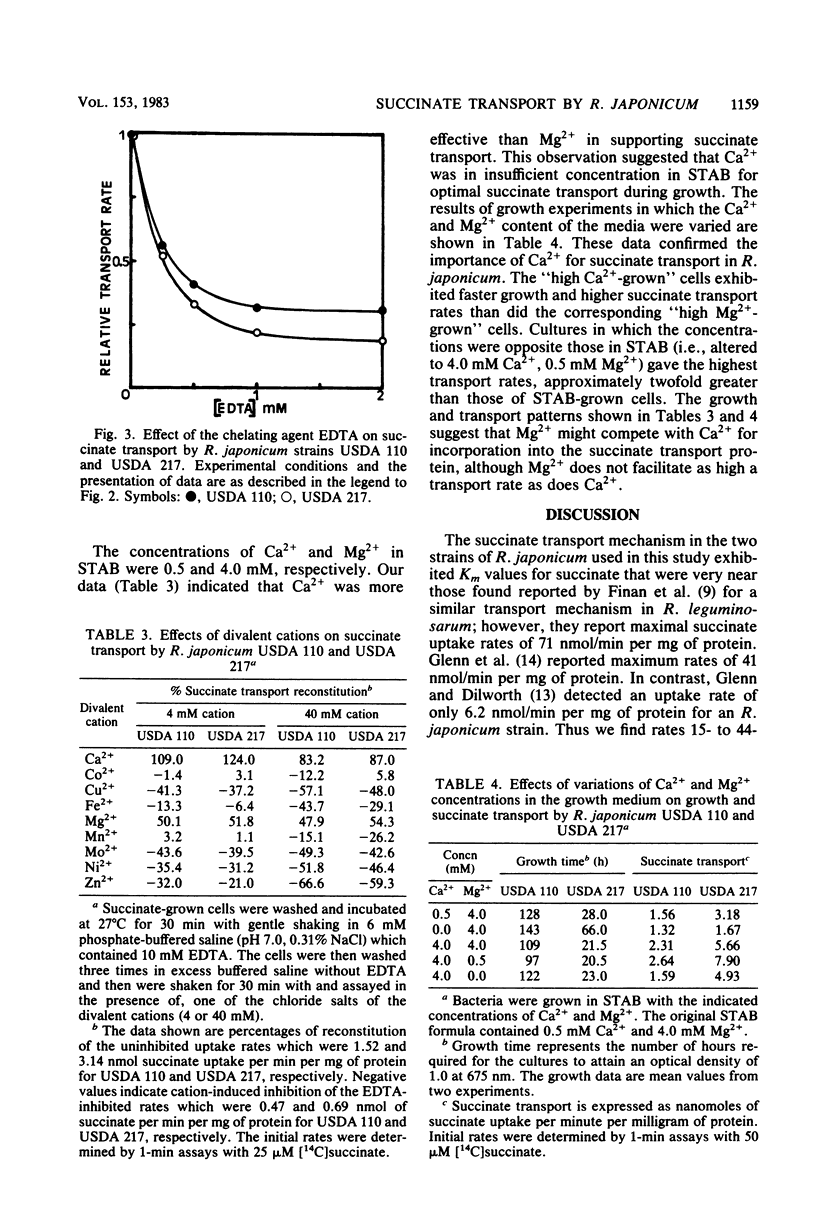
We have demonstrated that the transport of succinate into the cells of Rhizobium japonicum strains USDA 110 and USDA 217 is severely inhibited by cyanide, azide, and 2,4-dinitrophenol, but not by arsenate. These results suggest an active mechanism of transport that is dependent on an energized membrane, but does not directly utilize ATP. The apparent Km for succinate was 3.8 microM for strain USDA 110 and 1.8 microM for strain USDA 217; maximal transport velocities were 1.5 and 3.3 nmol of succinate per min per mg of protein, respectively. The expression of the succinate uptake activity was inducible rather than constitutive, with succinate and structurally related compounds being the most effective inducers. The mechanism showed some specificity for succinate and similar organic acids; fumarate and L-malate were classical competitive inhibitors of the system. In general, the best competing compounds were also the best carbon substrates for induction of succinate uptake activity. EDTA inhibited the transport of succinate, implying a role for divalent cations in the system. When various divalent cations were used to reconstitute EDTA-inhibited activity, Ca2+ was most effective, followed by Mg2+, which restored activity at about half the efficiency of Ca2+. Growth media that were supplemented with increased Ca2+ concentration supported more rapid growth with succinate as the carbon substrate, and cells from such media showed higher specific activities of succinate transport.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERGERSEN F. J. The bacterial component of soybean root nodules; changes in respiratory activity, cell dry weight and nucleic acid content with increasing nodule age. J Gen Microbiol. 1958 Oct;19(2):312–323. doi: 10.1099/00221287-19-2-312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergersen J. F., Turner G. L. Nitrogen fixation by the bacteroid fraction of breis of soybean root nodules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Aug 29;141(3):507–515. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornish-Bowden A. A simple graphical method for determining the inhibition constants of mixed, uncompetitive and non-competitive inhibitors. Biochem J. 1974 Jan;137(1):143–144. doi: 10.1042/bj1370143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finan T. M., Wood J. M., Jordan D. C. Succinate transport in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Bacteriol. 1981 Oct;148(1):193–202. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.1.193-202.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiol A., Arias A., Cerveñansky C., Martínez-Drets G. Succinate dehydrogenase mutant of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1621–1623. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1621-1623.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghei O. K., Kay W. W. Properties of an inducible C 4 -dicarboxylic acid transport system in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):65–79. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.65-79.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Cameron M. J. Transport of C4-dicarboxylic acids in salmonella typhimurium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Sep;190(1):281–289. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay W. W., Kornberg H. L. The uptake of C4-dicarboxylic acids by Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jan;18(2):274–281. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01240.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyser H. H., Bohlool B. B., Hu T. S., Weber D. F. Fast-growing rhizobia isolated from root nodules of soybean. Science. 1982 Mar 26;215(4540):1631–1632. doi: 10.1126/science.215.4540.1631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-de Drets G., Arias A., Rovira de Cutinella M. Fast- and slow-growing rhizobia: differences in sucrose utilization and invertase activity. Can J Microbiol. 1974 Apr;20(4):605–609. doi: 10.1139/m74-092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-De Drets G., Arias A. Enzymatic basis for differentiation of Rhizobium into fast- and slow-growing groups. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):467–470. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.467-470.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. Chemiosmotic coupling in oxidative and photosynthetic phosphorylation. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1966 Aug;41(3):445–502. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1966.tb01501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronson C. W., Lyttleton P., Robertson J. G. C(4)-dicarboxylate transport mutants of Rhizobium trifolii form ineffective nodules on Trifolium repens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4284–4288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeter J. G. Carbohydrates in Soybean Nodules: II. DISTRIBUTION OF COMPOUNDS IN SEEDLINGS DURING THE ONSET OF NITROGEN FIXATION. Plant Physiol. 1980 Sep;66(3):471–476. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.3.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban J. E., Dazzo F. B. Succinate-Induced Morphology of Rhizobium trifolii 0403 Resembles That of Bacteroids in Clover Nodules. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jul;44(1):219–226. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.1.219-226.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries G. E., van Brussel A. A., Quispel A. Mechanism of regulation of glucose transport in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):872–879. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.872-879.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


