Abstract
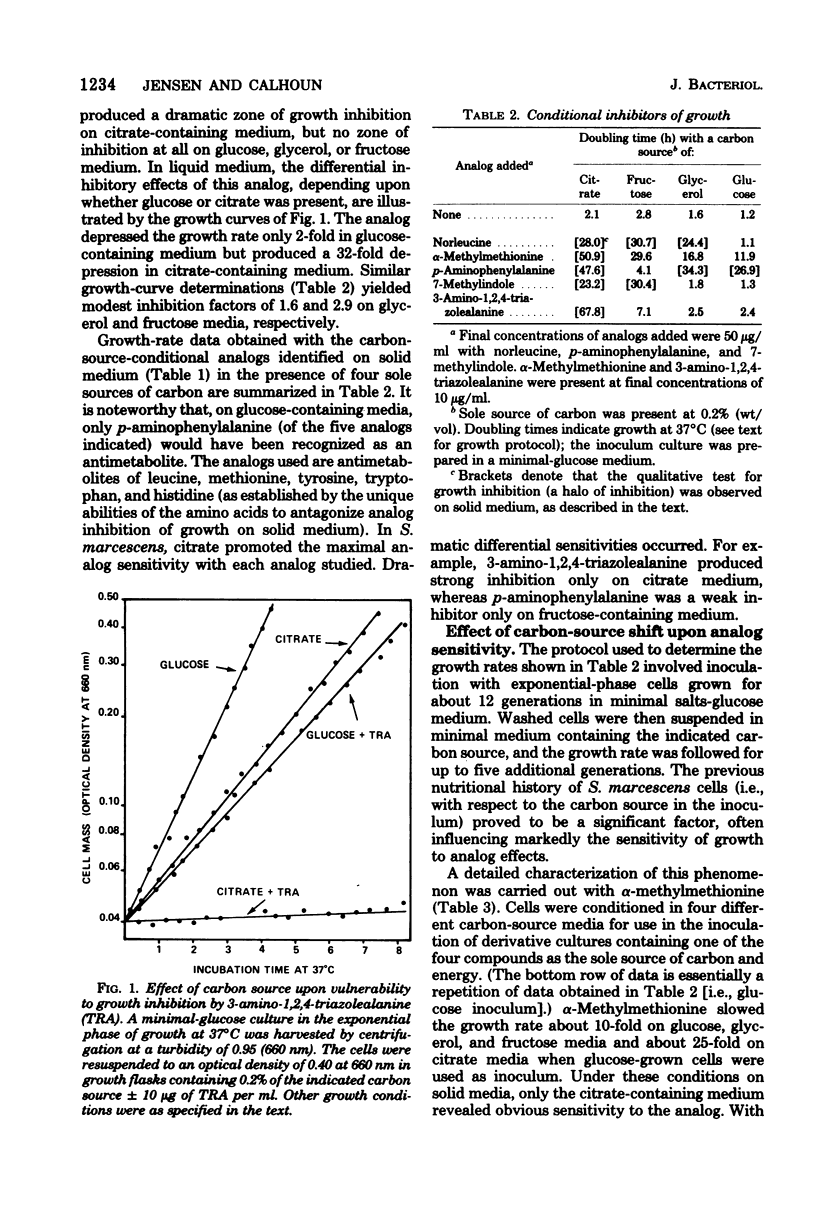
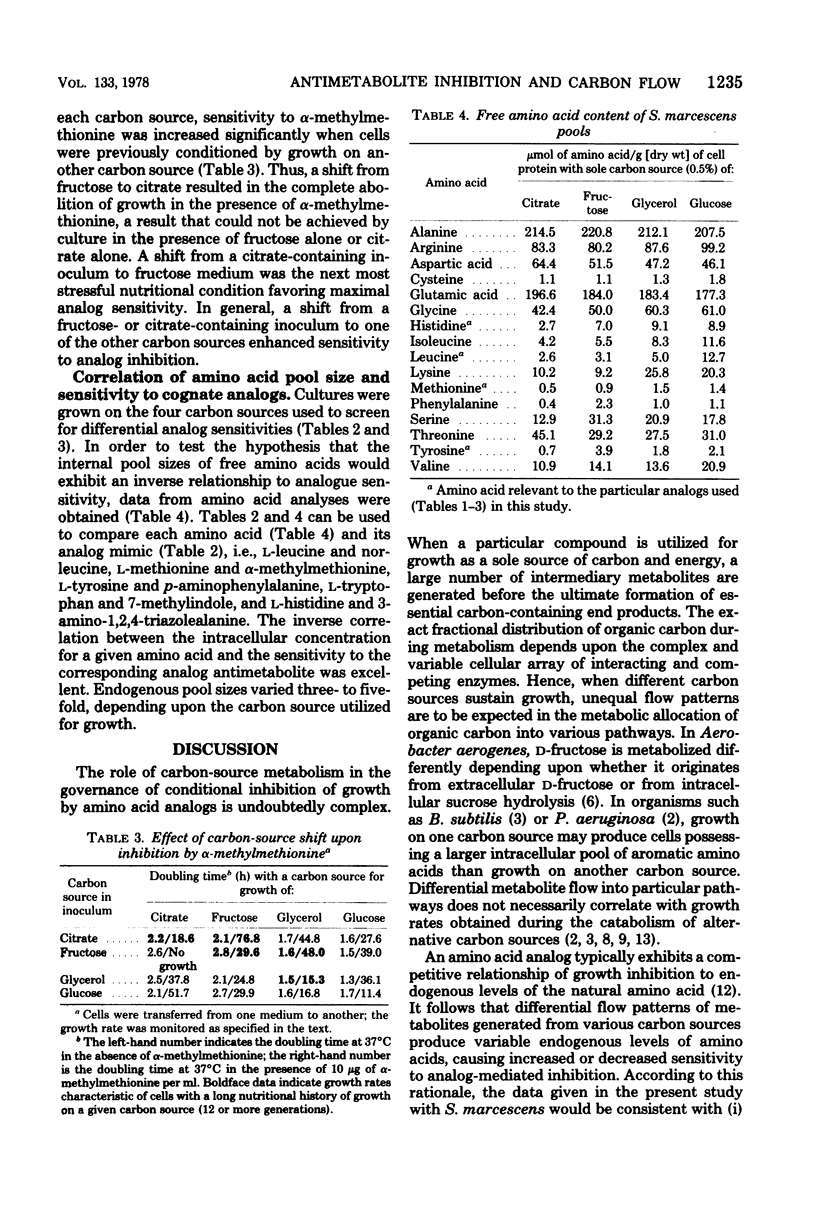
In Serratia marcescens, analogs of leucine (norleucine), methionine (alpha-methylmethionine), histidine (3-amino-1,2,4-triazolealanine), tyrosine (p-aminophenylalanine), and tryptophan (7-methylindole) are conditional inhibitors of growth; inhibition occurs during the metabolism of some carbon sources but not with others. A further increase in sensitivity to growth inhibition by these analogs can be accomplished through the use of particular combinations of carbon sources present in the inoculum and in the subsequent analog-containing culture medium. Variable sensitivity to analog-mediated inhibition of growth observed during growth on glucose, glycerol, fructose, or citrate correlated inversely with the intracellular pool sizes of the amino acids cognate to the analogs used. The above-cited results, in conjunction with previous results obtained with Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Bacillus subtilis, involve diverse biochemical pathways and suggest that nutritional manipulation to alter the pattern of carbon flow in microorganisms is a generally useful means to accomplish increased sensitivity to growth inhibition by metabolite analogs.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown H. D., Satyanarayana T., Umbarger H. E. Biosynthesis of branched-chain amino acids in yeast: effect of carbon source on leucine biosynthetic enzymes. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):959–969. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.959-969.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calhoun D. H., Jensen R. A. Significance of altered carbon flow in aromatic amino acid synthesis: an approach to the isolation of regulatory mutants in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):365–372. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.365-372.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champney W. S., Jensen R. A. Metabolic influences on tyrosine excretion in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):351–359. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.351-359.