Abstract
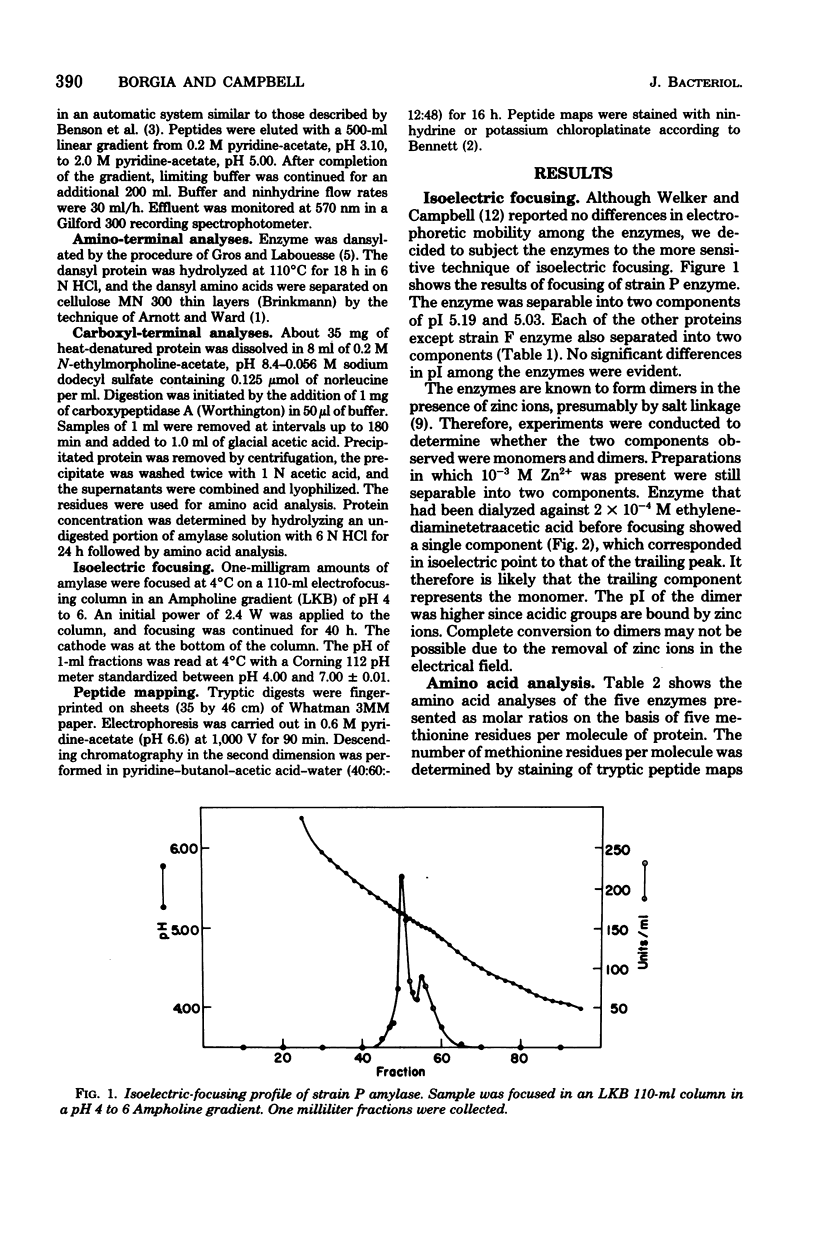
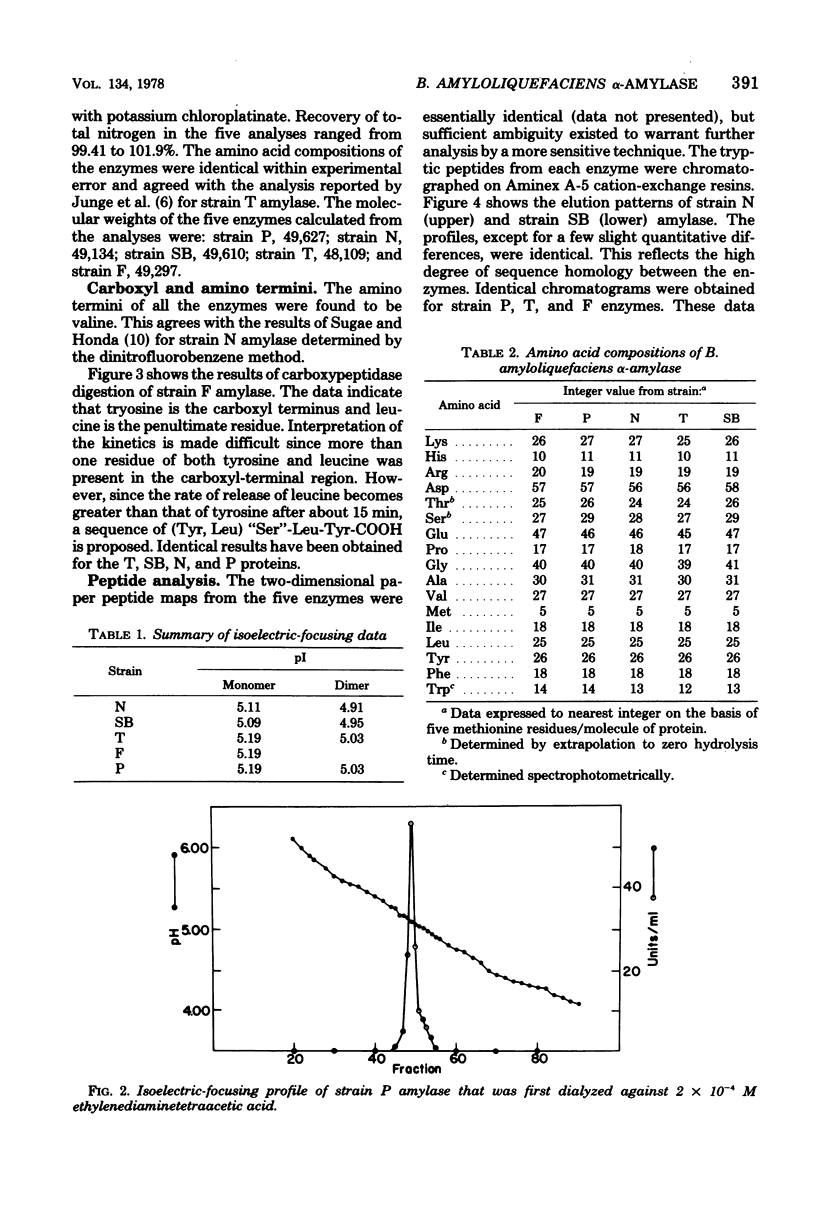
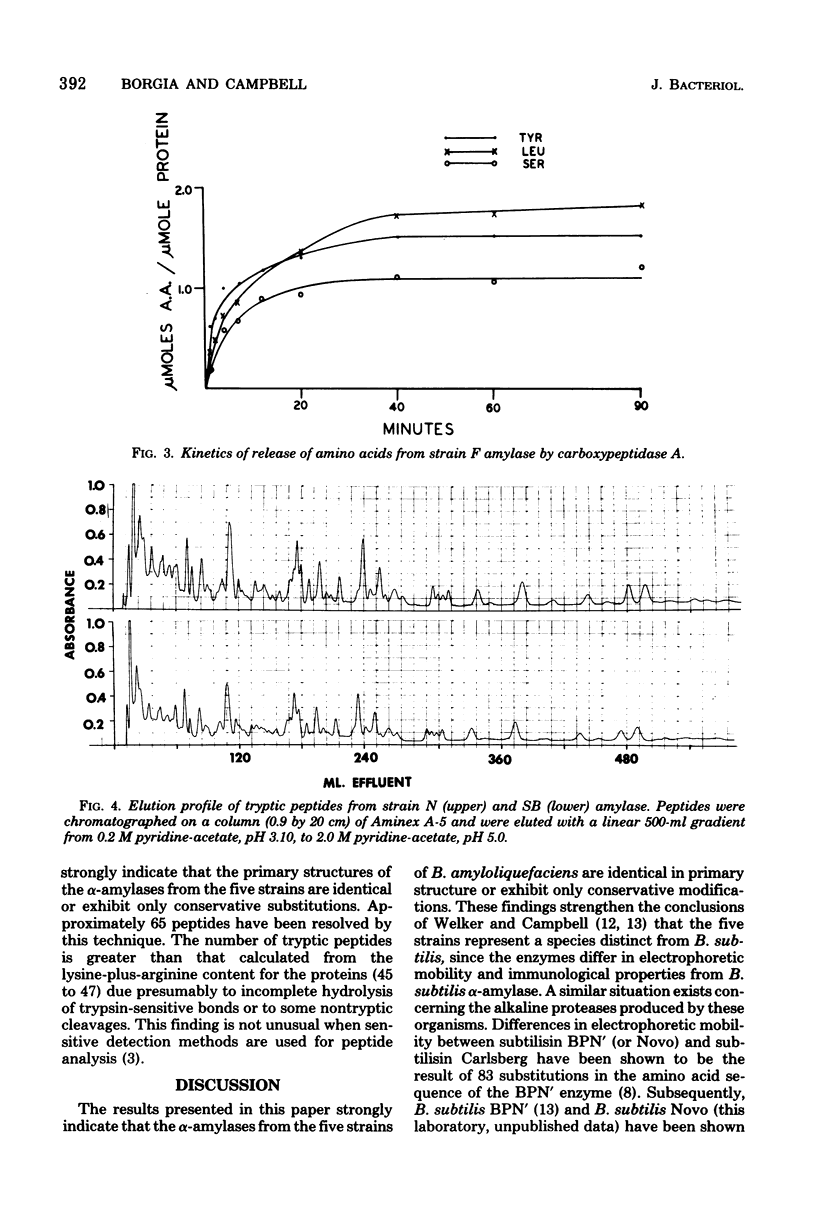
The alpha-amylases from five strains of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens were compared to determine whether differences in primary structure are responsible for variations in catalytic properties previously reported among the enzymes. Amino acid analysis established virtually identical compositions for the proteins. Reaction with dimethylaminoaphthylene sulfonylchloride indicated the amino-terminal amino acid of each amylase to be valine. Carboxyl termini of the enzymes have been determined by digestion with carboxypeptidase A. The resulting kinetic data indicate tyrosine as the carboxyl terminus and leucine as the penultimate residue for all five proteins. Isoelectric focusing of the enzymes yielded isoelectric points in the pH range of 5.09 to 5.18. Tryptic digests of the enzymes chromatographed on a cation-exchange column showed identical elution patterns. It is concluded that the primary structure of the amylase from the five strains is identical or exhibits only conservative substitutions.