Abstract
An indigenous Neisseria gonorrhoeae conjugative plasmid, pLE2450, was tested for its ability to mediate chromosomal gene transfer between gonococcal strains. Plasmid-mediated chromosomal transfer was detected at a low frequency and can be used to establish certain linkage relationships between amino acid and antibiotic resistance markers.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baron E. S., Saz A. K., Kopecko D. J., Wohlhieter J. A. Transfer of plasmid-borne beta-lactamase in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Aug;12(2):270–280. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.2.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas G. D., Sox T., Blackman E., Sparling P. F. Factors affecting genetic transformation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):983–992. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.983-992.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carifo K., Catlin B. W. Neisseria gonorrhoeae auxotyping: differentiation of clinical isolates based on growth responses on chemically defined media. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Sep;26(3):223–230. doi: 10.1128/am.26.3.223-230.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W. Nutritional profiles of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Neisseria lactamica in chemically defined media and the use of growth requirements for gonococcal typing. J Infect Dis. 1973 Aug;128(2):178–194. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catlin B. W., Pace P. J. Auxotypes and penicillin susceptibilities of Neisseria gonorrhoeae isolated from patients with gonorrhea involving two or more sites. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Aug;12(2):147–156. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.2.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clowes R. C., Moody E. E. Chromosomal transfer from "recombination-deficient" strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Genetics. 1966 Apr;53(4):717–726. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.4.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein B. I., Sox T., Biswas G., Blackman E., Sparling P. F. Conjugal transfer of the gonococcal penicillinase plasmid. Science. 1977 Mar 11;195(4282):998–1000. doi: 10.1126/science.402693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elwell L. P., Roberts M., Mayer L. W., Falkow S. Plasmid-mediated beta-lactamase production in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Mar;11(3):528–533. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.3.528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guymon L. F., Sparling P. F. Altered crystal violet permeability and lytic behavior in antibiotic-resistant and -sensitive mutants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):757–763. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.757-763.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KELLOGG D. S., Jr, PEACOCK W. L., Jr, DEACON W. E., BROWN L., PIRKLE D. I. NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. I. VIRULENCE GENETICALLY LINKED TO CLONAL VARIATION. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jun;85:1274–1279. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.6.1274-1279.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammer R. B., Preston D. A., Turner J. R., Hawley L. C. Rapid detection of ampicillin-resistant Haemophilus influenzae and their susceptibility to sixteen antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jul;8(1):91–94. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg D. S., Jr, Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Schroeter A. L., Reising G. Neisseria gonorrhoeae. II. Colonial variation and pathogenicity during 35 months in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1968 Sep;96(3):596–605. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.3.596-605.