Abstract
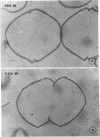
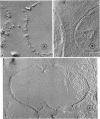
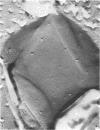
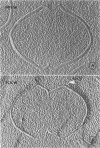
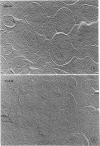
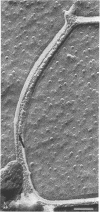
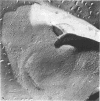
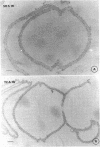
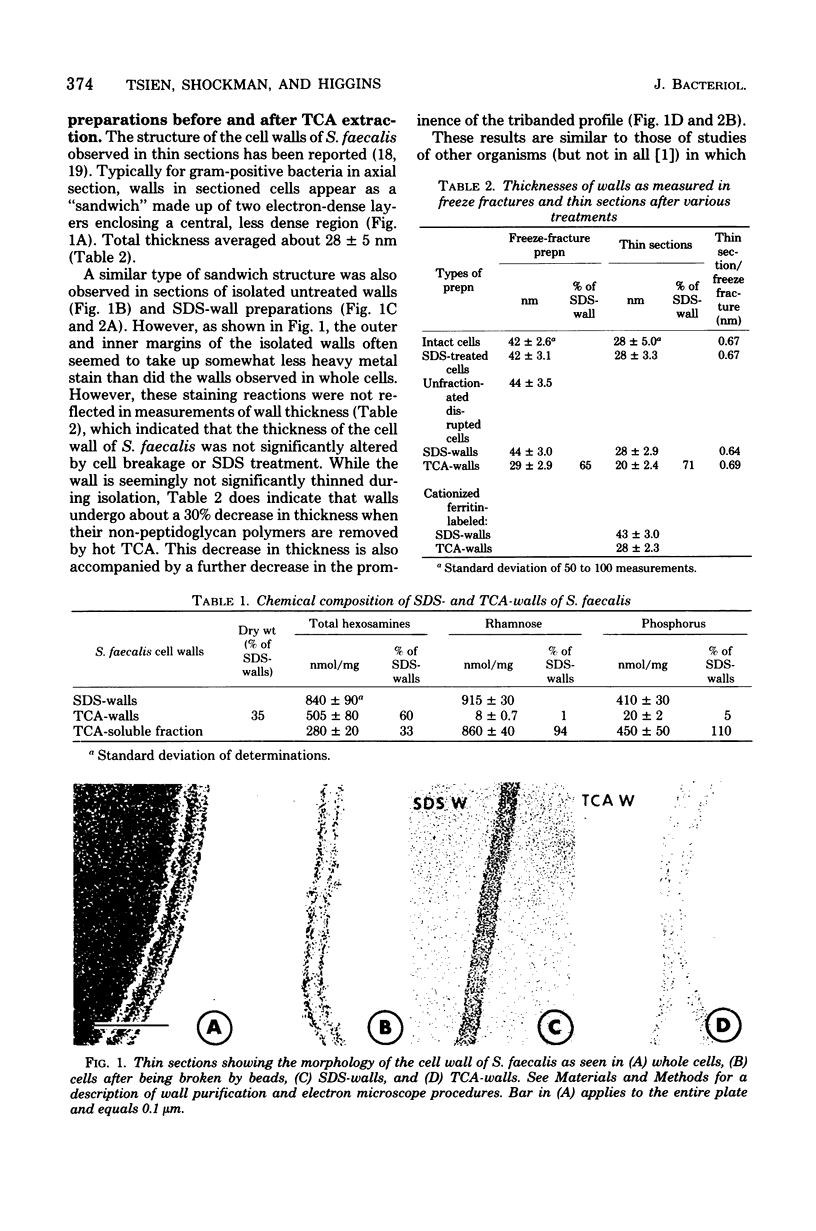
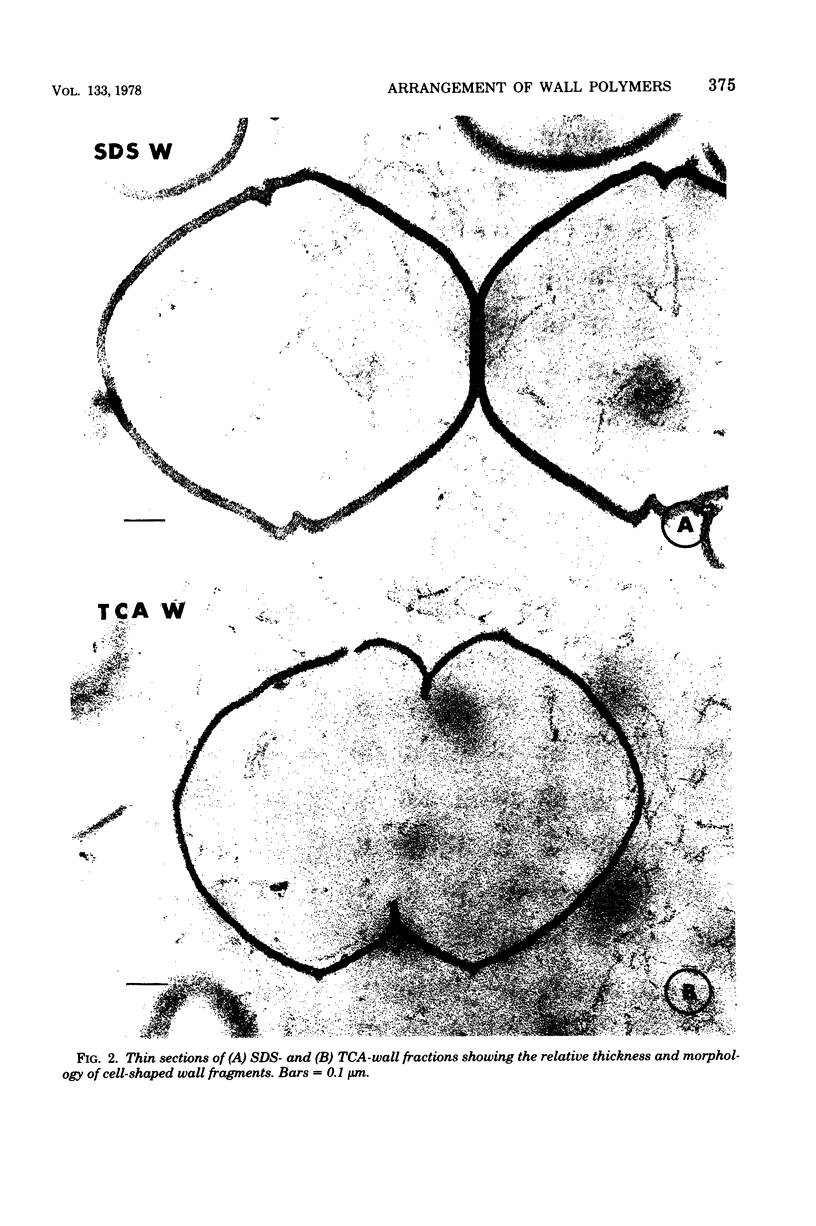
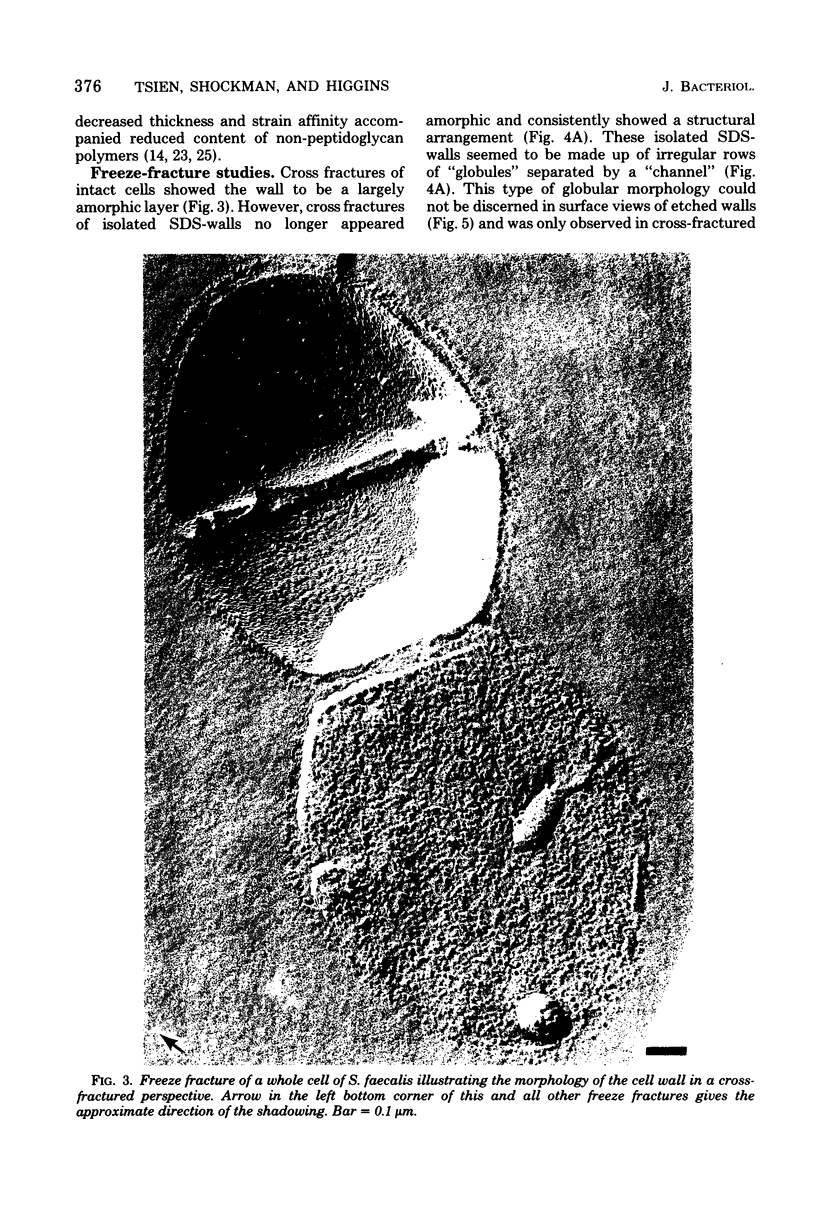
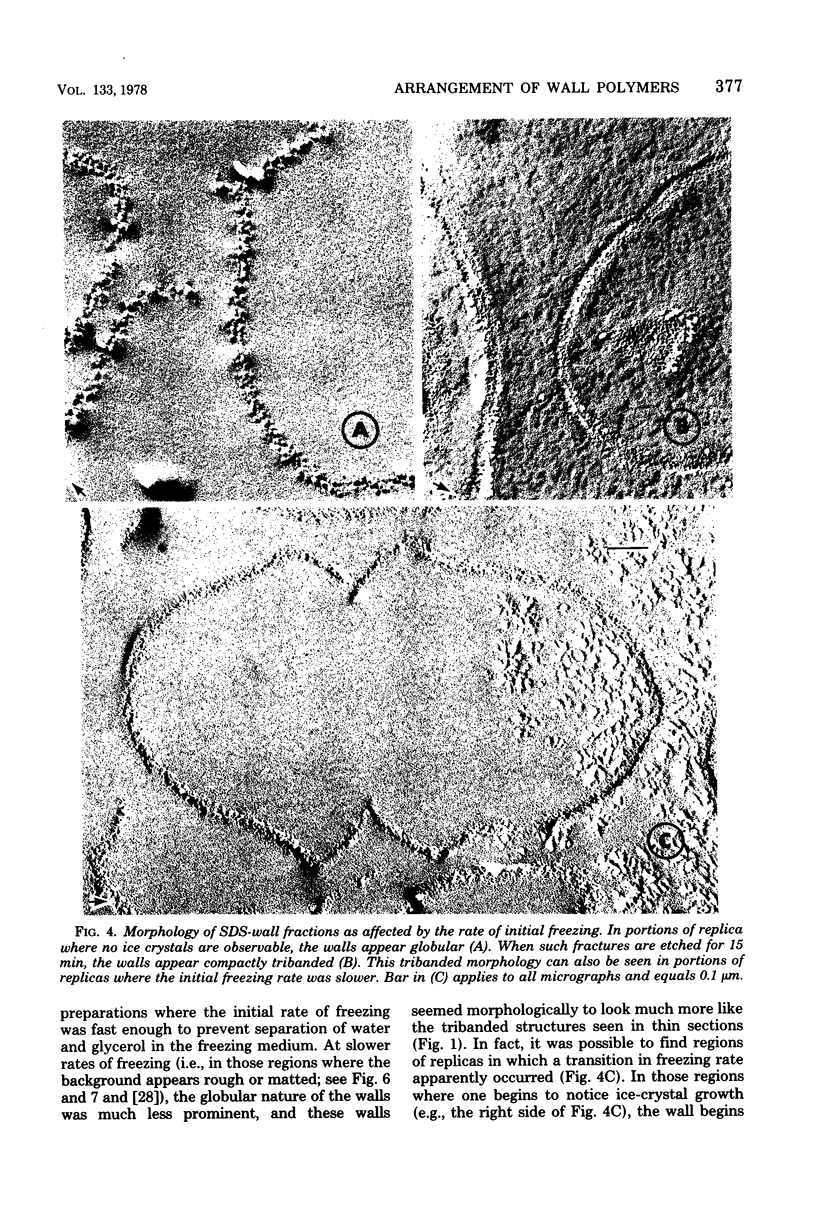
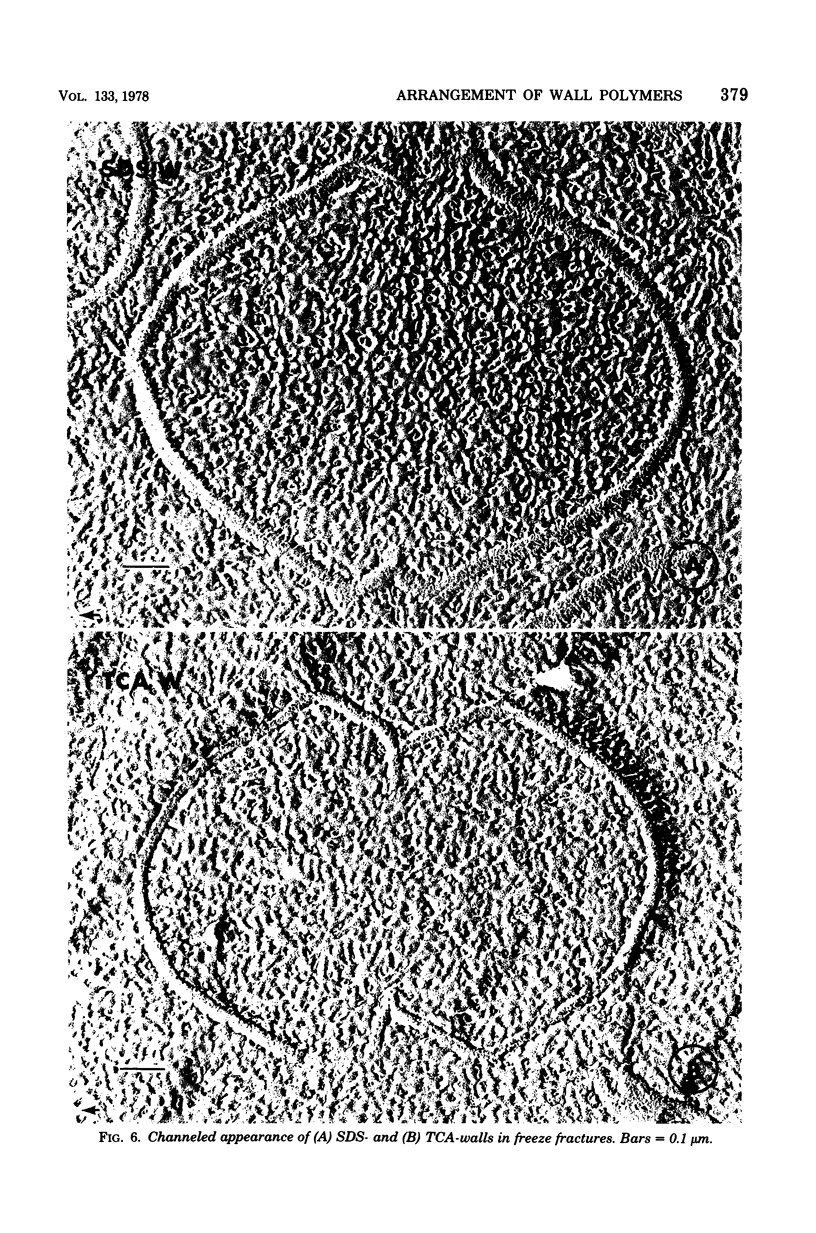
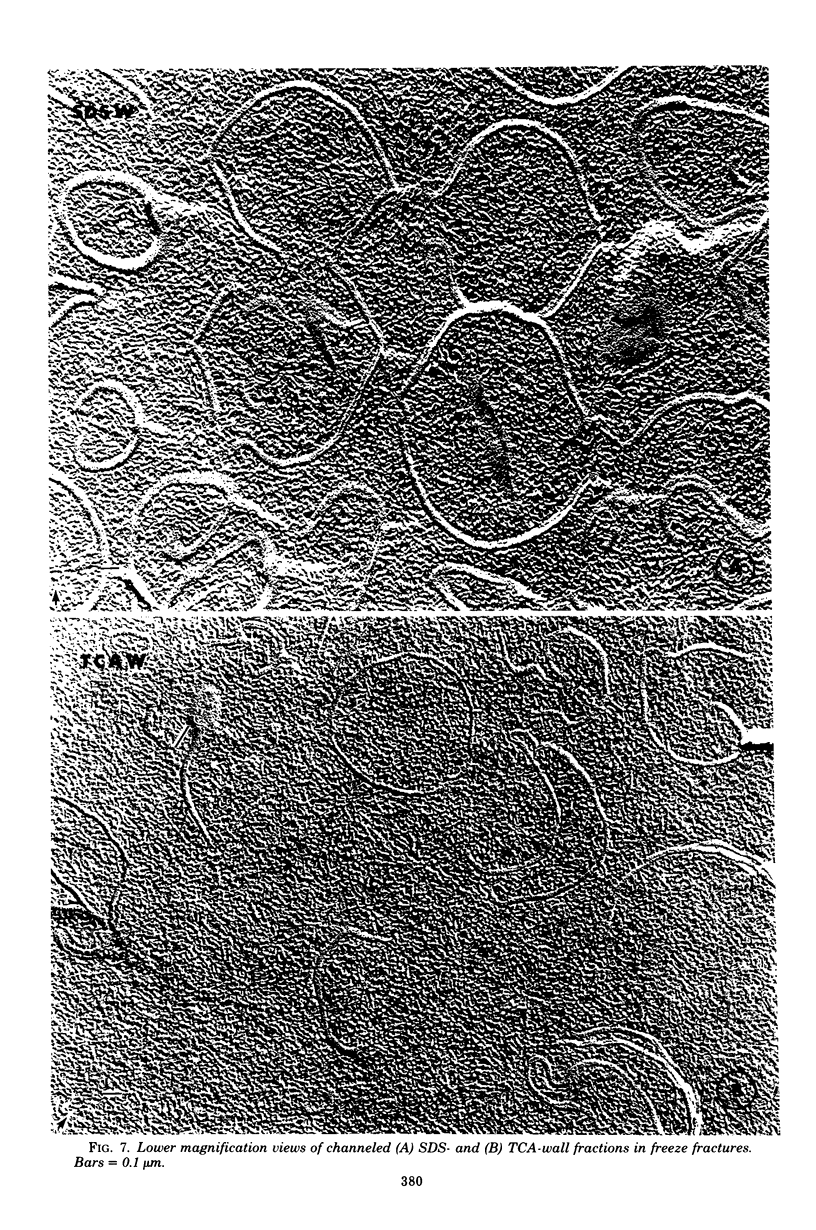
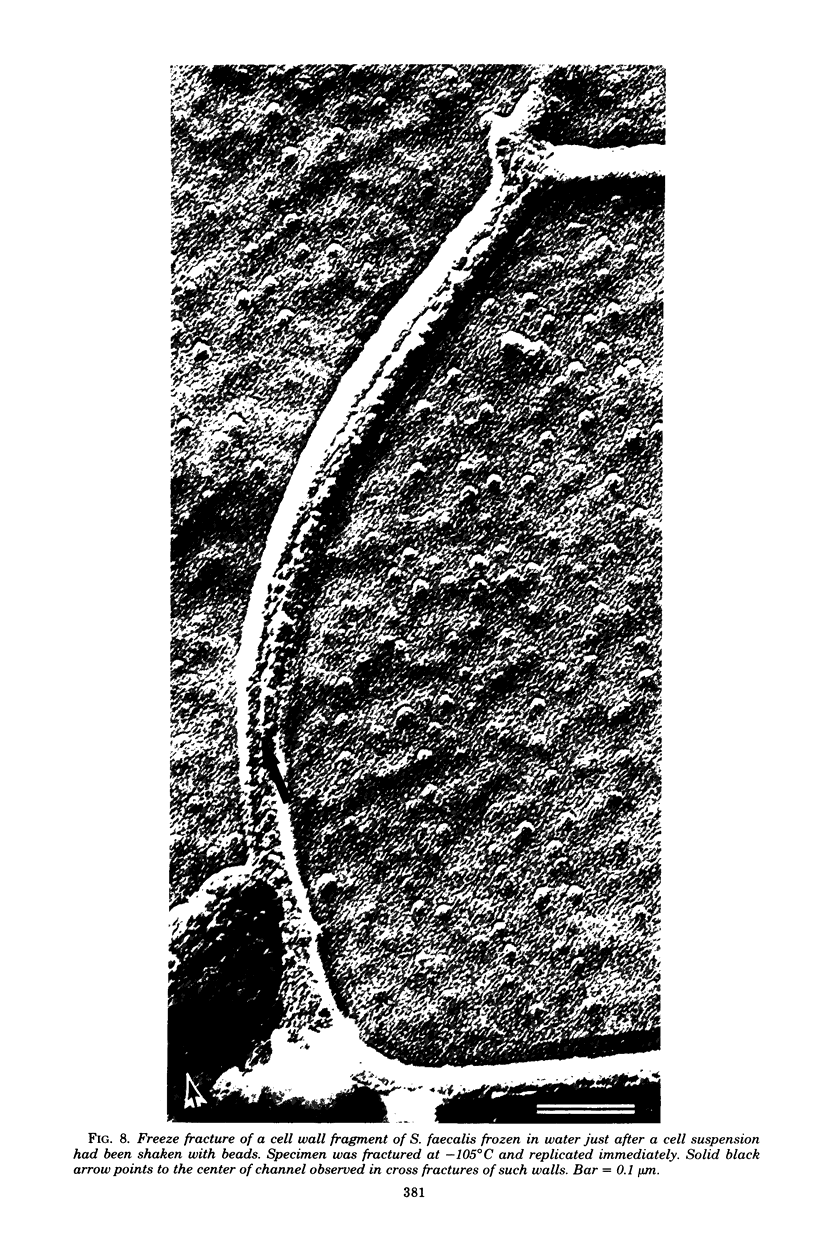
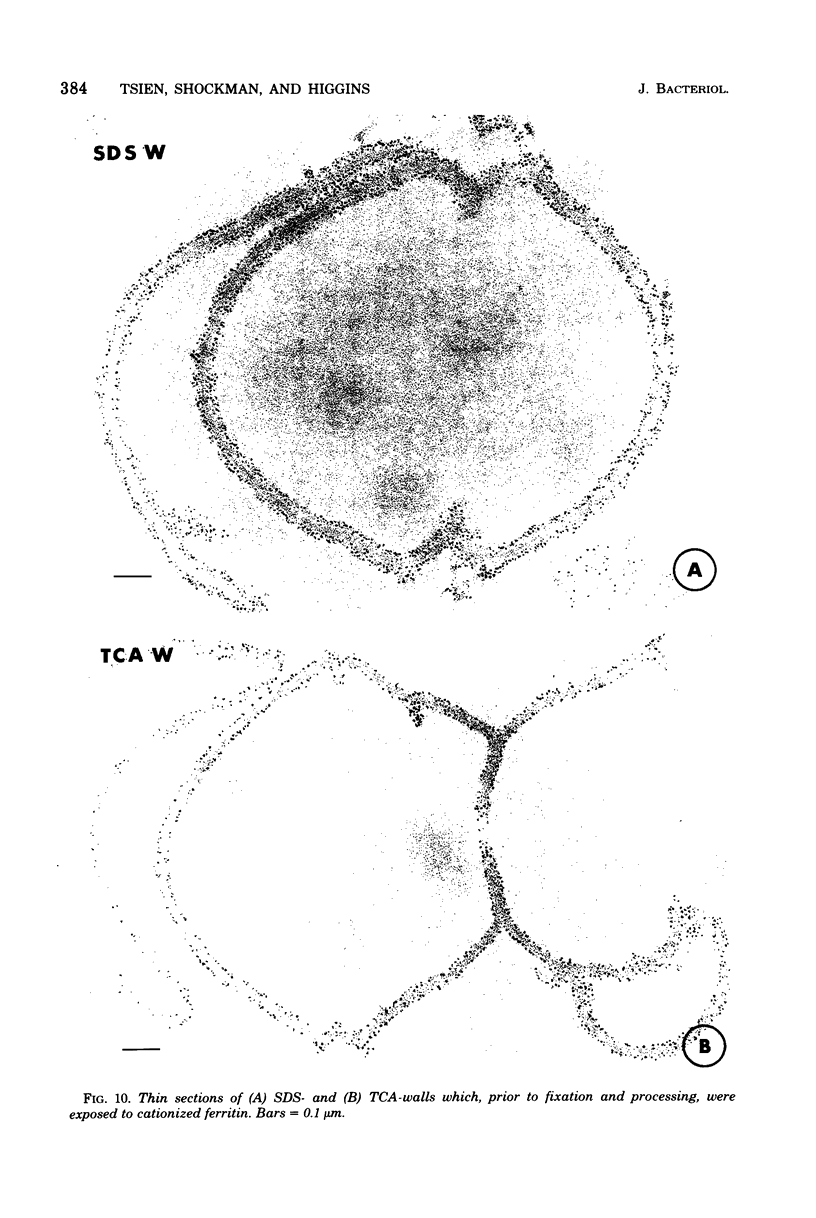
The structure of the cell wall of Streptococcus faecalis was studied in thin sections and freeze fractures of whole cells and partially purified wall fractions. Also, the structures of wall preparations treated with hot trichloroacetic acid to remove non-peptidoglycan wall polymers were compared with wall preparations that possess a full complement of accessory polymers. The appearance of the wall varied with the degree of hydration of preparations and