Abstract
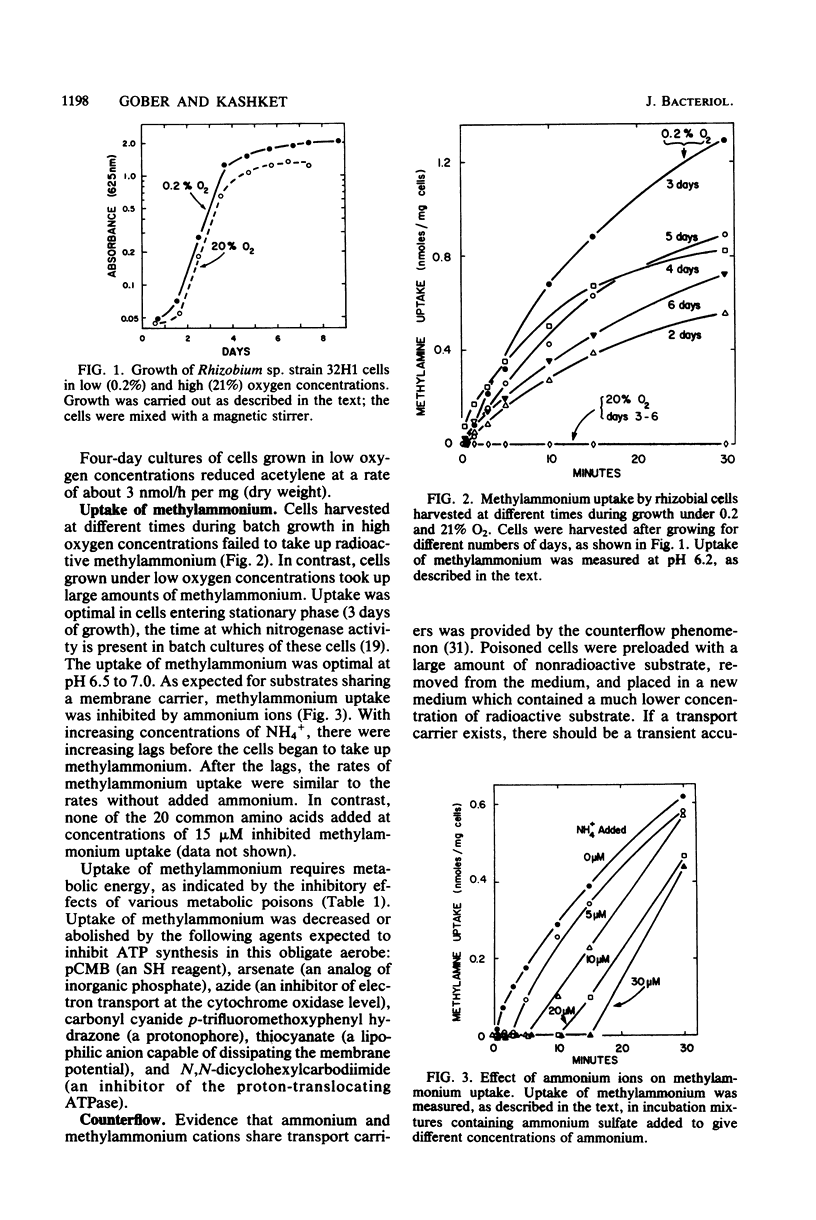
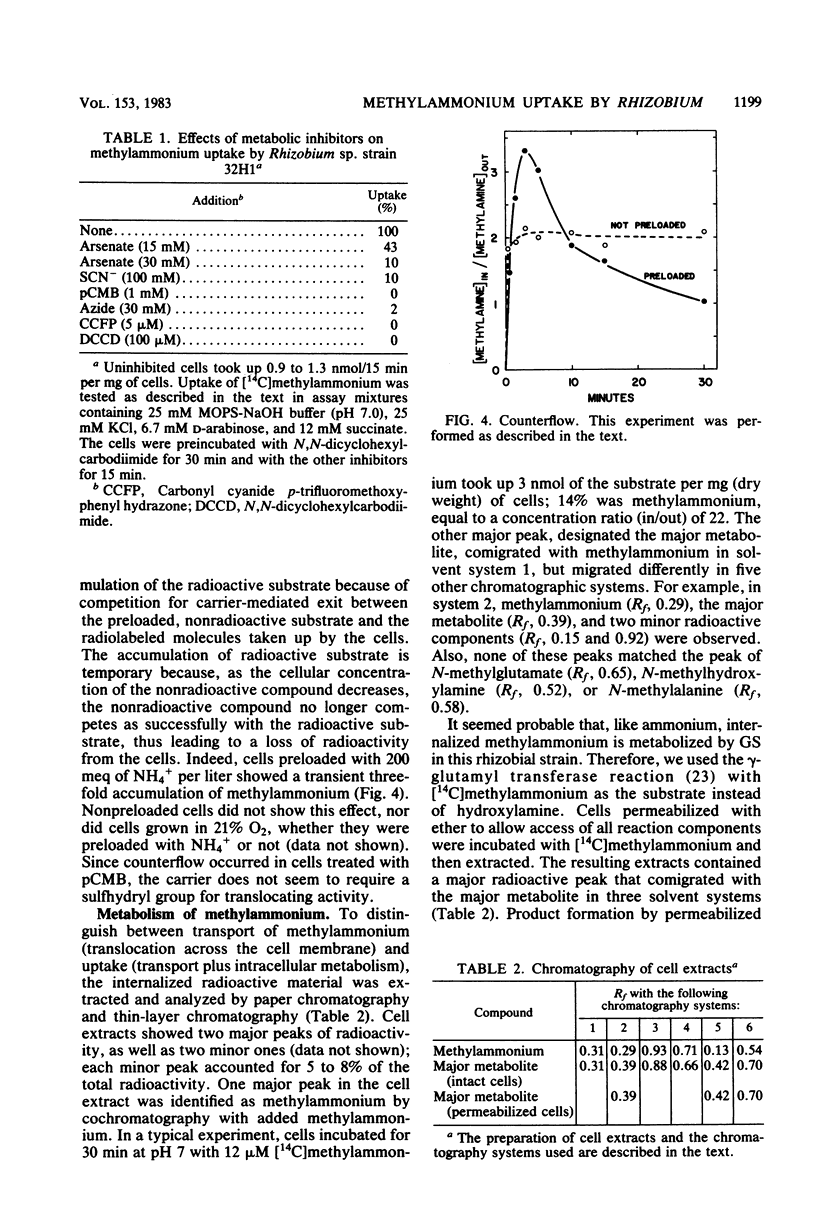
We present evidence that methylammonium is transported into cowpea Rhizobium sp. strain 32H1 cells by a membrane carrier whose natural substrate is ammonium. After growth in low (0.2%) oxygen, which is necessary for nitrogen fixation by these cells, respiring rhizobial cells took up [14C]methylammonium to high intracellular levels. Cells grown in atmospheric (21%) oxygen did not take up methylammonium. Uptake (transport plus metabolism) was maximal in cells harvested in the early stationary phase of batch culture and had a distinct pH optimum of 6.5 to 7.0. Uptake was inhibited by metabolic poisons that dissipate the proton motive force or inhibit ATP synthesis. Inhibition of uptake by ammonium and the counterflow phenomenon indicated that ammonium and methylammonium share a transport carrier. Of the methylammonium taken up, about 15% was accumulated to intracellular levels 20 times higher than those in the medium; most of the methylammonium was metabolized to gamma-N-methylglutamine.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes E. M., Jr, Zimniak P. Transport of ammonium and methylammonium ions by Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):512–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.512-516.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellion E., Khan M. Y., Romano M. J. Transport of methylamine by Pseudomonas sp. MA. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):786–790. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.786-790.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender R. A., Janssen K. A., Resnick A. D., Blumenberg M., Foor F., Magasanik B. Biochemical parameters of glutamine synthetase from Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):1001–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.1001-1009.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darrow R. A., Knotts R. R. Two forms of glutamine synthetase in free-living root-nodule bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 23;78(2):554–559. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90214-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. K., Moore R. A. Ammonium and methylammonium transport by the nitrogen-fixing bacterium Azotobacter vinelandii. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):435–442. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.435-442.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Barker S. L. Effects of potassium ions on the electrical and pH gradients across the membrane of Streptococcus lactis cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1017–1023. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1017-1023.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. Proton motive force in growing Streptococcus lactis and Staphylococcus aureus cells under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):369–376. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.369-376.