Abstract
Aggregative amoebae of Dictyostelium minutum are not attracted by cyclic AMP; they are sensitive to various attracting sources from which yeast extract was chosen to purify the chemoattractant. A small acrasin-like species-specific molecule which contains glycine and C5H5N5 has been purified 30,000-fold. Several characteristics of this chemotactic molecule, which is inactivated by an enzyme that is not species specific, are described.
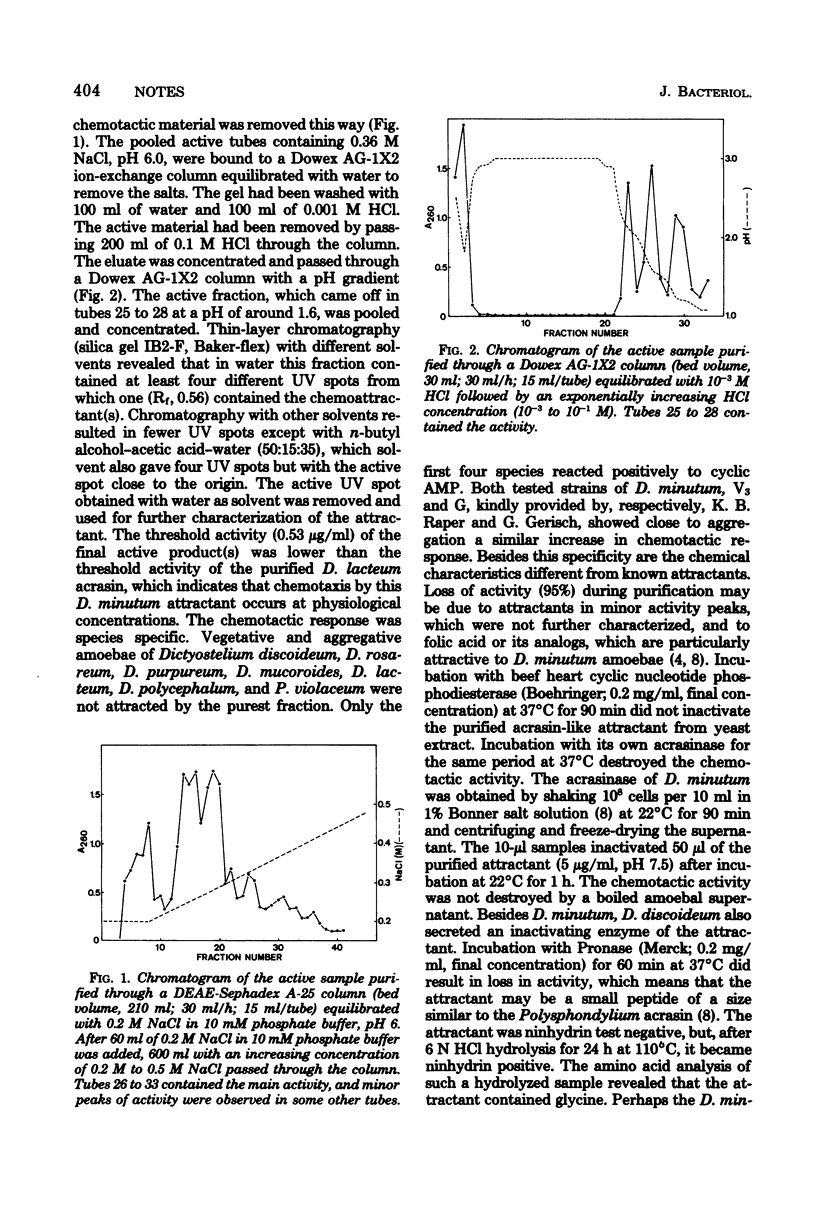
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Konijn T. M. Microbiological assay of cyclic 3',5'-AMP. Experientia. 1970 Apr 15;26(4):367–369. doi: 10.1007/BF01896891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., van Haastert P. J., Krens F. A., Konijn T. M. An acrasin-like attractant from yeast extract specific for Dictyostelium lacteum. Dev Biol. 1977 Jun;57(2):450–453. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90229-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan P., Hall E. M., Bonner J. T. Determination of the active portion of the folic acid molecule in cellular slime mold chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):185–191. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.185-191.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wurster B., Pan P., Tyan G. G., Bonner J. T. Preliminary characterization of the acrasin of the cellular slime mold Polysphondylium violaceum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):795–799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