physical removal of the cell membrane from the wall before study. Seen in freeze fractures of whole cells, the fully hydrated wall seemed to be a thick, largely amorphic layer. Breaking cells with beads caused the cell membrane to separate from the wall and transformed the wall from a predominantly amorphic layer to a structure seemingly made up of two rows of "cobblestones" enclosing a central channel of lower density. Dehydration of walls seemingly caused the cobblestones to be transformed into two bands which continued to be separated by a channel. This channel was also observed in isolated wall preparations treated with hot trichloroacetic acid to remove non-peptidoglycan polymers. These observations are consistent with the interpretation that both peptidogylcan and non-peptidoglycan polymers are concentrated at the outer and inner surfaces of cell walls. These observations are discussed in relation to possible models of wall structure and assembly.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARCHIBALD A. R., ARMSTRONG J. J., BADDILEY J., HAY J. B. Teichoic acids and the structure of bacterial walls. Nature. 1961 Aug 5;191:570–572. doi: 10.1038/191570a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald A. R., Coapes H. E. The interaction of concanavalin A with teichoic acids and bacterial walls. Biochem J. 1971 Jul;123(4):665–667. doi: 10.1042/bj1230665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer H., Farr D. R., Horisberger M. Ultrastructural localization of cell wall teichoic acids in Streptococcus faecalis by means of concanavalin A. Arch Mikrobiol. 1974 Apr 10;97(1):17–26. doi: 10.1007/BF00403041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Uptake and retention of metals by cell walls of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1502–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1502-1518.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birdsell D. C., Doyle R. J., Morgenstern M. Organization of teichoic acid in the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):726–734. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.726-734.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleiweis A. S., Young F. E., Krause R. M. Cell walls of group D streptococci. II. Chemical studies on the type 1 antigen purified from the autolytic digest of cell walls. