Abstract
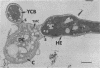
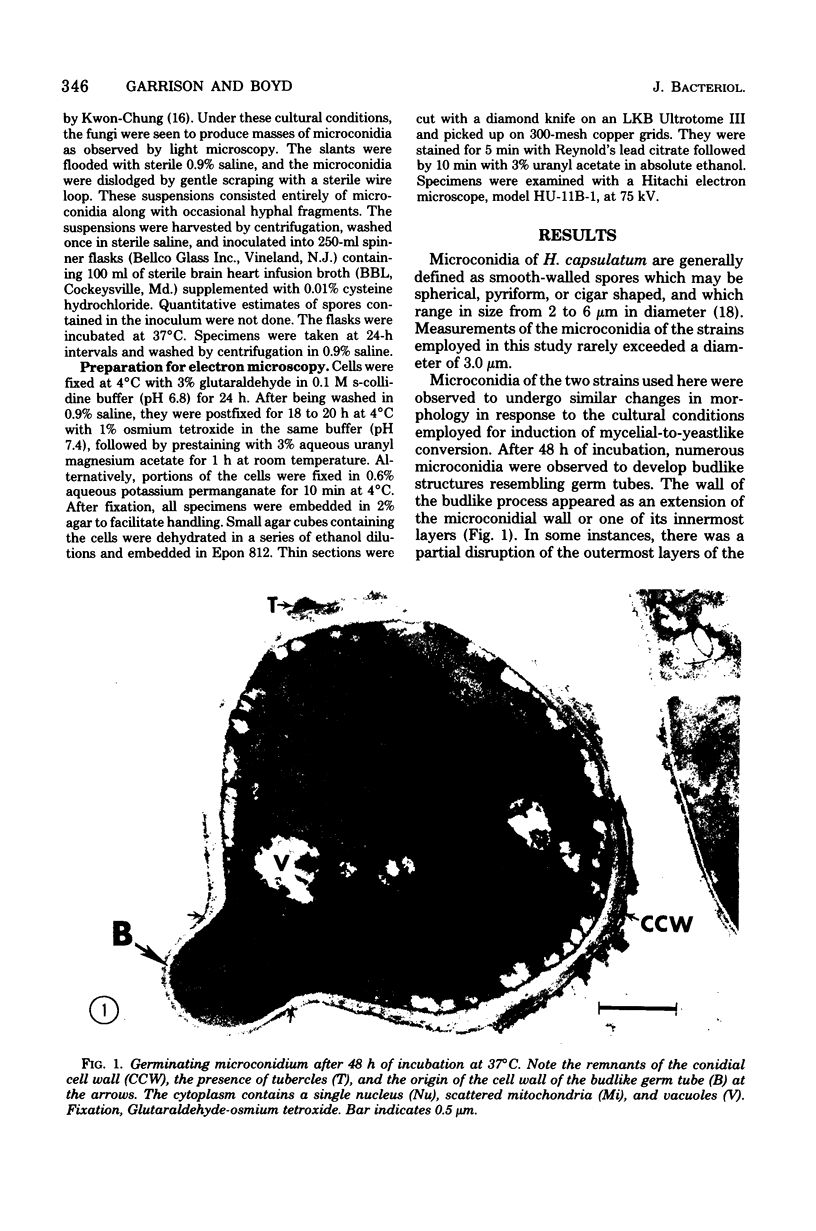
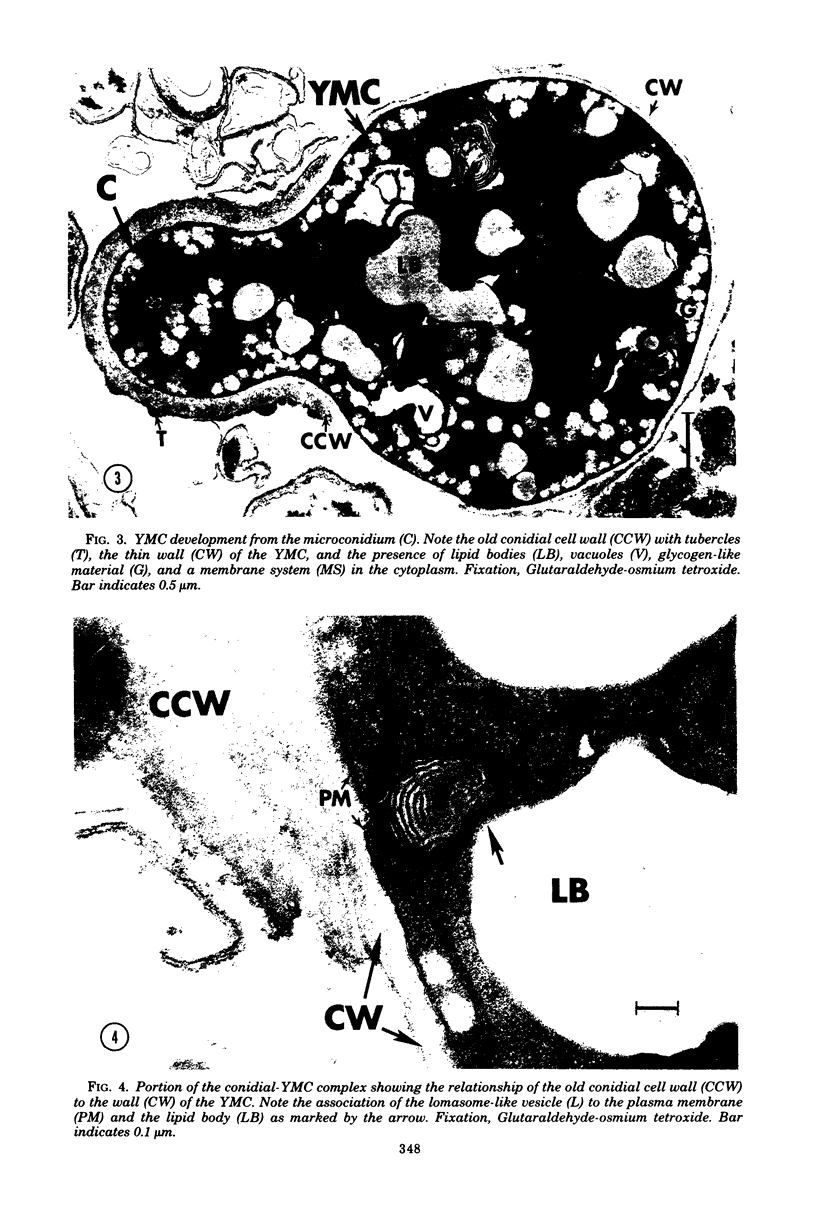
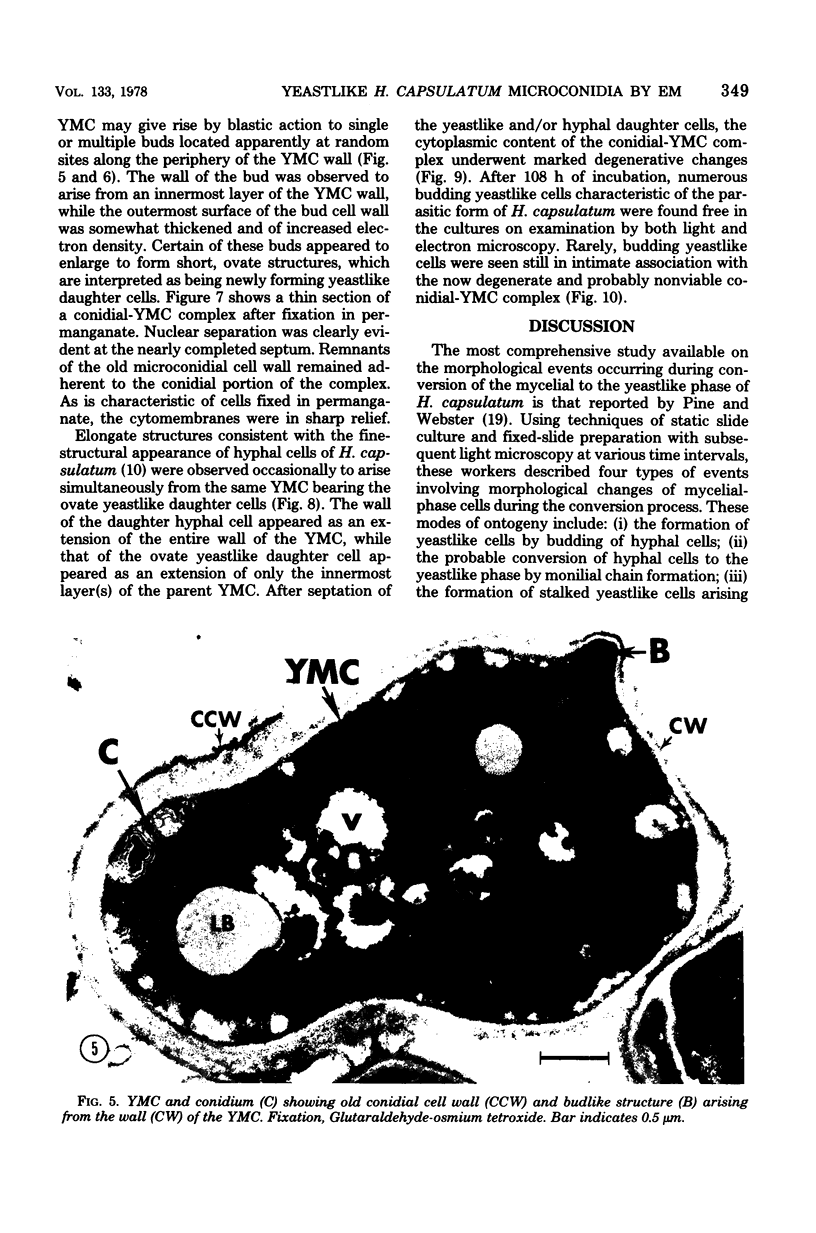
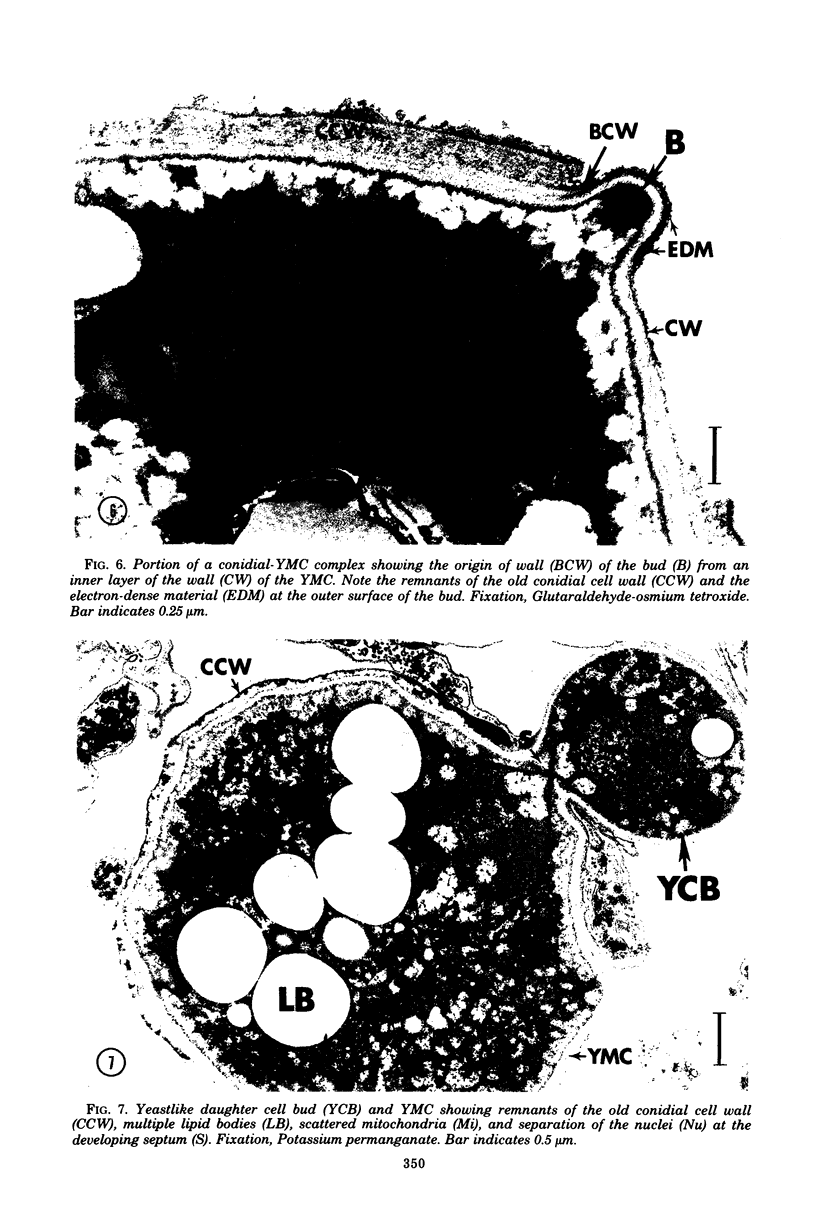
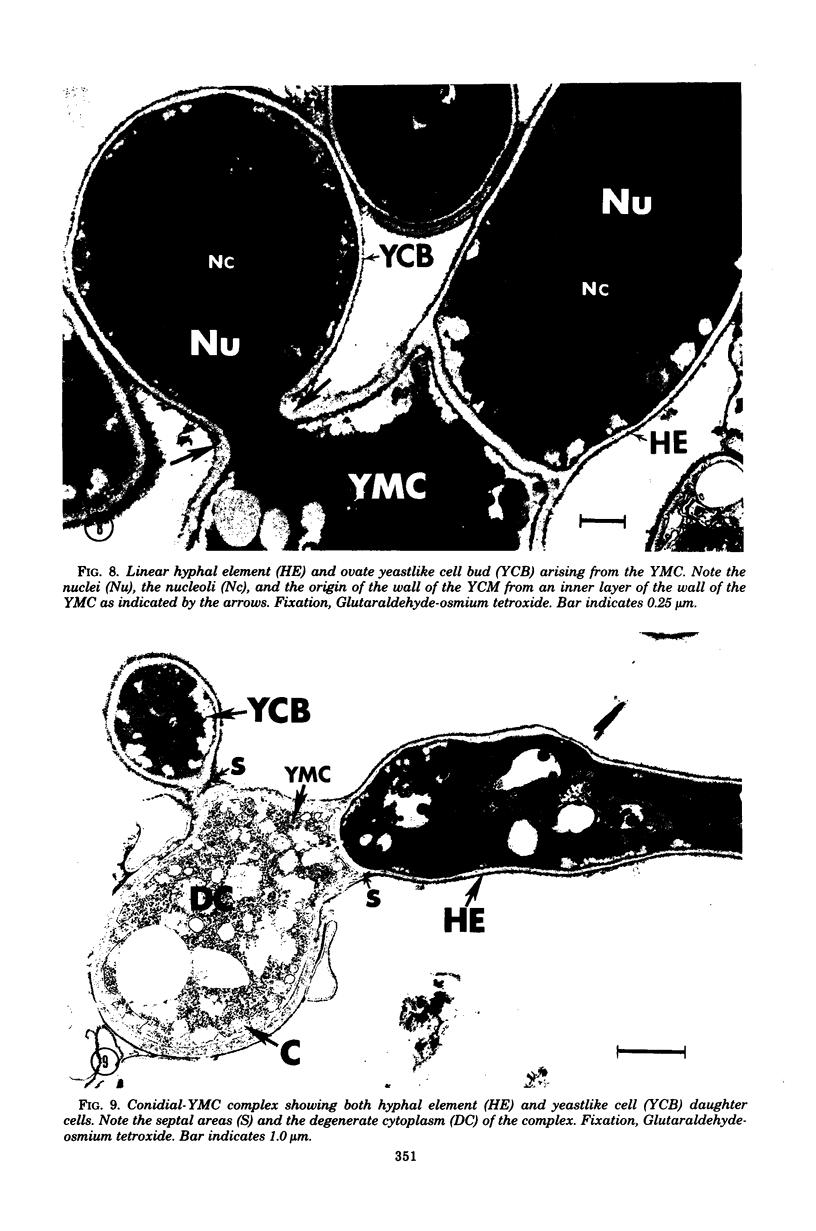
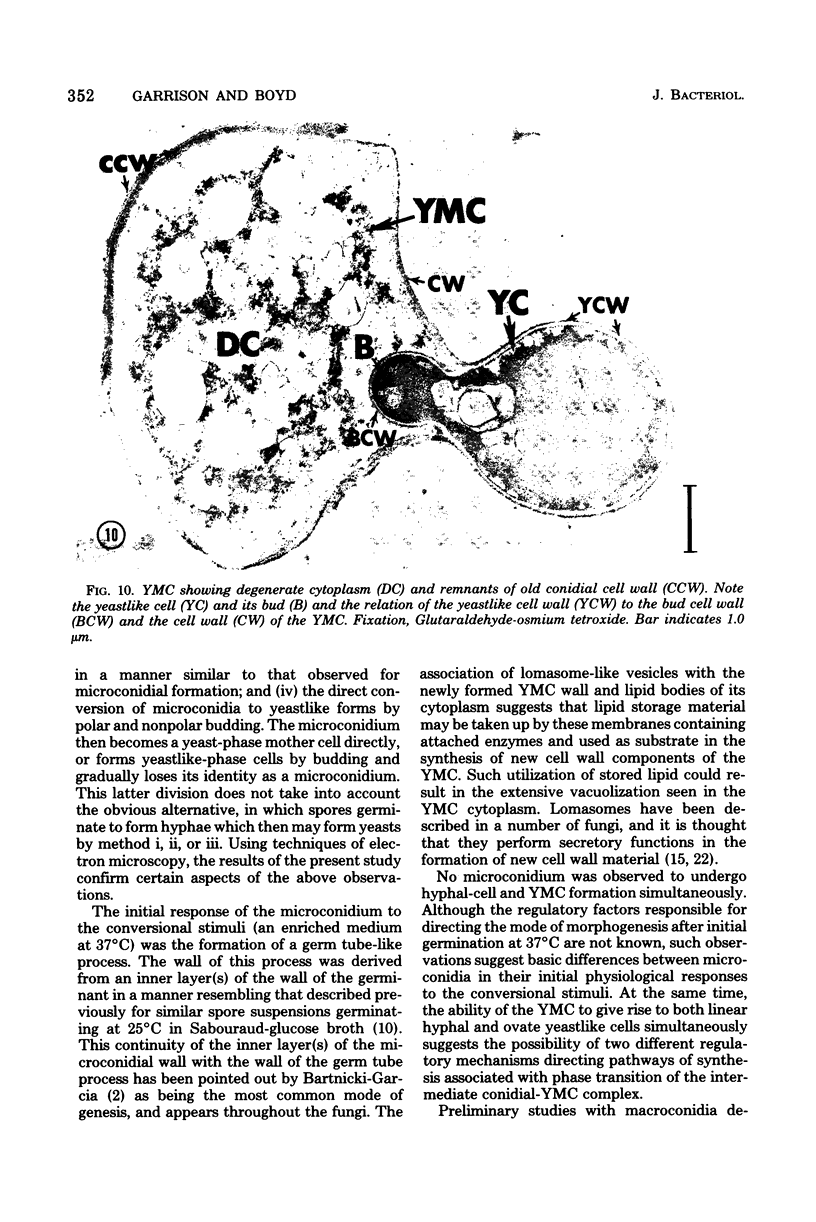
Fine details of the sequential morphological events occurring during transition of microconidia (spores less than 5 micrometer in diameter) to the yeastlike phase of Histoplasma capsulatum as seen in ultrathin section are described and illustrated by electron micrographs. Masses of microconidia were obtained when the fungas was grown on a garden soil extract medium. Spores were incubated under in vitro environmental conditions conducive for phase transition (an enriched medium at 37 degrees C). Within 48 h of incubation, the microconidia either germinated to give rise to a short mycelium or the germ tube process became a yeast mother cell without further extension. The wall of the yeast mother cell was