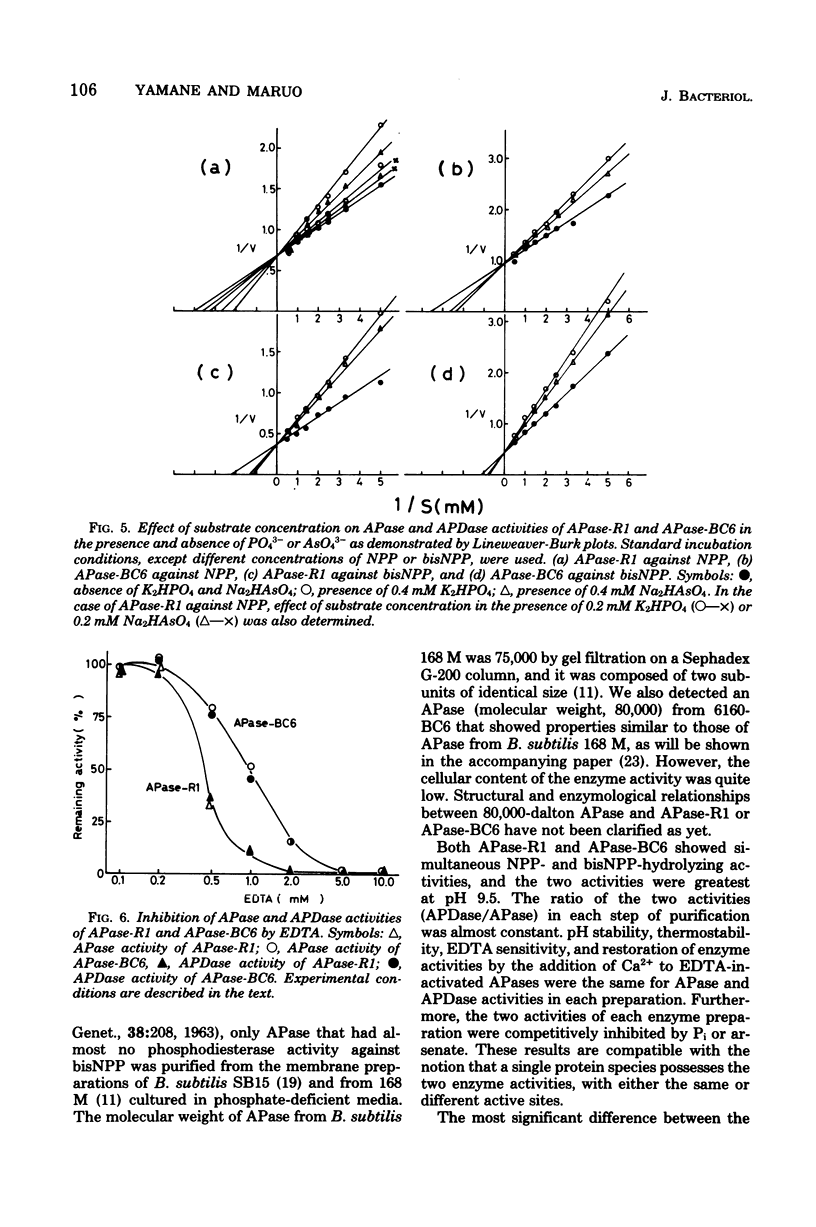
Abstract
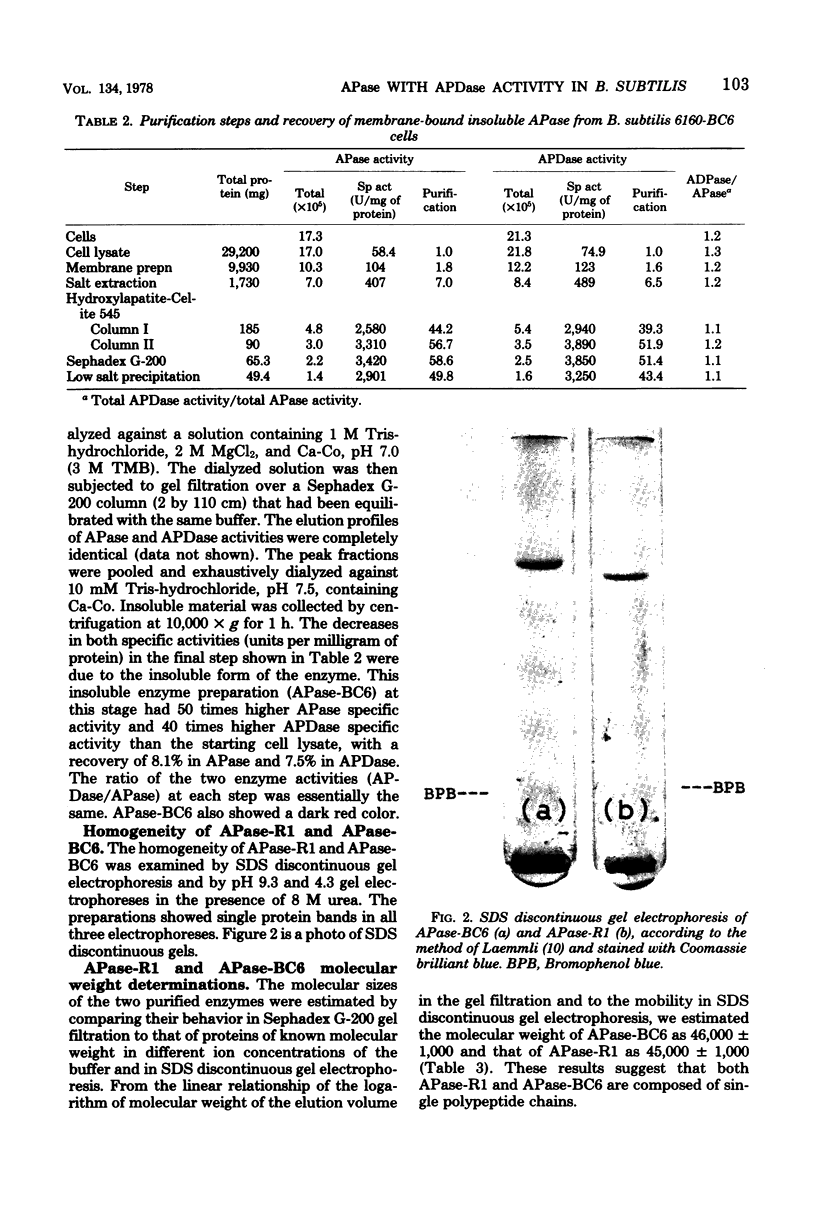
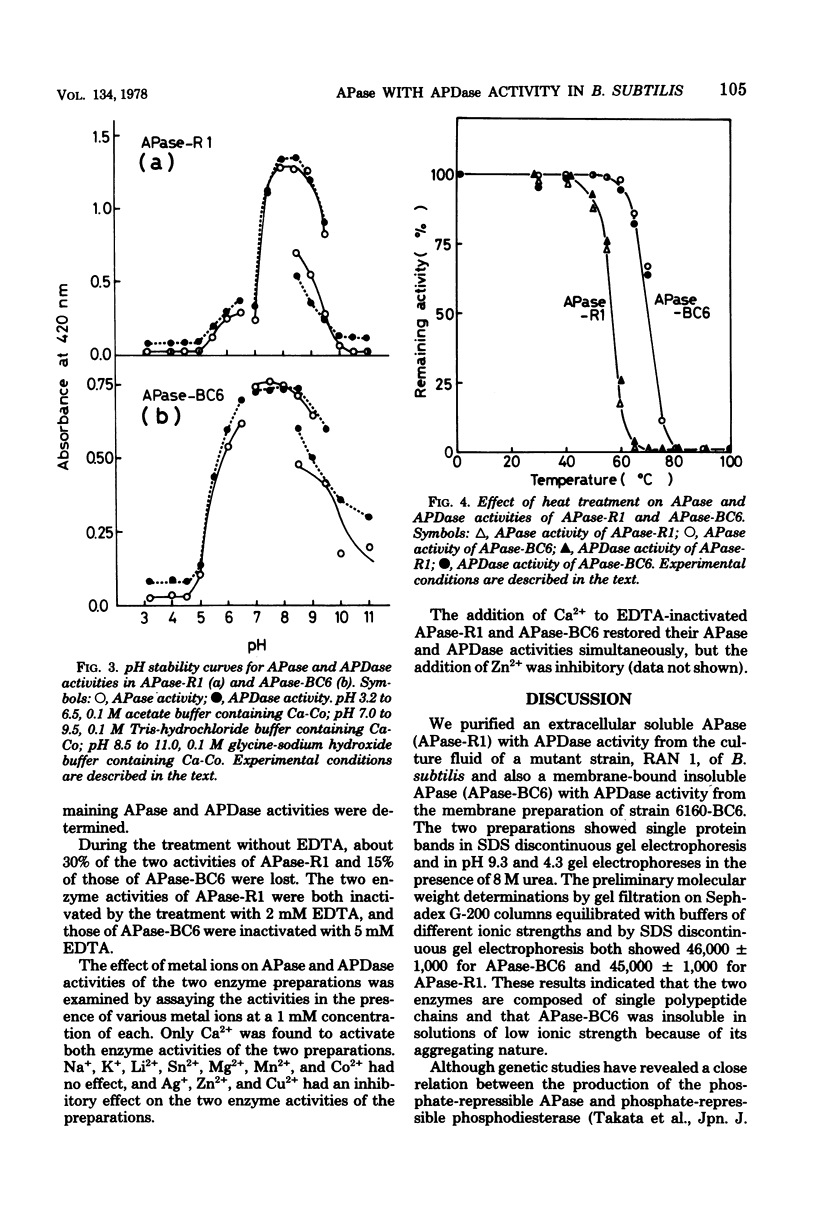
A membrane-bound insoluble alkaline phosphatase (APase) and an extracellular soluble APase were purified, respectively, from a membrane preparation of Bacillus subtilis 6160-BC6, which carries a mutation to produce APase constitutively, and from a culture fluid of a mutant strain. RAN 1, isolated from strain 6160-BC6, which produces an extracellular soluble APase. The two preparations were homogeneous, as judged by sodium dodecyl sulfate discontinuous gel electrophoresis and by gel electrophoreses in the presence of 8 M urea at pH 9.3 and 4.3. RAN 1 APase was crystallized. Both preparations possessed phosphatase and phosphodiesterase activities, and their pH optima were both at 9.5. They were competitively inhibited by phosphate or arsenate and were activated by the addition of Ca2+ but not by Zn2+. The APase and alkaline phosphodiesterase activities seemed to be contained in the same protein molecule. The molecular weight of 6160-BC6 APase was estimated to be 46,000 +/- 1,000, and that of RAN 1 APase was estimated to be 45,000 +/- 1,000. The largest difference between the 6160-BC6 and RAN 1 APase's was in solubility in low-ionic-strength solutions. Present results suggest that each enzyme is composed of a single polypeptide chain and that 6160-BC6 APase aggregates in solutions of low ionic strength.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. J. The estimation of phosphorus. Biochem J. 1940 Jun;34(6):858–865. doi: 10.1042/bj0340858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh B. K., Wouters J. T., Lampen J. O. Distribution of the sites of alkaline phosphatase(s) activity in vegetative cells of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):928–937. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.928-937.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn A. R., Mandelstam J. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis 168. Comparison of alkaline phosphatase from sporulating and vegetative cells. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(2):129–138. doi: 10.1042/bj1230129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glew R. H., Heath E. C. Studies on the extracellular alkaline phosphatase of Micrococcus sodonensis. I. Isolation and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1556–1565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn J. A., Schaffel S. D., McNicholas J. M., Hulett F. M. Biochemical localization of the alkaline phosphatase of Bacillus licheniformis as a function of culture age. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):1010–1019. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.1010-1019.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulett-Cowling F. M., Campbell L. L. Purification and properties of an alkaline phosphatase of Bacillus licheniformis. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 13;10(8):1364–1371. doi: 10.1021/bi00784a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulett F. M., Schaffel S. D., Campbell L. L. Subunits of the alkaline phosphatase of Bacillus licheniformis: chemical, physicochemical, and dissociation studies. J Bacteriol. 1976 Nov;128(2):651–657. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.2.651-657.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Hégarat J. C., Anagnostopoulos C. Purification, subunit structure and properties of two repressible phosphohydrolases of Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 15;39(2):525–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03151.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki T., Minami Z., Ikeda Y. The genetics of alkaline phosphatase formation in Bacillus subtilis. Genetics. 1965 Nov;52(5):1093–1100. doi: 10.1093/genetics/52.5.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal N. G., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes by osmotic shock from Escherichia coli in exponential phase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3055–3062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petitclerc C., Lazdunski C., Chappelet D., Moulin A., Lazdunski M. The functional properties of the Zn2(plus)-and Co2(plus)-alkaline phosphatases of Escherichia coli. Labelling of the active site with pyrophosphate, complex formation with arsenate, and reinvestigation of the role of the zinc atoms. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Jun;14(2):301–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb00290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISFELD R. A., LEWIS U. J., WILLIAMS D. E. Disk electrophoresis of basic proteins and peptides on polyacrylamide gels. Nature. 1962 Jul 21;195:281–283. doi: 10.1038/195281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J., Barrett K. The reversible dissociation of the alkaline phosphatase of Escherichia coli. I. Formation and reactivation of subunits. J Biol Chem. 1965 Nov;240(11):4284–4292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Tsugita A. Phosphoesterases of Bacillus subtilis. II. Crystallization and properties of alkaline phosphatase. J Biochem. 1967 Feb;61(2):231–241. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Tsugita A. Phosphoesterases of Bacillus subtilis. I. Purification and properties of phosphodiesterases. J Biochem. 1966 Oct;60(4):372–380. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. A., Tristram H. Localization in the Cell and Extraction of Alkaline Phosphatase from Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1045–1051. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1045-1051.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Lampen J. O. Membrane penicillinase of Bacillus licheniformis 749/C, a phospholipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):3212–3213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamane K., Maruo B. Alkaline phosphatase possessing alkaline phosphodiesterase activity and other phosphodiesterases in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):108–114. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.108-114.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]