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1381–1387. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1381-1387.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger M. M. Teichoic acids: antigenic determinants, chain separation, and their location in the cell wall. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):910–917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carstensen E. L., Marquis R. E. Passive electrical properties of microorganisms. 3. Conductivity of isolated bacterial cell walls. Biophys J. 1968 May;8(5):536–548. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(68)86506-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole R. M., Popkin T. J., Boylan R. J., Mendelson N. H. Ultrastructure of a temperature-sensitive rod- mutant of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):793–810. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.793-810.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., McDannel M. L., Helman J. R., Streips U. N. Distribution of teichoic acid in the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):152–158. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.152-158.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T. S., Ward J. B., Wyrick P. B., Rogers H. J. Ultrastructural study of the reversion of protoplasts of Bacillus licheniformis to bacilli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):905–917. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.905-917.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsberg C. W., Wyrick P. B., Ward J. B., Rogers H. J. Effect of phosphate limitation on the morphology and wall composition of Bacillus licheniformis and its phosphoglucomutase-deficient mutants. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):969–984. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.969-984.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garland J. M., Archibald A. R., Baddiley J. An electron microscopic study of the location of teichoic acid and its contribution to staining reactions in walls of Streptococcus faecalis 8191. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Jul;89(1):73–86. doi: 10.1099/00221287-89-1-73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glauert A. M., Thornley M. J. The topography of the bacterial cell wall. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:159–198. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. L., Daneo-Moore L., Boothby D., Shockman G. D. Effect of inhibition of deoxyribonucleic acid and protein synthesis on the direction of cell wall growth in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):681–692. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.681-692.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. L., Shockman G. D. Early changes in the ultrastructure of Streptococcus faecalis after amino acid starvation. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jul;103(1):244–253. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.1.244-253.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph R., Shockman G. D. Synthesis and excretion of glycerol teichoic acid during growth of two streptococcal species. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):333–338. