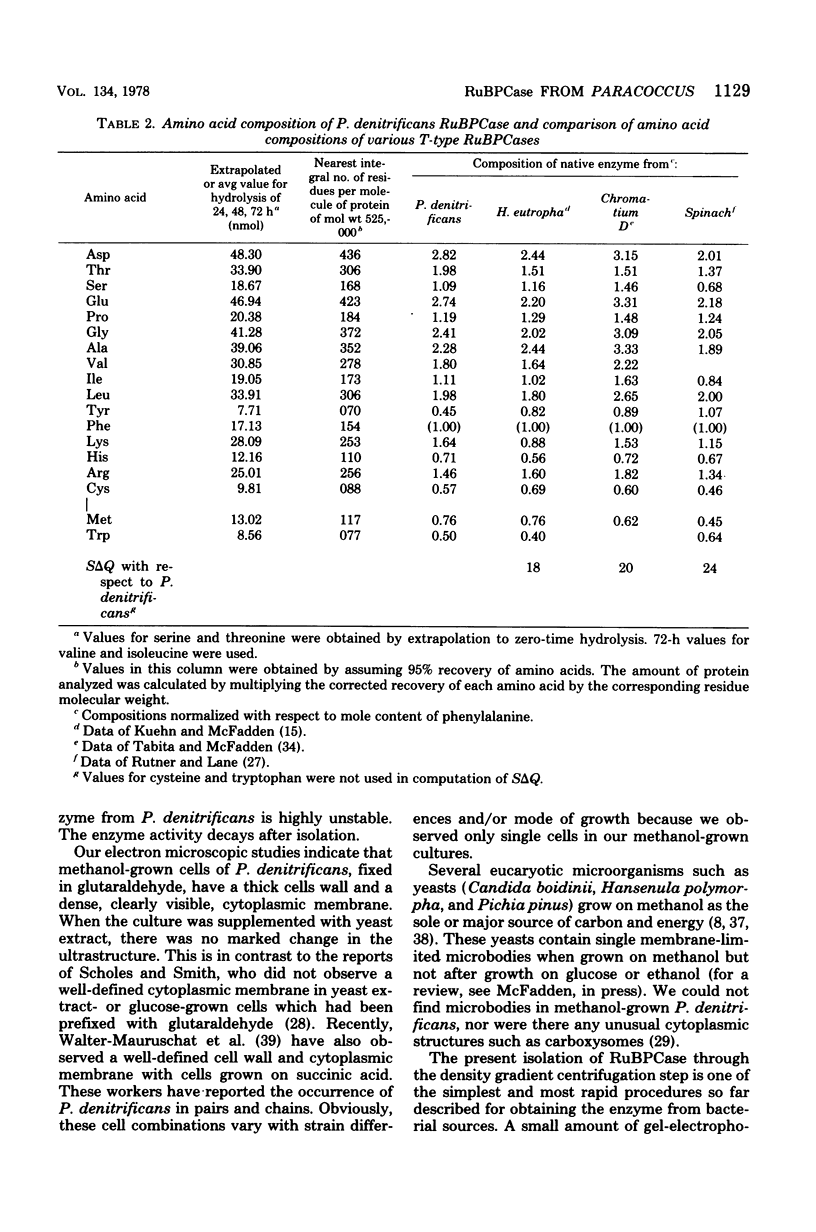
Abstract
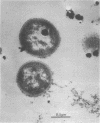
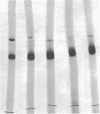
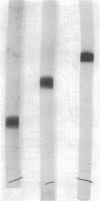
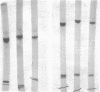
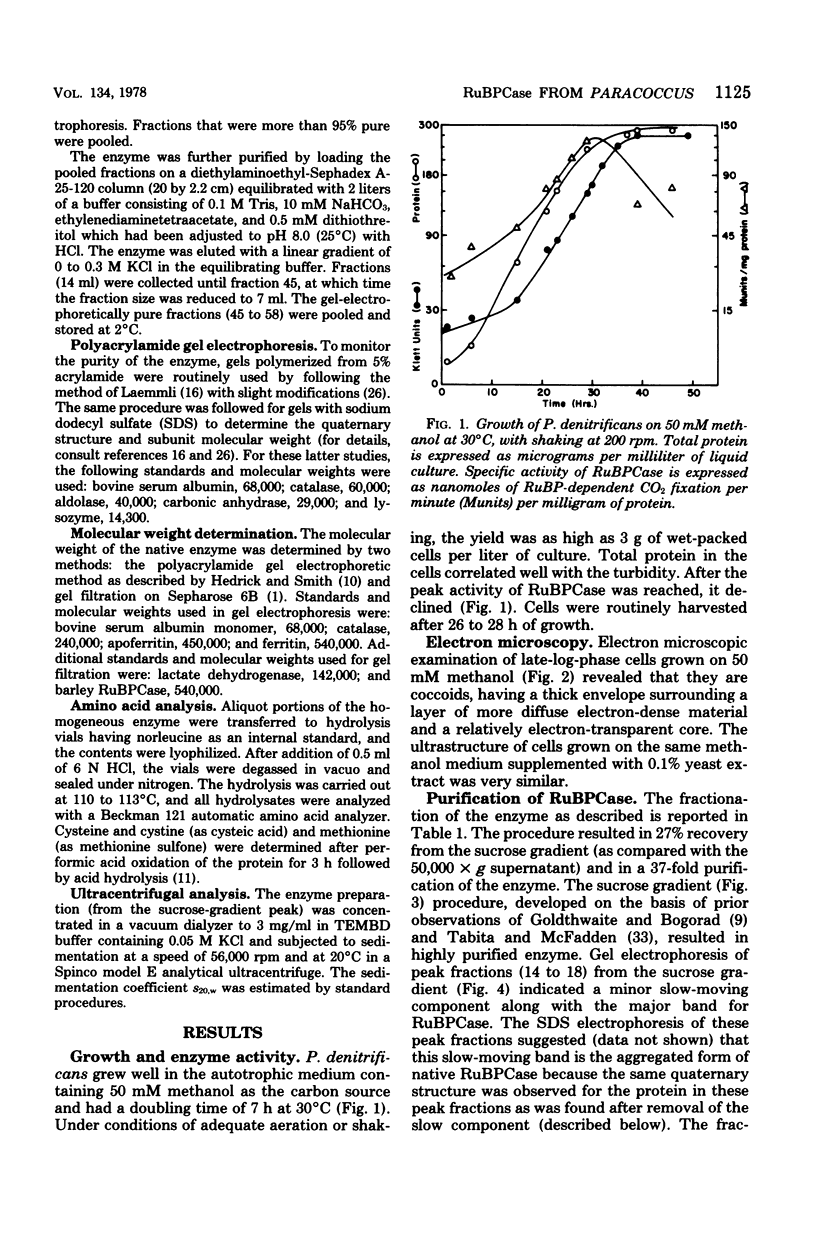
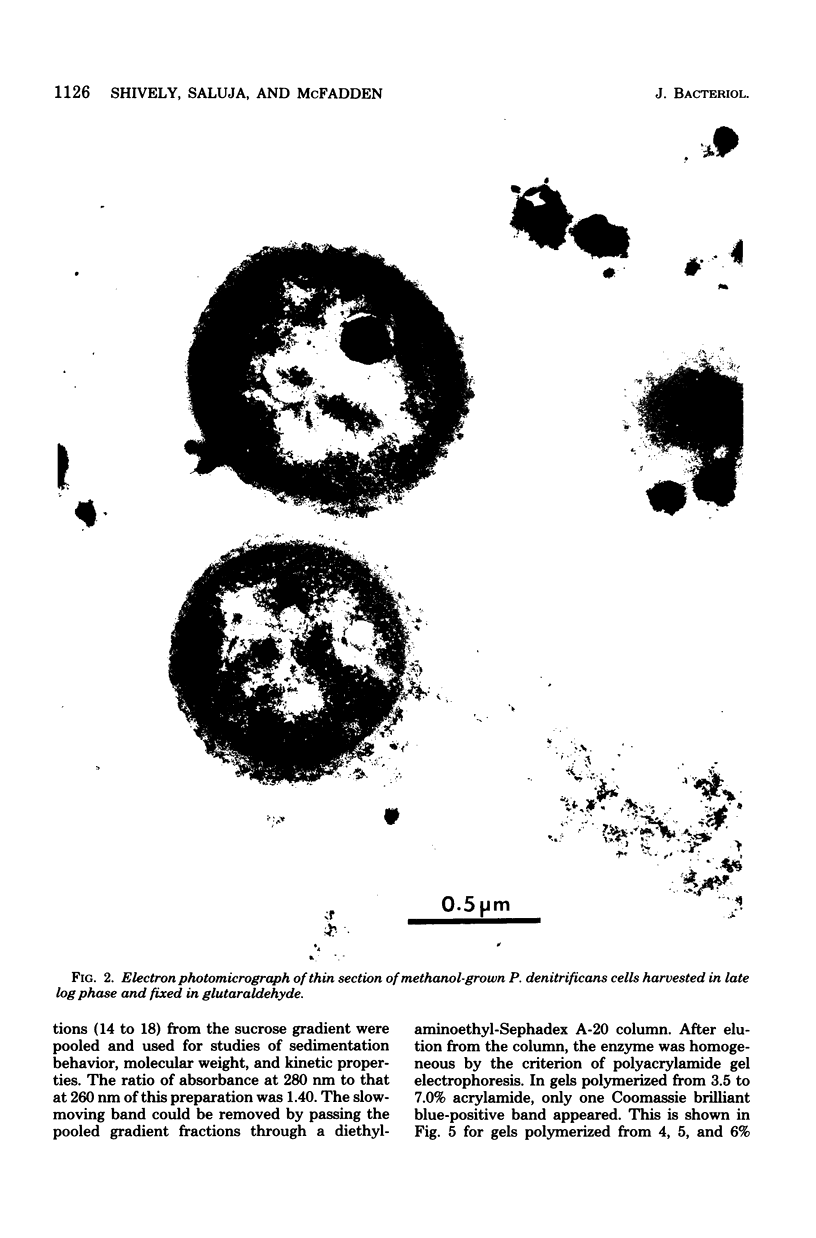
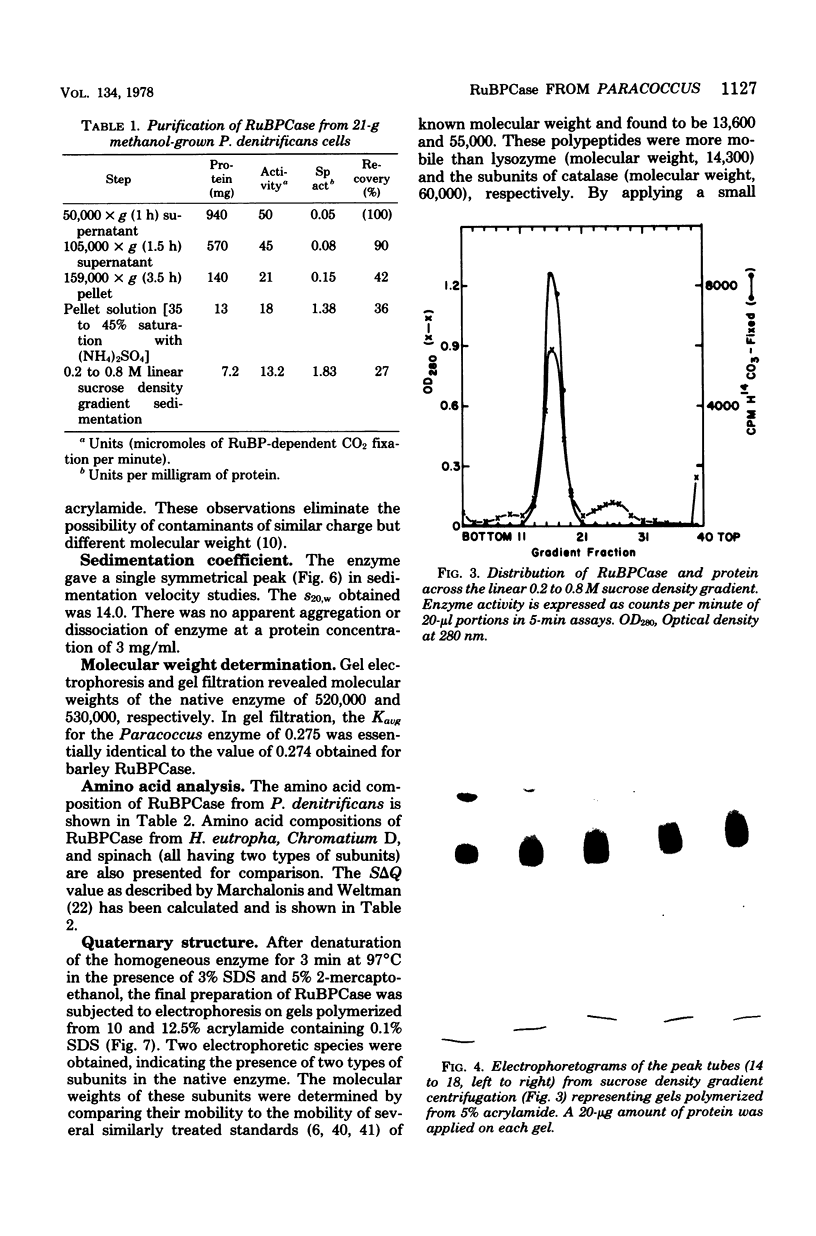
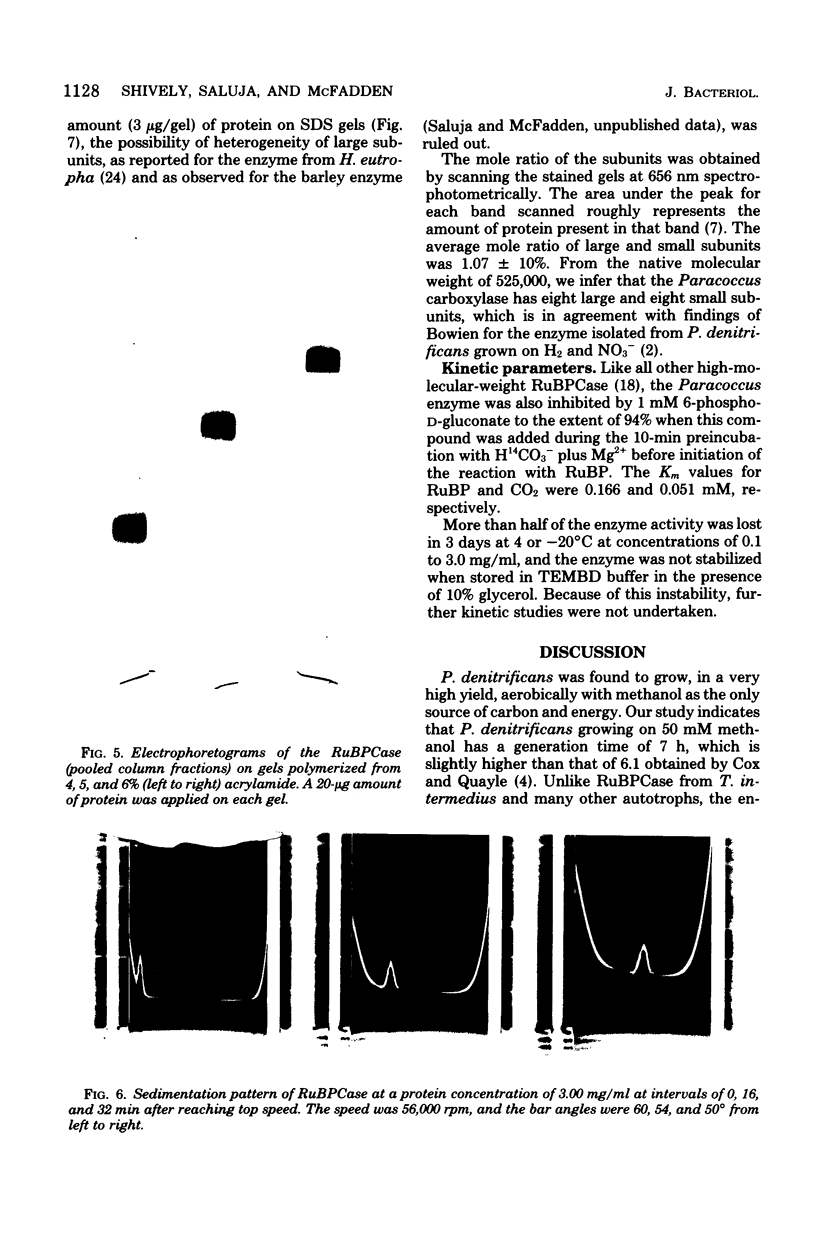
Paracoccus denitrificans grows on methanol as the sole source of energy and carbon, which it assimilates aerobically via the reductive pentose phosphate cycle. This gram-negative bacterium grew rapidly on 50 mM methanol (generation time, 7 h, 30 degrees C) in excellent yield (3 g of wet-packed cells per liter of culture). Electron microscopic studies indicated that the late-log-phase cells were coccoid, having a thick envelope surrounding a layer of more diffuse electron-dense material and a relatively electron-transparent core. Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in the 15,000 X g supernatant of fresh cells had specific activities (micromoles of CO2 fixed per minute per milligram of protein) of 0.026, 0.049, 0.085, 0.128, and 0.034 during the lag, early, mild-, and late log, and late stationary phases, respectively. The enzyme was purified 40-fold by pelleting at 159,000 X g, salting out, sedimentation into a 0.2 to 0.8 M linear sucrose gradient, and elution from a diethylaminoethyl-Sephadex column. The enzyme was homogeneous by the criteria of electrophoresis on polyacrylamide gels polymerized from several acrylamide concentrations and sedimentation behavior. The molecular weight of the native enzyme, as measured by gel electrophoresis and gel filtration, averaged 525,000. Sodium dodecyl sulfate dissociated the enzyme into two types of subunits with molecular weights of 55,000 and 13,600. The S20,w of the enzyme was 14.0 Km values for ribulose bisphosphate and CO2 were 0.166 and 0.051 mM, respectively, and the enzyme was inhibited to the extent of 94% by 1 mM 6-phosphogluconate.