thin and smooth, and its cytoplasmic content was ultrastructurally complex, consisting of numerous lipid bodies, vacuoles, glycogen-like deposits, and membrane systems. Within 96 h, the mother cell underwent multipolar budding to form simultaneously linear hyphal and/or ovate yeastlike daughter cells. During the transition, new cell wall materials of the germ tube, the mother cell, and yeastlike daughter cells arose by blastic action from the innermost layer(s) of the wall of the precursor form. Lomasome-like vesicles were often seen in association with areas of new cell wall formation. After organellar migration into and septation of the daughter cells, the yeast mother cell's cytoplasmic content underwent marked degenerative changes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. L., Marcus S. Sporulation characteristics of Histoplasma capsulatum. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1968 Nov 13;36(2):179–187. doi: 10.1007/BF02049684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartnicki-Garcia S. Cell wall chemistry, morphogenesis, and taxonomy of fungi. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1968;22:87–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.22.100168.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Cook K. M., Ney F. G., Hatch T. Influence of Particle Size upon the Retention of Particulate Matter in the Human Lung. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1950 Apr;40(4):450–480. doi: 10.2105/ajph.40.4.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis T. E., Jr, Domer J. E., Li Y. T. Cell wall studies of Histoplasma capsulatum and Blastomyces dermatitidis using autologous and heterologous enzymes. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):978–987. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.978-987.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domer J. E., Hamilton J. G., Harkin J. C. Comparative study of the cell walls of the yeastlike and mycelial phases of Histoplasma capsulatum. J Bacteriol. 