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.333-338.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROBERTS N. R., LEINER K. Y., WU M. L., FARR A. L. The quantitative histochemistry of brain. I. Chemical methods. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauck J., Glaser L. On the mode of in vivo assembly of the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1180–1187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millward G. R., Reaveley D. A. Electron microscope observations on the cell walls of some gram-positive bacteria. J Ultrastruct Res. 1974 Mar;46(3):309–326. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(74)90059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirelman D., Bracha R., Sharon N. Studies on the elongation of bacterial cell wall peptidoglycan and its inhibition by penicillin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 May 10;235(0):326–347. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb43275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pooley H. M. Turnover and spreading of old wall during surface growth of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1127–1138. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1127-1138.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin L. A., Bertaud W. S. Temperature and contamination dependent freeze-etch images of frozen water and glycerol solutions. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Oct;37(1):146–168. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibull C. Electron microscope studies on aldehyde-fixed, unstained microbial cells. J Ultrastruct Res. 1973 Apr;43(1):150–159. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(73)90075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Lipoteichoic acids: a new class of bacterial antigen. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1161–1167. doi: 10.1126/science.46620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt P. J. Cell wall thickness, size distribution, refractive index ratio and dry weight content of living bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus). Nature. 1970 Apr 18;226(5242):277–279. doi: 10.1038/226277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]