Abstract
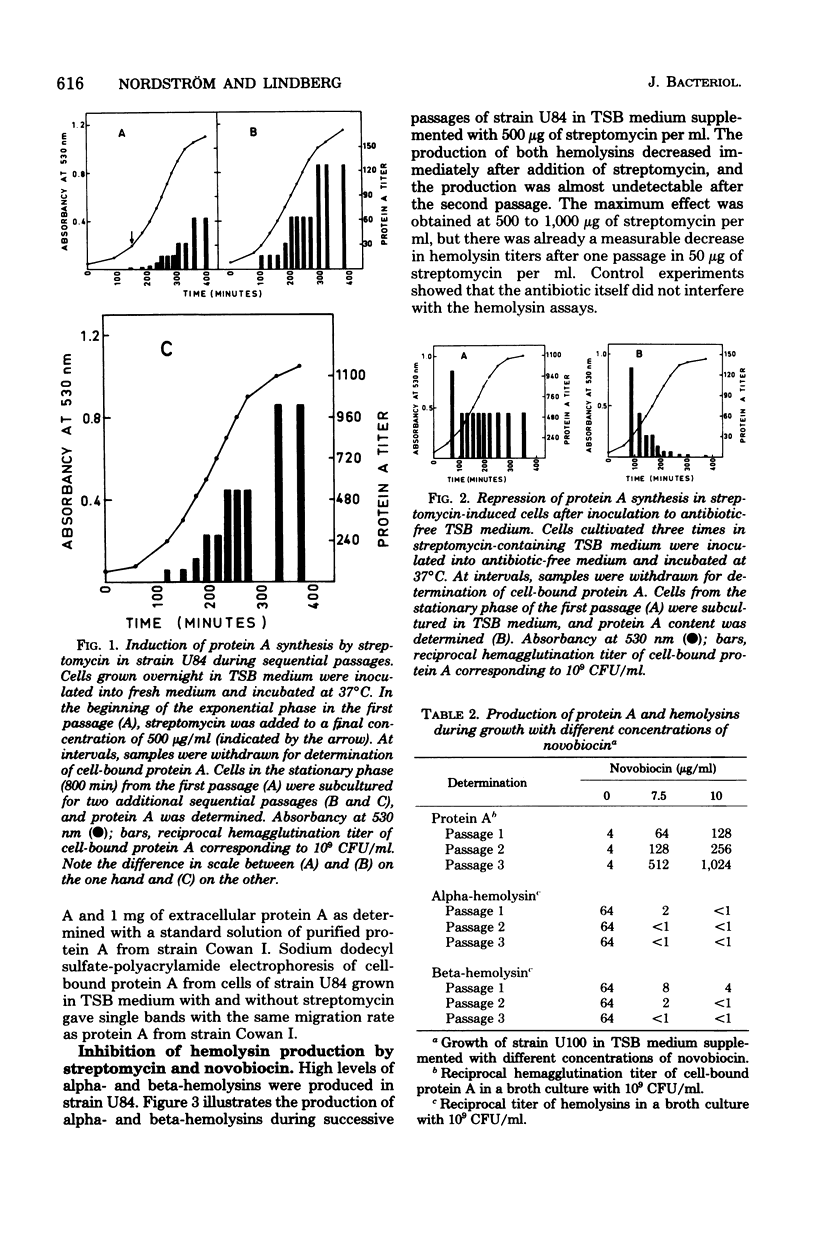
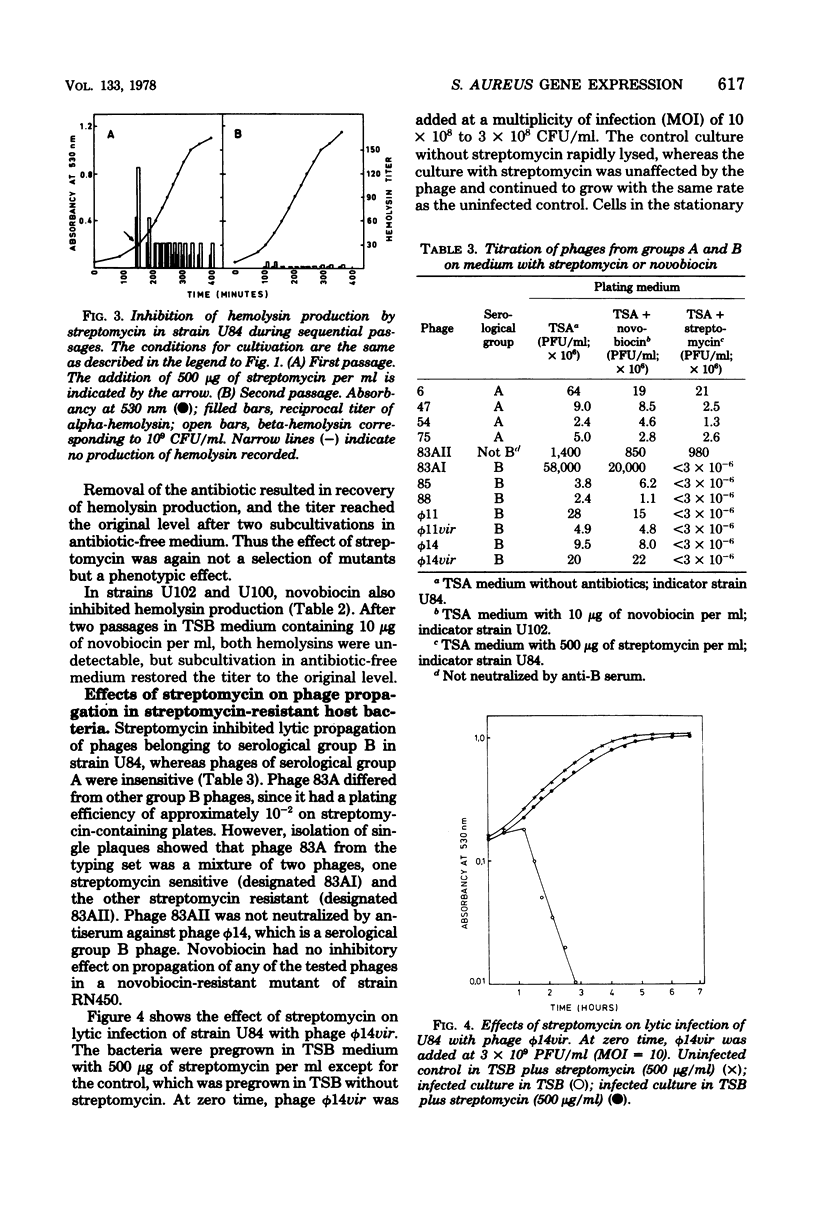
Streptomycin and novobiocin induced production of protein A and inhibited production of alpha- and beta-hemolysins in mutants of Staphylococcus aureus strains RN450 and RN1 resistant to these antibiotics. Streptomycin, but not novobiocin, also inhibited propagation of bacteriophages of serological group B, whereas phages of group A were unaffected. Streptomycin had to be present at adsorption of the phage, and 10 mM CACL2 reversed the inhibitory effect. Lysogenization and competence induction occurred in the presence of streptomycin, suggesting that some early phage genes were expressed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BROCK T. D., BROCK M. L. Effect of novobiocin on permeability of Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1959 Nov;85:176–185. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(59)90461-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROCK T. D., WOOLEY S. O. STREPTOMYCIN AS AN ANTIVIRAL AGENT: MODE OF ACTION. Science. 1963 Sep 13;141(3585):1065–1067. doi: 10.1126/science.141.3585.1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forsgren A., Nordström K., Philipson L., Sjöquist J. Protein A mutants of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jul;107(1):245–250. doi: 10.1128/jb.107.1.245-250.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funatsu G., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. 33. Location of amino-acid replacements in protein S12 isolated from Escherichia coli mutants resistant to streptomycin. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 28;68(3):547–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASER L. THE SYNTHESIS OF TEICHOIC ACIDS. II. POLYRIBITOL PHOSPHATE. J Biol Chem. 1964 Oct;239:3178–3186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. Novobiocin and coumermycin inhibit DNA supercoiling catalyzed by DNA gyrase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HINTON N. A., ORR J. H. The effect of antibiotics on the toxin production of Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiot Chemother (Northfield) 1960 Dec;10:758–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm H., Hjelm K., Sjöquist J. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Its isolation by affinity chromatography and its use as an immunosorbent for isolation of immunoglobulins. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 15;28(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80680-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. H., Stow M., Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. Function of teichoic acids and effect of novobiocin on control of Mg2+ at the bacterial membrane. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jan 13;229(2):53–55. doi: 10.1038/newbio229053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUMAR S., LINDORFER R. K. The characterization of staphylococcal toxins. I. The electrophoretic migration of the alpha hemolytic, dermonecrotic, lethal, and leucocidal activities of crude toxin. J Exp Med. 1962 Jun 1;115:1095–1106. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.6.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movitz J. Formation of extracellular protein A by Staphylococcus aureus. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep;68(1):291–299. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVICK R. P. ANALYSIS BY TRANSDUCTION OF MUTATIONS AFFECTING PENICILLINASE FORMATION IN STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Oct;33:121–136. doi: 10.1099/00221287-33-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. Properties of a cryptic high-frequency transducing phage in Staphylococcus aureus. Virology. 1967 Sep;33(1):155–166. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90105-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozaki M., Mizushima S., Nomura M. Identification and functional characterization of the protein controlled by the streptomycin-resistant locus in E. coli. Nature. 1969 Apr 26;222(5191):333–339. doi: 10.1038/222333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENBLUM E. D., TYRONE S. SEROLOGY, DENSITY, AND MORPHOLOGY OF STAPHYLOCOCCAL PHAGES. J Bacteriol. 1964 Dec;88:1737–1742. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.6.1737-1742.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudin L., Lindberg M. Thymineless bacteriophage induction in Staphylococcus aureus. I. High-frequency transduction with lysates containing a bacteriophage related to bacteriophage phi 11. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1357–1366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1357-1366.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudin L., Sjöström J. E., Lindberg M., Philipson L. Factors affecting competence for transformation in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Apr;118(1):155–164. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.1.155-164.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöquist J., Movitz J., Johansson I. B., Hjelm H. Localization of protein A in the bacteria. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Oct 17;30(1):190–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02086.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöquist J., Stålenheim G. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. IX. Complement-fixing activity of protein A-IgG complexes. J Immunol. 1969 Sep;103(3):467–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöström J. E., Lindberg M., Philipson L. Competence for transfection in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):576–585. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.576-585.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöström J. E., Philipson L. Role of the phi 11 phage genome in competence of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jul;119(1):19–32. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.1.19-32.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. H., Davis B. D. Mode of action of novobiocin in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):71–79. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.71-79.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISHNOW R. M., STROMINGER J. L., BIRGE C. H., THRENN R. H. BIOCHEMICAL EFFECTS OF NOVOBIOCIN ON STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS. J Bacteriol. 1965 Apr;89:1117–1123. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.4.1117-1123.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. J., Davis B. D. Cyclic blockade of initiation sites by streptomycin-damaged ribosomes in Escherichia coli: an explanation for dominance of sensitivity. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):377–390. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace B. J., Tai P. C., Davis B. D. Effect of streptomycin on the response of Escherichia coli ribosomes to the dissociation factor. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


