Abstract
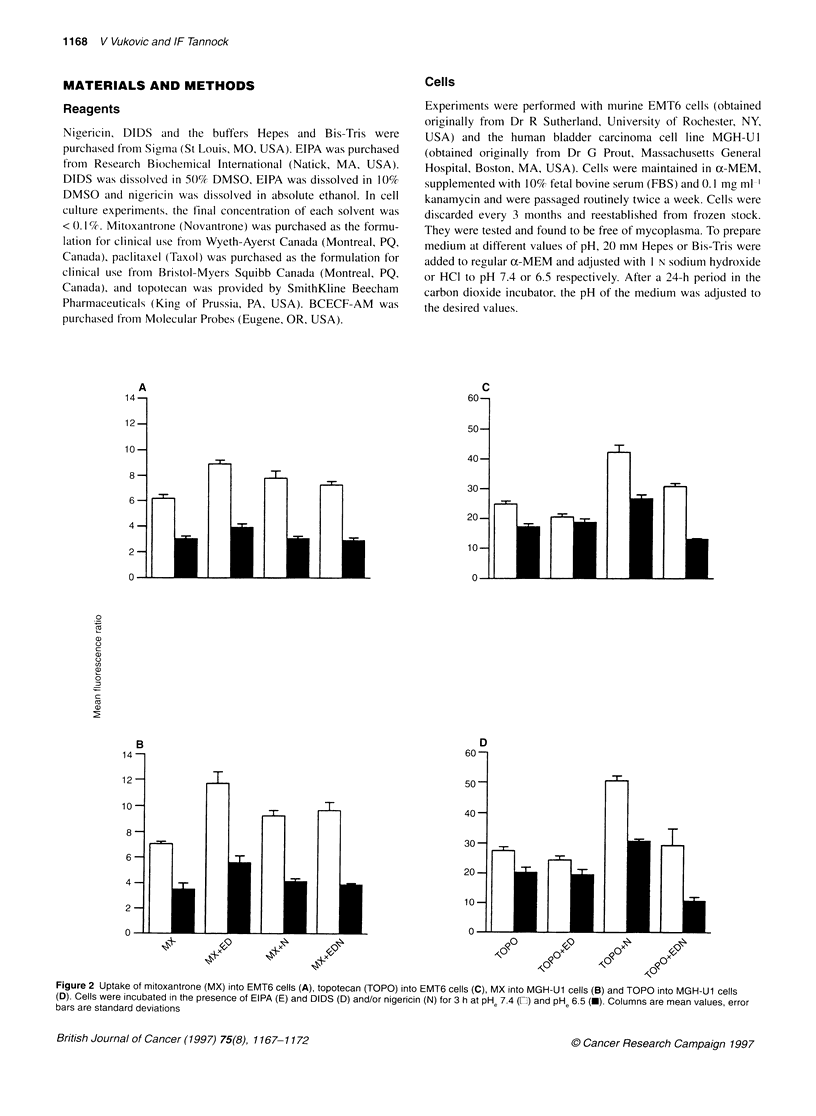
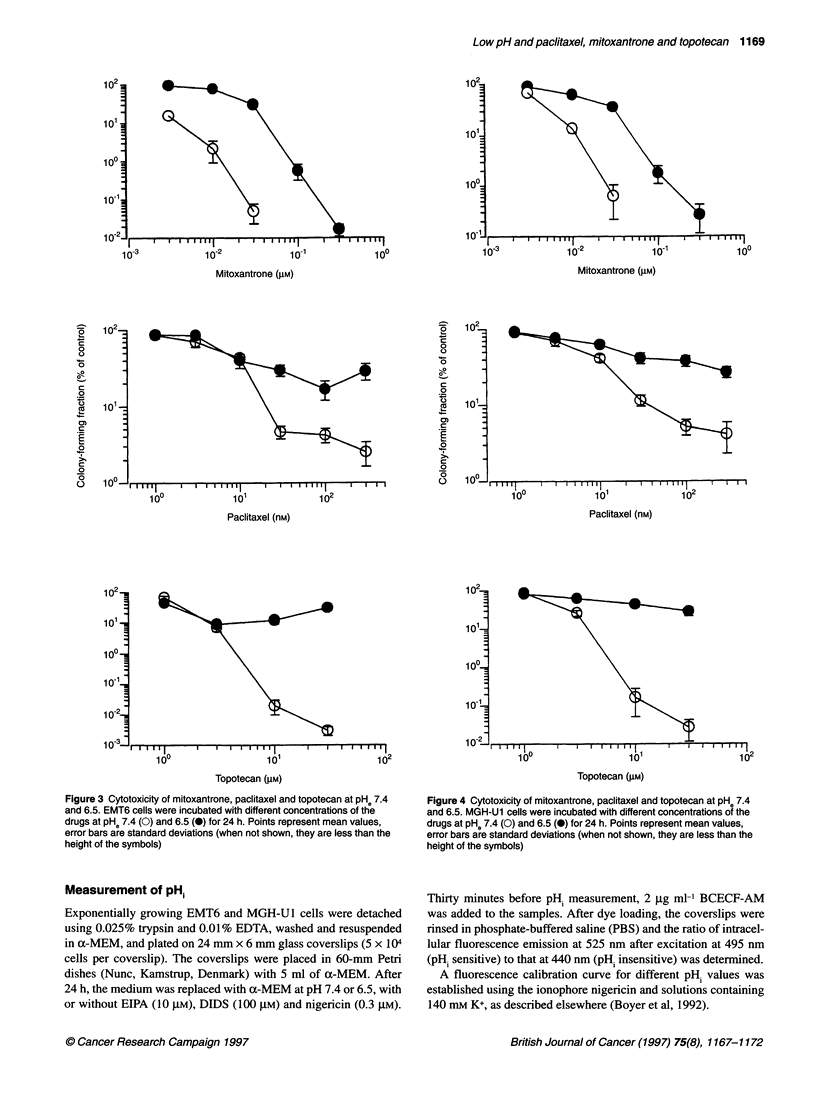
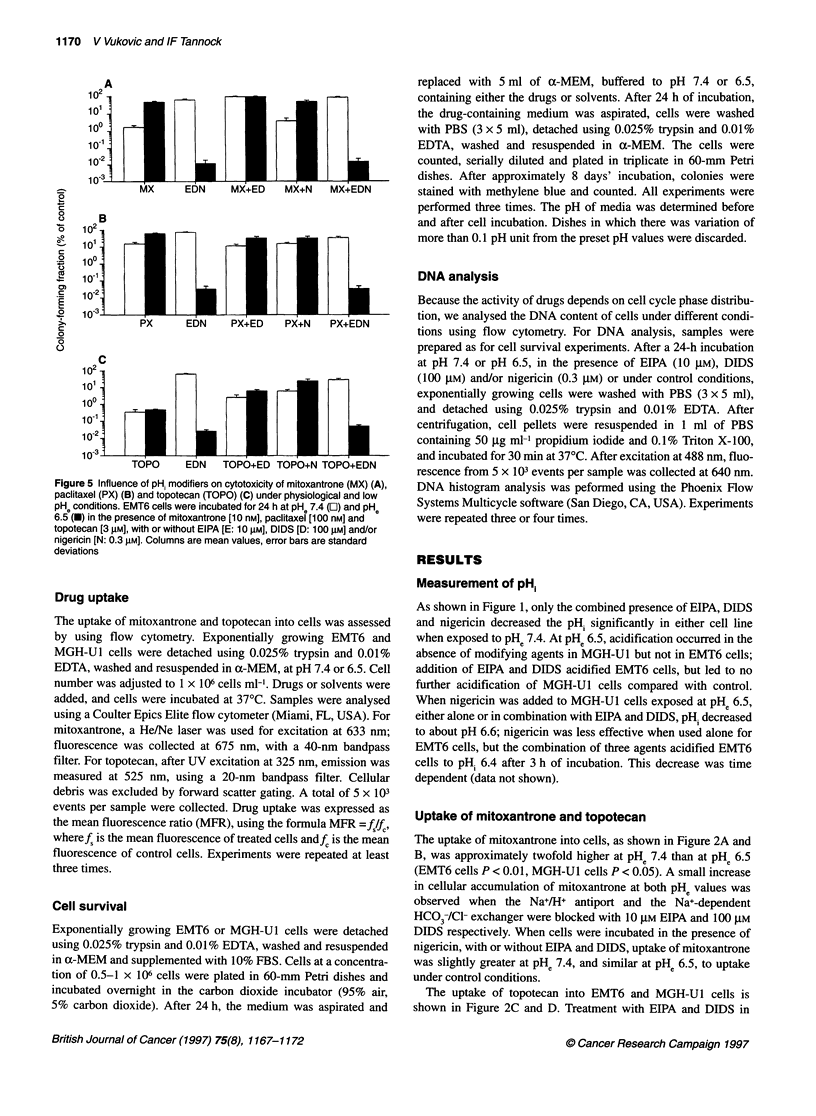
The extracellular pH (pHe) of solid tumours is often lower than in normal tissues, and this may influence the uptake and/or activity of anti-cancer drugs. The cytotoxicity of mitoxantrone, paclitaxel and topotecan was therefore assessed at low pHe and after manipulation of intracellular pH (pHi) in murine EMT6 and in human MGH-U1 cells. The cytotoxic efficacy of all three agents was reduced at pHe 6.5 as compared with pHe 7.4. The ionophore nigericin and inhibitors of membrane-based ion exchange mechanisms that regulate pHi (5-[N-ethyl-N-isopropyl] amiloride, EIPA; 4,4-diisothiocyanstilbene 2,2-disulphonic acid, DIDS) were used to cause intracellular acidification. Combined use of the cytostatic drugs with pHi modifiers reduced their cytotoxicity under both physiological and low-pHe conditions. The uptake into cells of mitoxantrone (a weak base) was inhibited at pHe 6.5 as compared with pHe 7.4, and smaller effects of low pHe to inhibit uptake of topotecan were also observed. DNA analysis of cell cycle distribution revealed that intracellular acidification, as observed during incubation at low pHe and/or using pHi modifiers, resulted in accumulation of cells in G1 phase, where they may be more resistant to these drugs. Reduced uptake of weak bases (mitoxantrone) at low pHe and altered cell cycle kinetics upon acidification are the postulated causes of reduced cytotoxicity of the agents investigated.
Full text
