Abstract
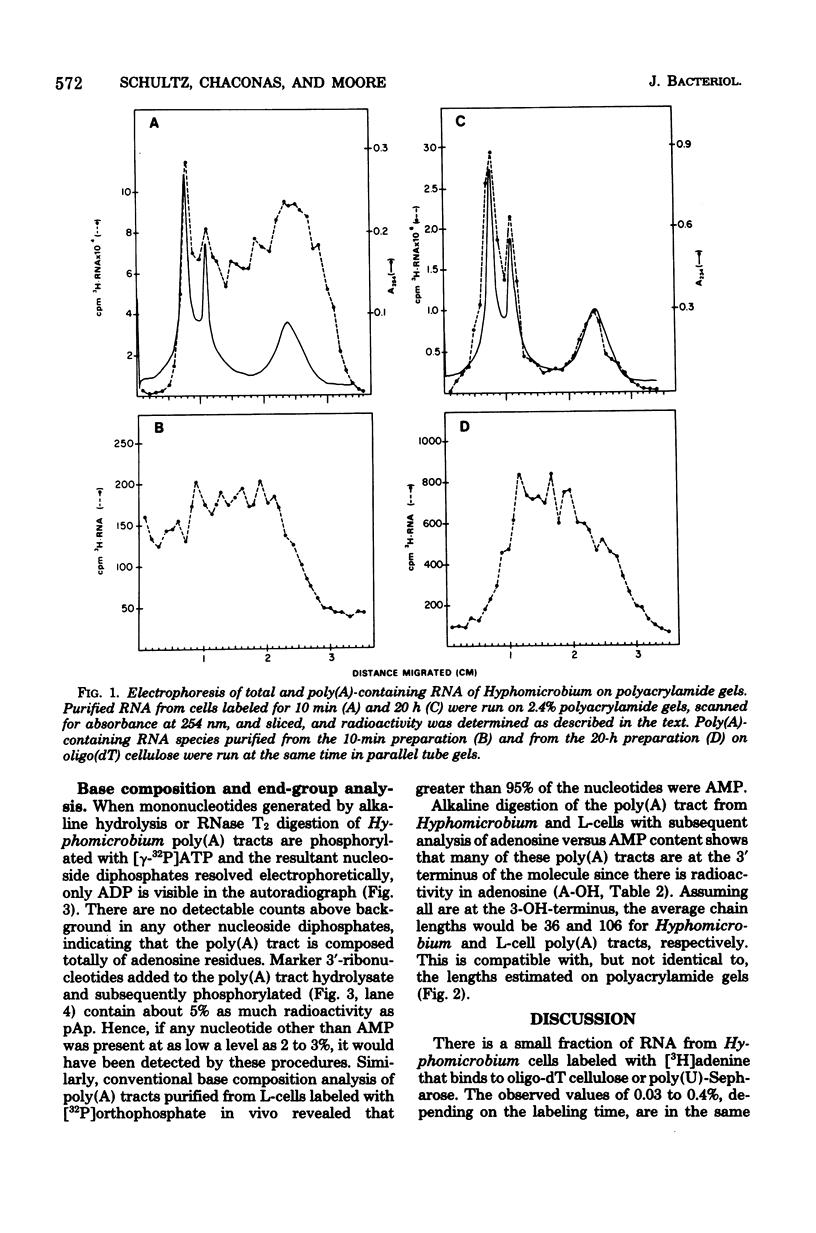
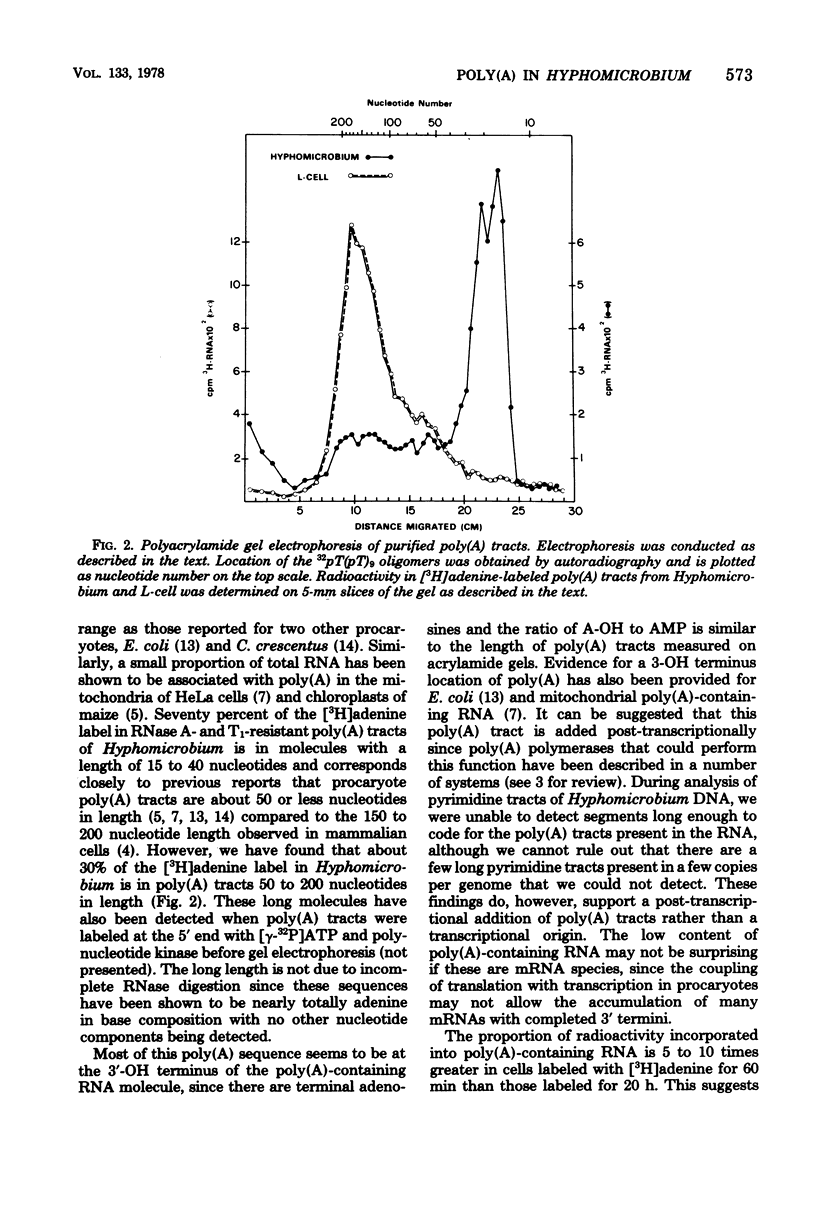
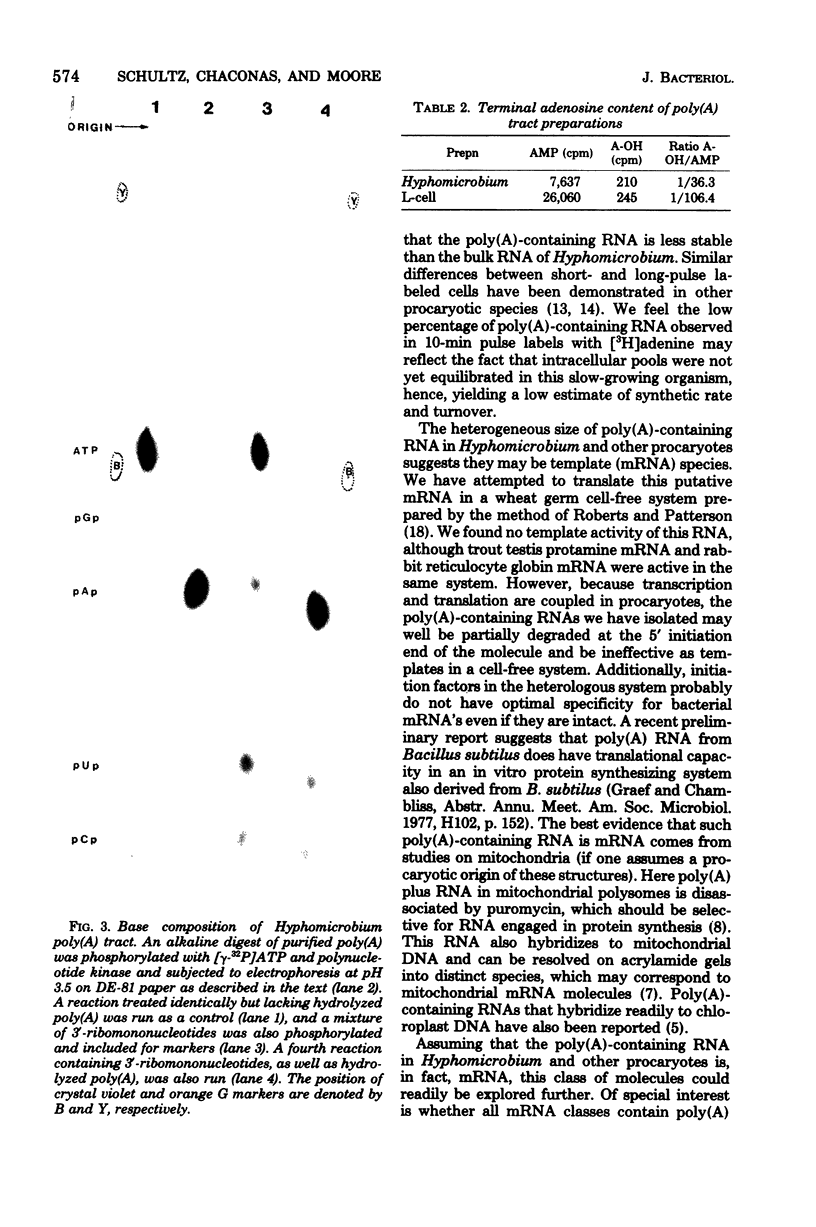
Heterogeneous RNA containing polyadenylic acid [poly(A)] sequence has been isolated from Hyphomicrobium by affinity chromatography on oligothymidylic acid cellulose and polyuridylic acid Sepharose columns. About 0.1 to 0.3% of [3H]adenine-labeled RNA over a 60-min period is associated with poly(A) sequences. This percentage decreases to about 0.03 in a 20-h labeling period. The poly(A) tracts recovered after digestion with ribonuclease A and T1 are composed of greater than 95% adenine residues and are up to 200 nucleotides in length with a predominant range of 15 to 40 nucleotides. Adenosine and AMP are present in the ratio of 1:36 in alkaline digests of Hyphomicrobium poly(A) tracts. This is compatible with nucleotide lengths determined on acrylamide gels and location at the 3'-OH terminus of the RNA molecule.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaconas G., van de Sande J. H., Church R. B. Convenient methods to determine the specific radioactivity of (gamma-32P)ATP of high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1975 Nov;69(1):312–316. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90595-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds M., Winters M. A. Polyadenylate polymerases. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;17:149–179. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. R. Messenger RNA metabolism of animal cells. Possible involvement of untranslated sequences and mRNA-associated proteins. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):269–288. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haff L. A., Bogorad L. Poly(adenylic acid)-containing RNA from plastids of maize. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 7;15(18):4110–4115. doi: 10.1021/bi00663a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn W. E., Pettijohn D. E., Van Ness J. One strand equivalent of the Escherichia coli genome is transcribed: complexity and abundance classes of mRNA. Science. 1977 Aug 5;197(4303):582–585. doi: 10.1126/science.327551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M., Penman S. Mitochondrial polyadenylic acid-containing RNA: localization and characterization. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 5;80(3):379–391. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M., Penman S. The messenger-like properties of the poly(A)plus RNA in mammalian mitochondria. Cell. 1974 Dec;3(4):335–339. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg U., Persson T. Isolation of mRNA from KB-cells by affinity chromatography on polyuridylic acid covalently linked to Sepharose. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Dec 4;31(2):246–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loening U. E. The fractionation of high-molecular-weight ribonucleic acid by polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):251–257. doi: 10.1042/bj1020251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. L., Hirsch P. Deoxyribonucleic acid base sequence homologies of some budding and prosthecate bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):256–261. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.256-261.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. L., Hirsch P. First generation synchrony of isolated Hyphomicrobium swarmer populations. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):418–423. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.418-423.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazato H., Venkatesan S., Edmonds M. Polyadenylic acid sequences in E. coli messenger RNA. Nature. 1975 Jul 10;256(5513):144–146. doi: 10.1038/256144a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta N., Sanders M., Newton A. Poly(adenylic acid) sequences in the RNA of Caulobacter crescenus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2343–2346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. P., La Torre J., Kelley D. E., Greenberg J. R. On the lability of poly(A) sequences during extraction of messenger RNA from polyribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 14;262(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Sande J. H., Kalisch B. W. Polymerization of oligodeoxythymidylates and oligoriboadenylates catalyzed by T4 polynucleotide ligase and their use as analytical markers in polyacrylamide-gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1976 Oct;75(2):509–521. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90106-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]