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khym J. X. An analytical system for rapid separation of tissue nucleotides at low pressures on conventional anion exchangers. Clin Chem. 1975 Aug;21(9):1245–1252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner D. Ammonium (methylammonium) transport by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 28;688(3):702–708. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90282-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner D. Ammonium uptake by nitrogen fixing bacteria I. Azotobacter vinelandii. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Jun 22;104(2):163–169. doi: 10.1007/BF00447319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner D., Fitzke E. Some properties of a new electrogenic transport system: the ammonium (methylammonium) carrier from Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 20;641(1):138–147. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90577-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner D. The transport of NH3 and NH4+ across biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 9;639(1):41–52. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(81)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung H. F., Wagner C. Gamma-glutamylmethylamide. A new intermediate in the metabolism of methylamine. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 10;244(15):4136–4140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laane C., Krone W., Konings W., Haaker H., Veeger C. Short-term effect of ammonium chloride on nitrogen fixation by Azotobacter vinelandii and by bacteroids of Rhizobium leguminosarum. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jan;103(1):39–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04286.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig R. A. Control of ammonium assimilation in Rhizobium 32H1. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):114–123. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.114-123.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig R. A., Signer E. R. Glutamine synthetase and control of nitrogen fixation in Rhizobium. Nature. 1977 May 19;267(5608):245–248. doi: 10.1038/267245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosberg H. P., Hoffmann-Berling H. DNA synthesis in nucleotide-permeable Escherichia coli cells. I. Preparation and properties of ether-treated cells. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jun 28;58(3):739–753. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod R. E., Meister A. Studies on glutamine synthetase from Escherichia coli. Formation of pyrrolidone carboxylate and inhibition by methionine sulfoximine. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3997–4002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. T., Wilson T. H. Counterflow of galactosides in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;196(2):336–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(70)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