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirven L. A., Thornsberry C. Transfer of beta-lactamase genes of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by conjugation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Jun;11(6):1004–1006. doi: 10.1128/aac.11.6.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier T. W., Beilstein H. R., Zubrzycki L. Multiple antibiotic resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jul;6(1):22–28. doi: 10.1128/aac.6.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maness M. J., Foster G. C., Sparling P. F. Ribosomal resistance to streptomycin and spectinomycin in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1293–1299. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1293-1299.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maness M. J., Sparling P. F. Multiple antibiotic resistance due to a single mutation in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Infect Dis. 1973 Sep;128(3):321–330. doi: 10.1093/infdis/128.3.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. W., Holmes K. K., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):712–717. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.712-717.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
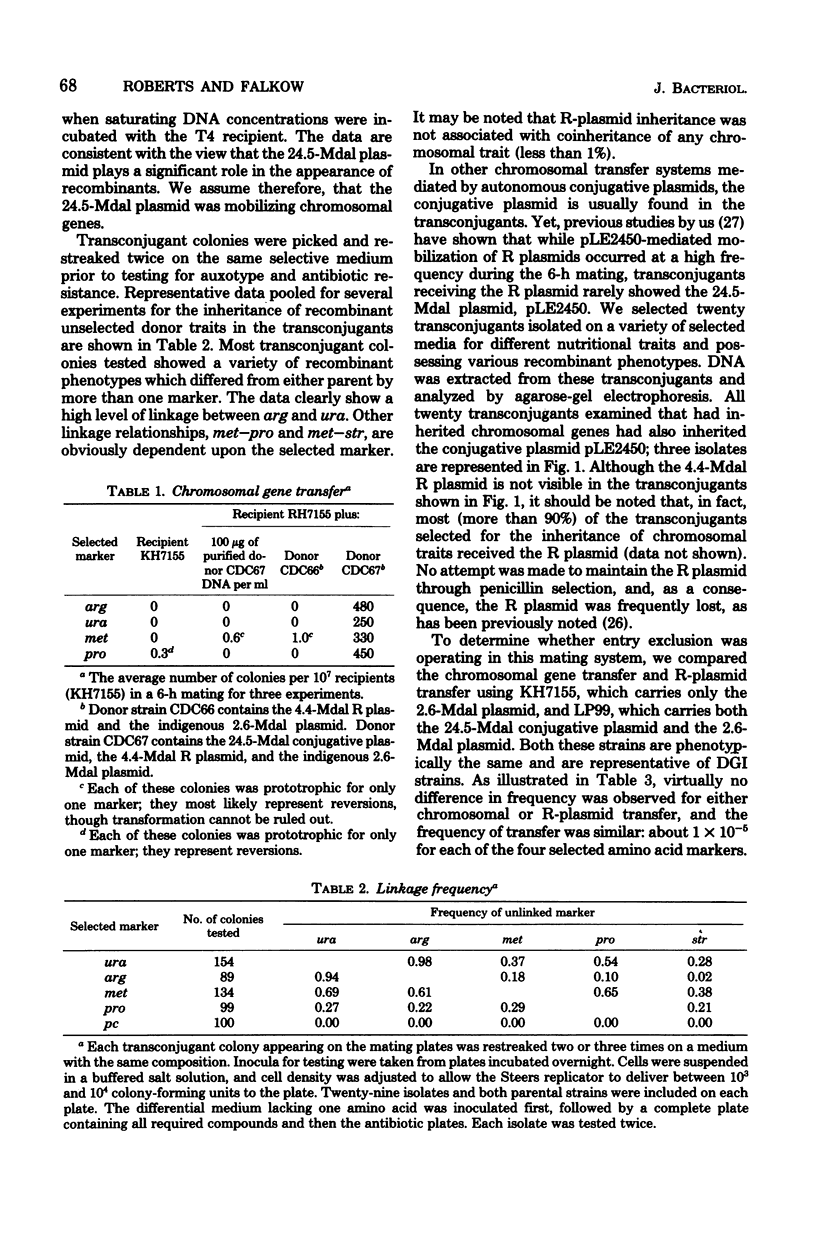
- Mayer L. W., Schoolnik G. K., Falkow S. Genetic studies on Neisseria gonorrhoeae from disseminated gonococcal infections. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):165–172. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.165-172.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce L. E., Meynell E. Specific chromosomal affinity of a resistant factor. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Jan;50(1):159–172. doi: 10.1099/00221287-50-1-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival A., Rowlands J., Corkill J. E., Alergant C. D., Arya O. P., Rees E., Annels E. H. Penicillinase-producing Gonococci in Liverpool. Lancet. 1976 Dec 25;2(8000):1379–1382. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91919-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I. Beta-lactamase-producing, penicillin-resistant gonococcus. Lancet. 1976 Sep 25;2(7987):656–657. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)92466-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Molecular characterization of two beta-lactamase-specifying plasmids isolated from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):557–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.557-563.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts M., Falkow S. Conjugal transfer of R plasmids in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Nature. 1977 Apr 14;266(5603):630–631. doi: 10.1038/266630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarubbi F. A., Jr, Blackman E., Sparling P. F. Genetic mapping of linked antibiotic resistance loci in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1284–1292. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1284-1292.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarubbi F. A., Jr, Sparling P. F., Blackman E., Lewis E. Loss of low-level antibiotic resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae due to env mutations. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):750–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.750-756.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F. Antibiotic resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Med Clin North Am. 1972 Sep;56(5):1133–1144. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32339-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparling P. F. Genetic transformation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae to streptomycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1364–1371. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1364-1371.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]