PDF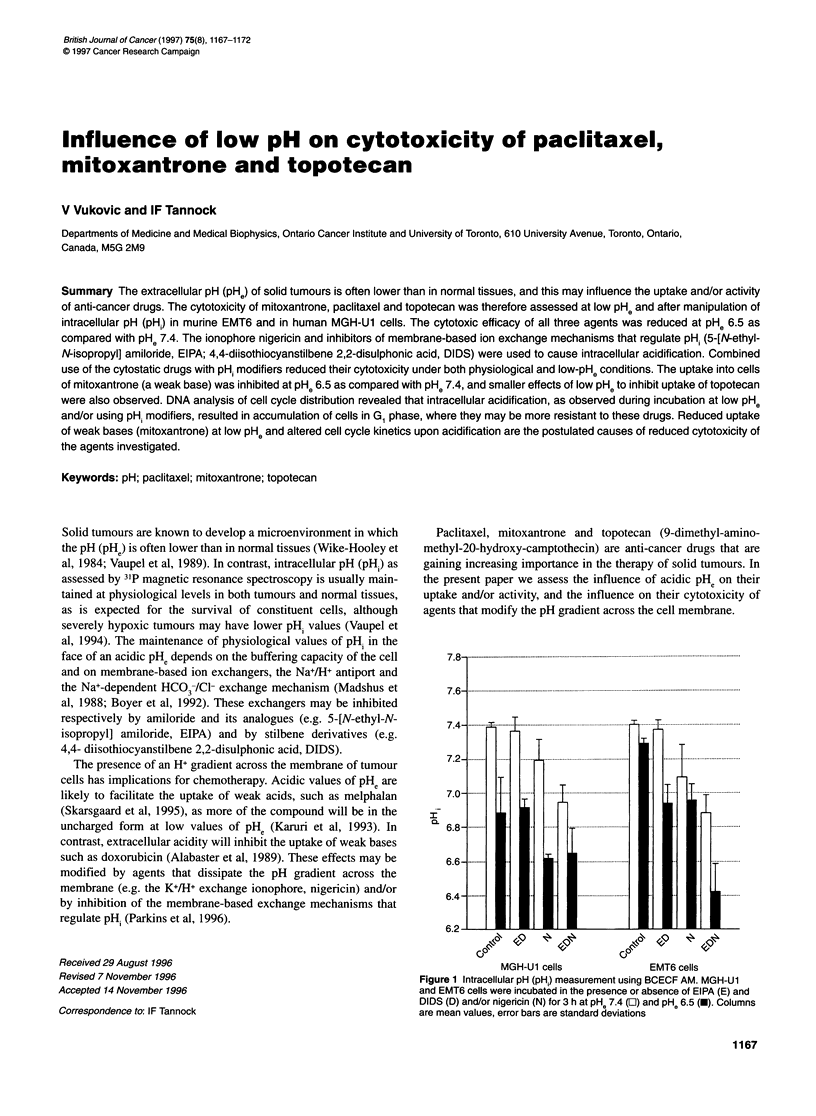

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alabaster O., Woods T., Ortiz-Sanchez V., Jahangeer S. Influence of microenvironmental pH on adriamycin resistance. Cancer Res. 1989 Oct 15;49(20):5638–5643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asaumi J., Kawasaki S., Nishikawa K., Kuroda M., Hiraki Y. Influence of the extracellular pH, an inhibitor of Na+/H+ exchanger and an inhibitor of Cl-/HCO3-exchanger on adriamycin accumulation. Anticancer Res. 1995 Jan-Feb;15(1):71–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer M. J., Tannock I. F. Regulation of intracellular pH in tumor cell lines: influence of microenvironmental conditions. Cancer Res. 1992 Aug 15;52(16):4441–4447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennequin C., Giocanti N., Favaudon V. Interaction of ionizing radiation with paclitaxel (Taxol) and docetaxel (Taxotere) in HeLa and SQ20B cells. Cancer Res. 1996 Apr 15;56(8):1842–1850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg R. P., Caranfa M. J., Holden K. G., Jakas D. R., Gallagher G., Mattern M. R., Mong S. M., Bartus J. O., Johnson R. K., Kingsbury W. D. Modification of the hydroxy lactone ring of camptothecin: inhibition of mammalian topoisomerase I and biological activity. J Med Chem. 1989 Mar;32(3):715–720. doi: 10.1021/jm00123a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huizing M. T., Misser V. H., Pieters R. C., ten Bokkel Huinink W. W., Veenhof C. H., Vermorken J. B., Pinedo H. M., Beijnen J. H. Taxanes: a new class of antitumor agents. Cancer Invest. 