1967 Aug;94(2):466–474. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.2.466-474.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domer J. E., Hamilton J. G. The readily extracted lipids of Histoplasma capsulatum and Blastomyces dermatitidis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 May 4;231(3):465–478. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(71)90114-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domer J. E. Monosaccharide and chitin content of cell walls of Histoplasma capsulatum and Blastomyces dermatitidis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;107(3):870–877. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.3.870-877.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florance E. R., Denison W. C., Allen T. C., Jr Ultrastructure of dormant and germinating conidia of Aspergillus nidulans. Mycologia. 1972 Jan-Feb;64(1):115–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison R. G., Boyd K. S. The fine structure of microconidial germination and vegetative cells of Histoplasma capsulatum. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1977 Feb-Mar;128(2):135–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD D. H. Observations on tissue cultures of mouse peritoneal exudates inoculated with Histoplasma capsulatum. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jul;78(1):69–78. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.1.69-78.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanetsuna F., Carbonell L. M., Gil F., Azuma I. Chemical and ultrastructural studies on the cell walls of the yeastlike and mycelial forms of Histoplasma capsulatum. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1974 Oct 15;54(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF02055967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi G. S., Guiliacci P. L. Cell wall studies of Histoplasma capsulatum. Sabouraudia. 1967 Feb;5(3):180–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozar F., Weijer J. Electron-dense structures in Neurospora crassa. II. Lomasome-like structures. Can J Genet Cytol. 1969 Sep;11(3):617–621. doi: 10.1139/g69-074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILNE H. A. The morphology and cytochemistry of H. capsulatum. J Med Lab Technol. 1957 Jul;14(3):142–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINE L., WEBSTER R. E. Conversion in strains of Histoplasma capsulatum. J Bacteriol. 1962 Jan;83:149–157. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.1.149-157.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukahara T. Electron microscopy of swelling and germinating conidiospores of Aspergillus niger. Sabouraudia. 1968 Jun;6(3):185–191. doi: 10.1080/00362176885190371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilsenach R., Kessel M. The role of lomasomes in wall formation in Penicillium vermiculatum. J Gen Microbiol. 1965 Sep;40(3):401–404. doi: 10.1099/00221287-40-3-401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]