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denor P., Courtright J. B. Requirement for specific carbon sources in the low temperature induction of glycerol kinase in Neurospora crassa. FEBS Lett. 1974 Nov 15;48(2):314–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80494-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelker N. E., Hanson T. E., Anderson R. L. Alternate pathways of D-fructose metabolism in Aerobacter aerogenes. A specific D-fructokinase and its preferential role in the metabolism of sucrose. J Biol Chem. 1970 Apr 25;245(8):2060–2065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leisinger T., O'Sullivan C., Haas D. Arginine analogues: effect on growth and on the first two enzymes of the arginine pathway in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Oct;84(2):253–260. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry O. H., Carter J., Ward J. B., Glaser L. The effect of carbon and nitrogen sources on the level of metabolic intermediates in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov;246(21):6511–6521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R., Moses V., Mowbray J. Evidence for metabolic compartmentation in Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):15–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02722.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer M. H., Baumann P., Baumann L. Pathways of D-fructose and D-glucose catabolism in marine species of Alcaligenes, Pseudomonas marina, and Alteromonas communis. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Mar 1;112(2):169–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00429331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbarger H. E. Metabolite analogs as genetic and biochemical probes. Adv Genet. 1971;16:119–140. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60356-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dijken J. P., Quayle J. R. Fructose metabolism in four Pseudomonas species. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Sep 28;114(3):281–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00446874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