1995;13(4):381–404. doi: 10.3109/07357909509031919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähde E., Glüsenkamp K. H., Rajewsky M. F. Protection of cultured malignant cells from mitoxantrone cytotoxicity by low extracellular pH: a possible mechanism for chemoresistance in vivo. Eur J Cancer. 1990 Feb;26(2):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(90)90290-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karuri A. R., Dobrowsky E., Tannock I. F. Selective cellular acidification and toxicity of weak organic acids in an acidic microenvironment. Br J Cancer. 1993 Dec;68(6):1080–1087. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madshus I. H. Regulation of intracellular pH in eukaryotic cells. Biochem J. 1988 Feb 15;250(1):1–8. doi: 10.1042/bj2500001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musgrove E., Seaman M., Hedley D. Relationship between cytoplasmic pH and proliferation during exponential growth and cellular quiescence. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Sep;172(1):65–75. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90093-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkins C. S., Chadwick J. A., Chaplin D. J. Inhibition of intracellular pH control and relationship to cytotoxicity of chlorambucil and vinblastine. Br J Cancer Suppl. 1996 Jul;27:S75–S77. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potmesil M. Camptothecins: from bench research to hospital wards. Cancer Res. 1994 Mar 15;54(6):1431–1439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotin D., Wan P., Grinstein S., Tannock I. Cytotoxicity of compounds that interfere with the regulation of intracellular pH: a potential new class of anticancer drugs. Cancer Res. 1987 Mar 15;47(6):1497–1504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarsgard L. D., Skwarchuk M. W., Vinczan A., Kristl J., Chaplin D. J. The cytotoxicity of melphalan and its relationship to pH, hypoxia and drug uptake. Anticancer Res. 1995 Jan-Feb;15(1):219–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundman-Engberg B., Tidefelt U., Paul C. Effect of cytokines on the toxicity of cytostatic drugs on leukemic cells in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Haematol. 1996 Jan-Feb;56(1-2):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1996.tb00285.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaupel P., Kallinowski F., Okunieff P. Blood flow, oxygen and nutrient supply, and metabolic microenvironment of human tumors: a review. Cancer Res. 1989 Dec 1;49(23):6449–6465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaupel P., Schaefer C., Okunieff P. Intracellular acidosis in murine fibrosarcomas coincides with ATP depletion, hypoxia, and high levels of lactate and total Pi. NMR Biomed. 1994 May;7(3):128–136. doi: 10.1002/nbm.1940070305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wike-Hooley J. L., Haveman J., Reinhold H. S. The relevance of tumour pH to the treatment of malignant disease. Radiother Oncol. 1984 Dec;2(4):343–366. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8140(84)80077-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


