Abstract
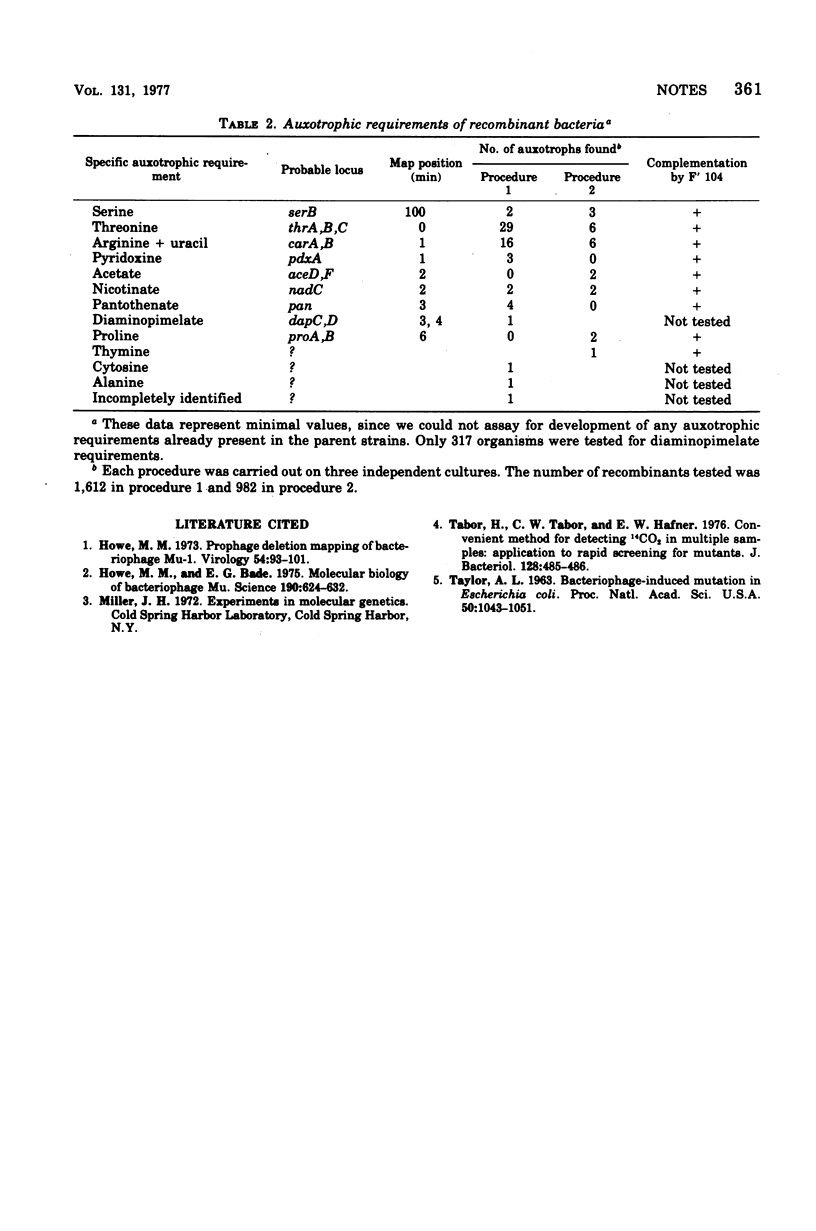
A method is described for markedly enriching a bacterial population for cells containing any given Mu insertion mutation. The method involves the transfer of a small piece of deoxyribonucleic acid from a Mu-infected Hfr donor donor strain to a suitable F- strain and a subsequent selection of those recombinant organisms that have received a Mu prophage from the donor. The method is particularly usefule for isolating mutants whose selection requires "brute-force" assay, since only a few hundred colonies have to be screened.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Howe M. M., Bade E. G. Molecular biology of bacteriophage mu. Science. 1975 Nov 14;190(4215):624–632. doi: 10.1126/science.1103291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe M. M. Prophage deletion mapping of bacteriophage Mu-1. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90118-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR A. L. BACTERIOPHAGE-INDUCED MUTATION IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Dec;50:1043–1051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.6.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor H., Tabor C. W., Hafner E. W. Convenient method for detecting 14CO2 in multiple samples: application to rapid screening for mutants. J Bacteriol. 1976 Oct;128(1):485–486. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.1.485-486.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


