Abstract
A simple two-step procedure for purification of enolase from germinated spores or vegetative cells of Bacillus megaterium is described. The procedure resulted in a 1,200-fold purification with production of homogeneous enzyme in approximately 75% yield; the enzymes from spores and cells seemed identical. The molecular weight of the native enzyme was 335,000, with a subunit molecular weight of 42,000. The enzyme required Mg2+ and was inhibited by ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and fluoride ions. The Michaelis constants for 2-phosphoglyceric acid and Mg2+ were 7.1 X 10(-4) and 4.7 X 10(-4) M, respectively.
Full text
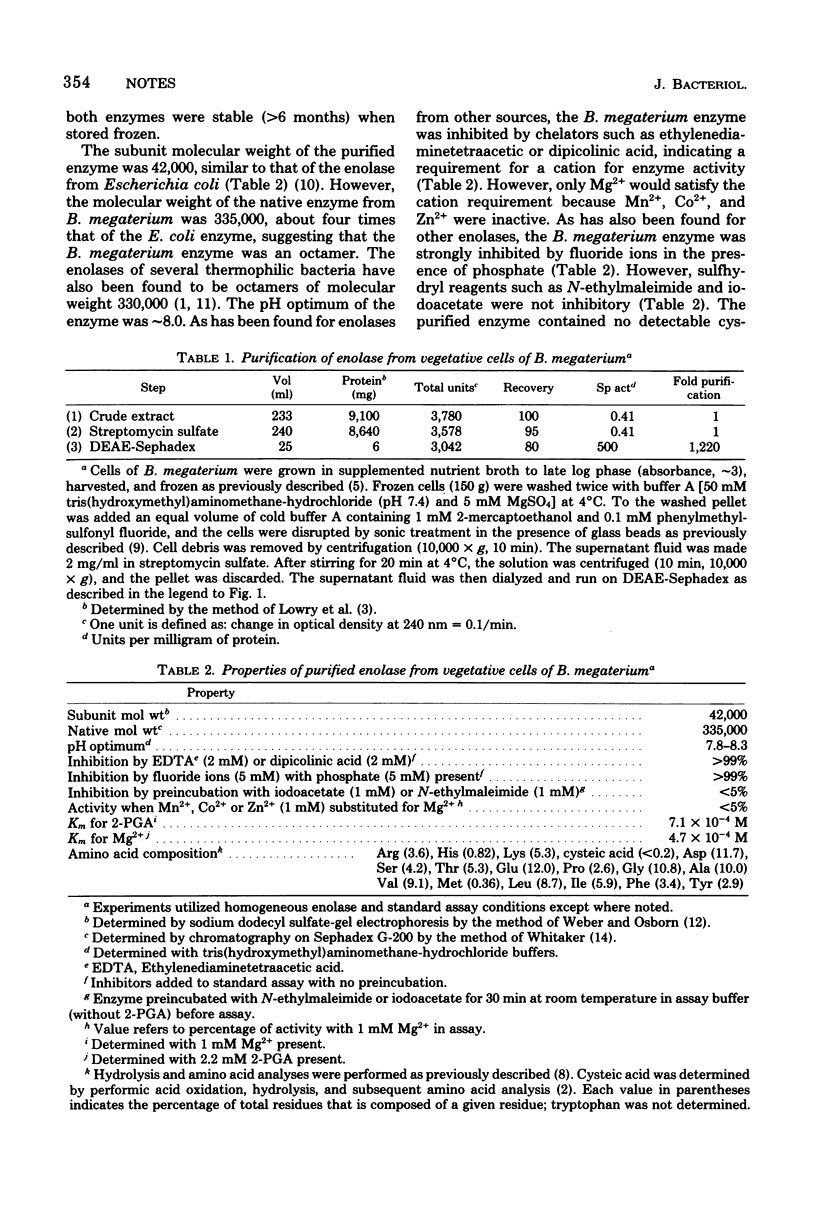
PDF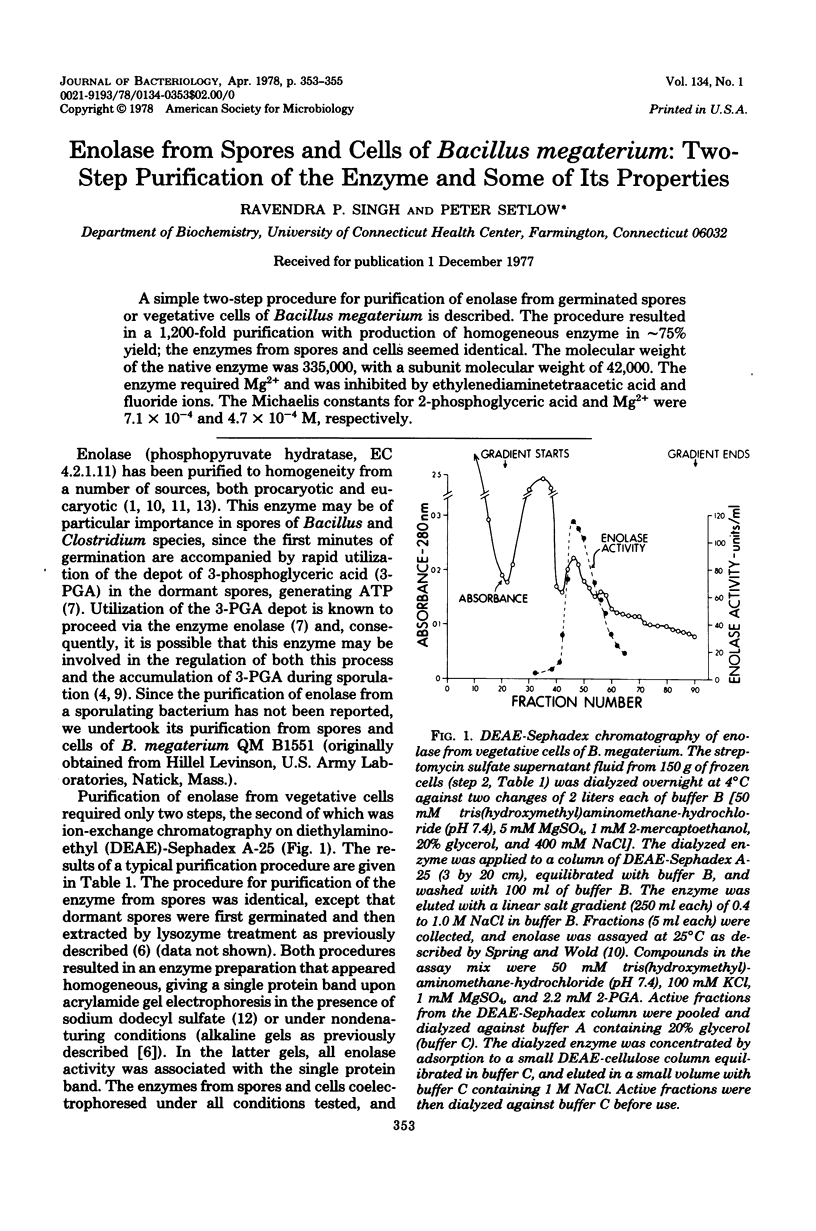

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes L. D., Stellwagen E. Enolase from the thermophile Thermus X-1. Biochemistry. 1973 Apr 10;12(8):1559–1565. doi: 10.1021/bi00732a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation and germination. XIX. Phosphate metabolism during sporulation. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 10;245(5):1137–1145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P. Identification of several unique low molecular weight basic proteins in dormant spores of Bacillus megaterium and their degradation during spore germination. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1110–1117. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80398-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation and germination. XXII. Energy metabolism in early stages of germination of Bacillus megaterium spores. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3637–3644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P., Primus G. Protein metabolism during germination of Bacillus megaterium spores. I. Protein synthesis and amino acid metabolism. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):623–630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow P. Purification and properties of a specific proteolytic enzyme present in spores of Bacillus magaterium. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 25;251(24):7853–7862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh R. P., Setlow B., Setlow P. Levels of small molecules and enzymes in the mother cell compartment and the forespore of sporulating Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1130–1138. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1130-1138.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spring T. G., Wold F. The purification and characterization of Escherichia coli enolase. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov 25;246(22):6797–6802. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellwagen E., Cronlund M. M., Barnes L. D. A thermostable enolase from the extreme thermophile Thermus aquaticus YT-1. Biochemistry. 1973 Apr 10;12(8):1552–1559. doi: 10.1021/bi00732a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WESTHEAD E. W., MCLAIN G. A PURIFICATION OF BREWERS' AND BAKERS' YEAST ENOLASE YIELDING A SINGLE ACTIVE COMPONENT. J Biol Chem. 1964 Aug;239:2464–2468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