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. The gel-filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):595–606. doi: 10.1042/bj0960595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. K., Bassham J. A. Activation and inhibition of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by 6-phosphogluconate. Plant Physiol. 1973 Oct;52(4):373–379. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.4.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. B., Quayle J. R. The autotrophic growth of Micrococcus denitrificans on Methanol. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;150(3):569–571. doi: 10.1042/bj1500569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker A. K., Rueckert R. R. Observations on molecular weight determinations on polyacrylamide gel. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):5074–5080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui S., Tanaka A., Kawamoto S., Yasuhara S., Teranishi Y., Osumi M. Ultrastructure of methanol-utilizing yeast cells: appearance of microbodies in relation to high catalase activity. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):317–328. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.317-328.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldthwaite J. J., Bogorad L. A one-step method for the isolation and determination of leaf ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. Anal Biochem. 1971 May;41(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. The oxidation of ribonuclease with performic acid. J Biol Chem. 1956 Apr;219(2):611–621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KORNBERG H. L., COLLINS J. F., BIGLEY D. The influence of growth substrates on metabolic pathways in Micrococcus denitrificans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 25;39:9–24. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima N., Wildman S. G. A model of the subunit structure of fraction I protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Dec 24;41(6):1463–1468. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90551-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn G. D., McFadden B. A. Ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Hydrogenomonas eutropha and Hydrogenomonas facilis. II. Molecular weight, subunits, composition, and sulfhydryl groups. Biochemistry. 1969 Jun;8(6):2403–2408. doi: 10.1021/bi00834a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A. Autotrophic CO2 assimilation and the evolution of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Sep;37(3):289–319. doi: 10.1128/br.37.3.289-319.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Lord J. M., Rowe A., Dilks S. Composition, quaternary structure, and catalytic properties of D-ribulose-1, 5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Euglena gracilis. Eur J Biochem. 1975 May;54(1):195–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb04129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Tabita F. R. D-ribulose-1, 5-diphosphate carboxylase and the evolution of autotrophy. Biosystems. 1974 Oct;6(2):93–112. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(74)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Tabita F. R., Kuehn G. D. Ribulose-diphosphate carboxylase from the hydrogen bacteria and Rhodospirillum rubrum. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:461–472. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen J. M., Lane M. D. Spinach ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. I. Purification and properties of the enzyme. Biochemistry. 1966 Jul;5(7):2350–2357. doi: 10.1021/bi00871a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purohit K., McFadden B. A., Cohen A. L. Purification, quaternary structure, composition, and properties of D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Thiobacillus intermedius. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):505–515. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.505-515.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purohit K., McFadden B. A. Heterogeneity of large subunits of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carbosylase from Hydrogenomonas eutropha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 23;71(4):1220–1227. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90784-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purohit K., McFadden B. A. Quaternary structure and oxygenase activity of D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Hydrogenomonas eutropha. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):415–421. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.415-421.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutner A. C., Lane M. D. Nonidentical subunits of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Aug 23;28(4):531–537. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90346-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholes P. B., Smith L. The isolation and properties of the cytoplasmic membrane of Micrococcus denitrificans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 12;153(2):350–362. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(68)90080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. M. Inclusion bodies of prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):167–187. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.001123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. D-ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. II. Quaternary structure, composition, catalytic, and immunological properties. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3459–3464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. Molecular and catalytic properties of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from the photosynthetic extreme halophile Ectothiorhodospira halophila. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1271–1277. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1271-1277.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. One-step isolation of microbial ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. Arch Microbiol. 1974;99(3):231–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00696237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A., Pfennig N. D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum Tassajara. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 21;341(1):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90079-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. Regulation of ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by 6-phospho-D-gluconate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1153–1159. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90831-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A., Yasuhara S., Kawamoto S., Fukui S., Osumi M. Development of Microbodies in the yeast Kloeckera growing on methanol. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):919–927. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.919-927.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walther-Mauruschat A., Aragno M., Mayer F., Schlegel H. G. Micromorphology of Gram-negative hydrogen bacteria. II. Cell envelope, membranes, and cytoplasmic inclusions. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Aug 26;114(2):101–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00410770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dijken J. P., Veenhuis M., Kreger-van Rij N. J., Harder W. Microbodies in methanol-assimilating yeasts. Arch Microbiol. 1975;102(1):41–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00428343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]