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnott M. S., Ward D. N. Separation of dansyl amino acids in a single analysis. Anal Biochem. 1967 Oct;21(1):50–56. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90082-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros C., Labouesse B. Study of the dansylation reaction of amino acids, peptides and proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Feb;7(4):463–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb19632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUNGE J. M., STEIN E. A., NEURATH H., FISCHER E. H. The amino acid composition of alpha-amylase from Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1959 Mar;234(3):556–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEIN E. A., FISCHER E. H. Bacillus subtilis alpha-amylase, a zinc-protein complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Apr 8;39:287–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. L., Markland F. S., Kasper C. B., DeLange R. J., Landon M., Evans W. H. The complete amino acid sequence of two types of subtilisin, BPN' and Carlsberg. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 25;241(24):5974–5976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welker N. E., Campbell L. L. Comparison of the alpha-amylase of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1131–1135. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1131-1135.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welker N. E., Campbell L. L. Crystallization and properties of alpha-amylase from five strains of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Biochemistry. 1967 Dec;6(12):3681–3689. doi: 10.1021/bi00864a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welker N. E., Campbell L. L. Unrelatedness of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1124–1130. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1124-1130.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamane K., Yamaguchi K., Maruo B. Purification and properties of a cross-reacting material related to -amylase and biochemical comparison with the parent -amylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 25;295(1):323–340. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



