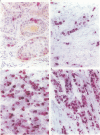
Abstract
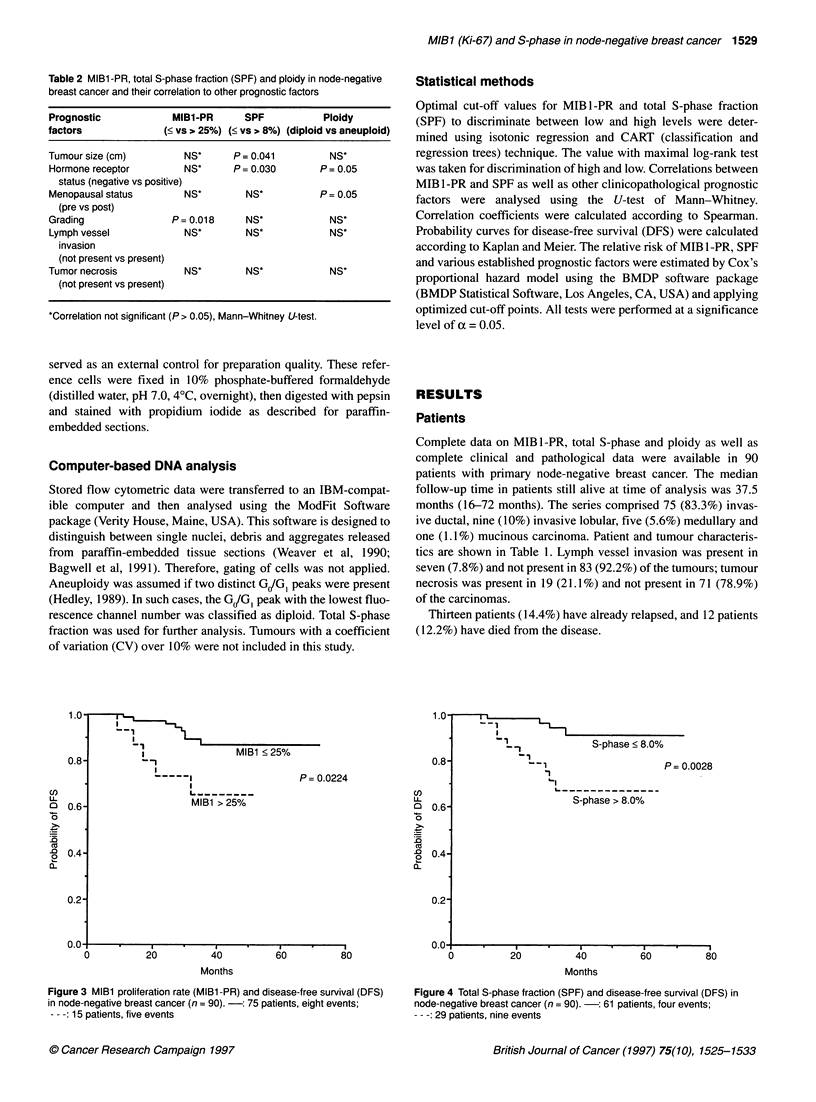
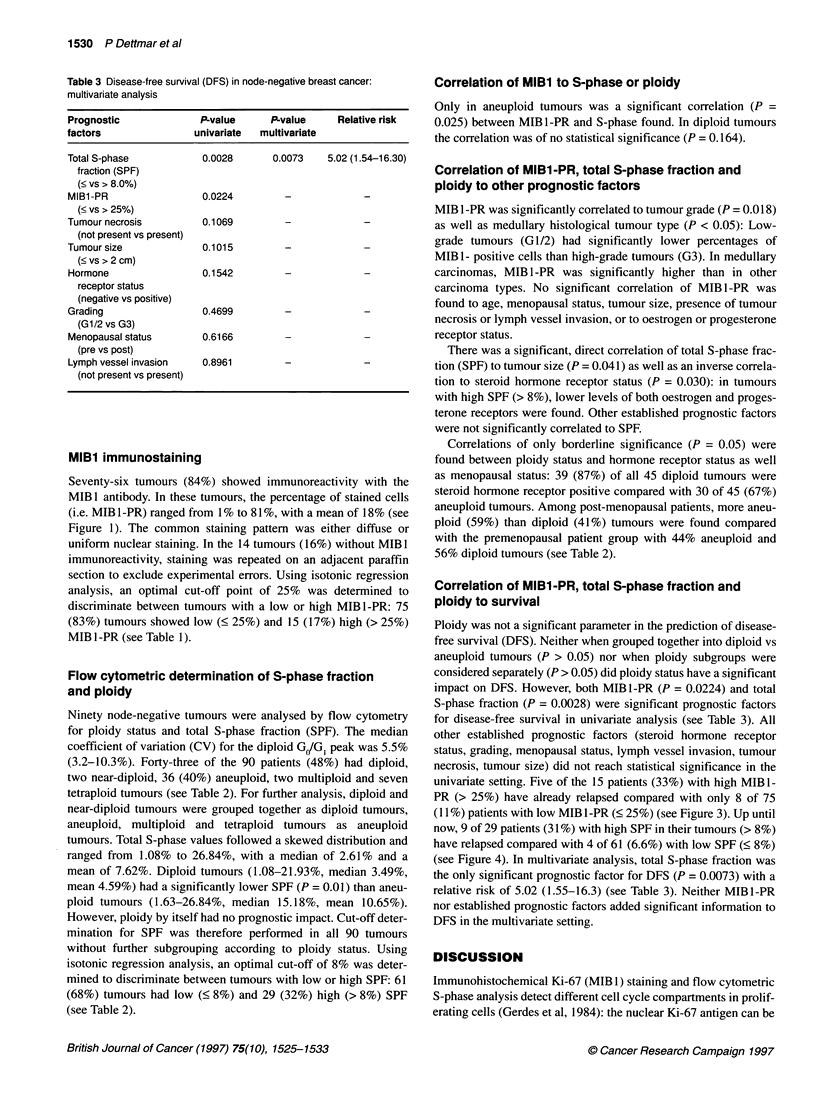
MIB1 proliferation rate (MIB1-PR) and total S-phase fraction (SPF) were retrospectively determined in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections of 90 primary node-negative breast carcinomas. None of the patients had received adjuvant systemic therapy. Median follow-up in patients still alive at the time of analysis was 37.5 months (16-72 months). Immunostaining of Ki-67 antigen was performed using the monoclonal antibody MIB1 and the APAAP technique. An adjacent 50-microm paraffin section was used for flow cytometric S-phase determination. Results were compared to established clinicopathological prognostic factors. MIB1-PR was significantly correlated to grading (P = 0.018); SPF was significantly correlated with tumour size (P = 0.041) and inversely with steroid hormone receptor status (P = 0.03). A significant correlation between MIB1-PR and SPF was found in aneuploid (P = 0.025) but not in diploid tumours (P = 0.164). In univariate analysis, both MIB1-PR (optimized cut-off of 25%) and SPF (optimized cut-off of 8%) were significant prognostic factors for disease-free survival (DFS) (MIB1-PR, P = 0.0224; SPF, P = 0.0028). In multivariate analysis, however, only SPF remained significant; it was the strongest prognostic factor for DFS (P = 0.0073), stronger than MIB1-PR or established clinicopathological prognostic factors. We thus conclude that MIB1-PR and SPF provide additional prognostic information in node-negative breast cancer. However, in our study, flow cytometrically determined SPF had the greater prognostic impact.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubele M., Auer G., Voss A., Falkmer U., Rutquist L. E., Höfler H. Different risk groups in node-negative breast cancer: prognostic value of cytophotometrically assessed DNA, morphometry and texture. Int J Cancer. 1995 Sep 27;63(1):7–12. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910630103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOOM H. J., RICHARDSON W. W. Histological grading and prognosis in breast cancer; a study of 1409 cases of which 359 have been followed for 15 years. Br J Cancer. 1957 Sep;11(3):359–377. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1957.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagwell C. B., Mayo S. W., Whetstone S. D., Hitchcox S. A., Baker D. R., Herbert D. J., Weaver D. L., Jones M. A., Lovett E. J., 3rd DNA histogram debris theory and compensation. Cytometry. 1991;12(2):107–118. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990120203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesterfeld S., Noll I., Noll E., Wohltmann D., Böcking A. Mitotic frequency as a prognostic factor in breast cancer. Hum Pathol. 1995 Jan;26(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(95)90113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattoretti G., Becker M. H., Key G., Duchrow M., Schlüter C., Galle J., Gerdes J. Monoclonal antibodies against recombinant parts of the Ki-67 antigen (MIB 1 and MIB 3) detect proliferating cells in microwave-processed formalin-fixed paraffin sections. J Pathol. 1992 Dec;168(4):357–363. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G. M., Dressler L. G., Owens M. A., Pounds G., Oldaker T., McGuire W. L. Prediction of relapse or survival in patients with node-negative breast cancer by DNA flow cytometry. N Engl J Med. 1989 Mar 9;320(10):627–633. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198903093201003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell J. L., Falini B., Erber W. N., Ghosh A. K., Abdulaziz Z., MacDonald S., Pulford K. A., Stein H., Mason D. Y. Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP complexes). J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Feb;32(2):219–229. doi: 10.1177/32.2.6198355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuevas E., Jones D. B., Wright D. H. Immunohistochemical detection of tumour growth fraction (Ki-67 antigen) in formalin-fixed and routinely processed tissues. J Pathol. 1993 Apr;169(4):477–478. doi: 10.1002/path.1711690415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dervan P. A., Gilmartin L. G., Loftus B. M., Carney D. N. Breast carcinoma kinetics. Argyrophilic nucleolar organizer region counts correlate with Ki67 scores. Am J Clin Pathol. 1989 Oct;92(4):401–407. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/92.4.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler L. G., Seamer L. C., Owens M. A., Clark G. M., McGuire W. L. DNA flow cytometry and prognostic factors in 1331 frozen breast cancer specimens. Cancer. 1988 Feb 1;61(3):420–427. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19880201)61:3<420::aid-cncr2820610303>3.0.co;2-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher B., Slack N. H., Bross I. D. Cancer of the breast: size of neoplasm and prognosis. Cancer. 1969 Nov;24(5):1071–1080. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196911)24:5<1071::aid-cncr2820240533>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasparini G., Boracchi P., Verderio P., Bevilacqua P. Cell kinetics in human breast cancer: comparison between the prognostic value of the cytofluorimetric S-phase fraction and that of the antibodies to Ki-67 and PCNA antigens detected by immunocytochemistry. Int J Cancer. 1994 Jun 15;57(6):822–829. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910570610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J., Lemke H., Baisch H., Wacker H. H., Schwab U., Stein H. Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1710–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J., Li L., Schlueter C., Duchrow M., Wohlenberg C., Gerlach C., Stahmer I., Kloth S., Brandt E., Flad H. D. Immunobiochemical and molecular biologic characterization of the cell proliferation-associated nuclear antigen that is defined by monoclonal antibody Ki-67. Am J Pathol. 1991 Apr;138(4):867–873. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J., Schwab U., Lemke H., Stein H. Production of a mouse monoclonal antibody reactive with a human nuclear antigen associated with cell proliferation. Int J Cancer. 1983 Jan 15;31(1):13–20. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910310104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorczyca W., Markiewski M., Kram A., Tuziak T., Domagala W. Immunohistochemical analysis of bcl-2 and p53 expression in breast carcinomas: their correlation with Ki-67 growth fraction. Virchows Arch. 1995;426(3):229–233. doi: 10.1007/BF00191359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D., Magee H., Kierce B., Ball R., Dervan P., O'Meara A. Evaluation of Ki-67 reactivity in neuroblastoma using paraffin embedded tissue. Pathol Res Pract. 1995 Mar;191(2):87–91. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(11)80557-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbeck N., Moniwa N., Busch E., Schmitt M., Jänicke F., Fellbaum C., Höfler H., Graeff H. Durchflusszytometrische DNA-Analyse von reinen Zellkernen aus formalin-fixierten Paraffinschnitten beim primären Mammakarzinom: Korrelation mit anderen Prognosefaktoren. Gynakol Rundsch. 1991;31 (Suppl 2):299–302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley D. W. Flow cytometry using paraffin-embedded tissue: five years on. Cytometry. 1989 May;10(3):229–241. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990100302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley D. W., Friedlander M. L., Taylor I. W. Application of DNA flow cytometry to paraffin-embedded archival material for the study of aneuploidy and its clinical significance. Cytometry. 1985 Jul;6(4):327–333. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990060409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley D. W., Friedlander M. L., Taylor I. W., Rugg C. A., Musgrove E. A. Method for analysis of cellular DNA content of paraffin-embedded pathological material using flow cytometry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Nov;31(11):1333–1335. doi: 10.1177/31.11.6619538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley D. W., Rugg C. A., Gelber R. D. Association of DNA index and S-phase fraction with prognosis of nodes positive early breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 1;47(17):4729–4735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isola J. J., Helin H. J., Helle M. J., Kallioniemi O. P. Evaluation of cell proliferation in breast carcinoma. Comparison of Ki-67 immunohistochemical study, DNA flow cytometric analysis, and mitotic count. Cancer. 1990 Mar 1;65(5):1180–1184. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19900301)65:5<1180::aid-cncr2820650525>3.0.co;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallioniemi O. P., Blanco G., Alavaikko M., Hietanen T., Mattila J., Lauslahti K., Lehtinen M., Koivula T. Improving the prognostic value of DNA flow cytometry in breast cancer by combining DNA index and S-phase fraction. A proposed classification of DNA histograms in breast cancer. Cancer. 1988 Nov 15;62(10):2183–2190. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19881115)62:10<2183::aid-cncr2820621019>3.0.co;2-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallioniemi O. P. Comparison of fresh and paraffin-embedded tissue as starting material for DNA flow cytometry and evaluation of intratumor heterogeneity. Cytometry. 1988 Mar;9(2):164–169. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990090211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallioniemi O. P., Hietanen T., Mattila J., Lehtinen M., Lauslahti K., Koivula T. Aneuploid DNA content and high S-phase fraction of tumour cells are related to poor prognosis in patients with primary breast cancer. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1987 Mar;23(3):277–282. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(87)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamel O. W., Franklin W. A., Ringus J. C., Meyer J. S. Thymidine labeling index and Ki-67 growth fraction in lesions of the breast. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jan;134(1):107–113. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lellé R. J., Heidenreich W., Stauch G., Gerdes J. The correlation of growth fractions with histologic grading and lymph node status in human mammary carcinoma. Cancer. 1987 Jan 1;59(1):83–88. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19870101)59:1<83::aid-cncr2820590119>3.0.co;2-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly S. M., Camplejohn R. S., Barnes D. M., Millis R. R., Rubens R. D., Richards M. A. Node-negative breast cancer: prognostic subgroups defined by tumor size and flow cytometry. J Clin Oncol. 1990 Dec;8(12):2040–2046. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1990.8.12.2040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüschoff J., Neumann K., Contractor H., Plate K., Thomas C. Assessment of nucleolar organizer regions by automatic image analysis in breast cancer: correlation with DNA content, proliferation rate, receptor status and histopathological grading. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 1990;116(5):480–485. doi: 10.1007/BF01612998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahin A. A., Ro J., Ro J. Y., Blick M. B., el-Naggar A. K., Ordonez N. G., Fritsche H. A., Smith T. L., Hortobagyi G. N., Ayala A. G. Ki-67 immunostaining in node-negative stage I/II breast carcinoma. Significant correlation with prognosis. Cancer. 1991 Aug 1;68(3):549–557. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19910801)68:3<549::aid-cncr2820680318>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigurdsson H., Baldetorp B., Borg A., Dalberg M., Fernö M., Killander D., Olsson H. Indicators of prognosis in node-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1990 Apr 12;322(15):1045–1053. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199004123221505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toikkanen S., Joensuu H., Klemi P. The prognostic significance of nuclear DNA content in invasive breast cancer--a study with long-term follow-up. Br J Cancer. 1989 Nov;60(5):693–700. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1989.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheijen R., Kuijpers H. J., van Driel R., Beck J. L., van Dierendonck J. H., Brakenhoff G. J., Ramaekers F. C. Ki-67 detects a nuclear matrix-associated proliferation-related antigen. II. Localization in mitotic cells and association with chromosomes. J Cell Sci. 1989 Apr;92(Pt 4):531–540. doi: 10.1242/jcs.92.4.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veronese S. M., Gambacorta M., Gottardi O., Scanzi F., Ferrari M., Lampertico P. Proliferation index as a prognostic marker in breast cancer. Cancer. 1993 Jun 15;71(12):3926–3931. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930615)71:12<3926::aid-cncr2820711221>3.0.co;2-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vielh P., Chevillard S., Mosseri V., Donatini B., Magdelenat H. Ki67 index and S-phase fraction in human breast carcinomas. Comparison and correlations with prognostic factors. Am J Clin Pathol. 1990 Dec;94(6):681–686. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/94.6.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver D. L., Bagwell C. B., Hitchcox S. A., Whetstone S. D., Baker D. R., Herbert D. J., Jones M. A. Improved flow cytometric determination of proliferative activity (S-phase fraction) from paraffin-embedded tissue. Am J Clin Pathol. 1990 Nov;94(5):576–584. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/94.5.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Moore D. H., 2nd, Vartanian R. Correlation of Ki-67 antigen expression with mitotic figure index and tumor grade in breast carcinomas using the novel "paraffin"-reactive MIB1 antibody. Hum Pathol. 1994 Apr;25(4):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(94)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]