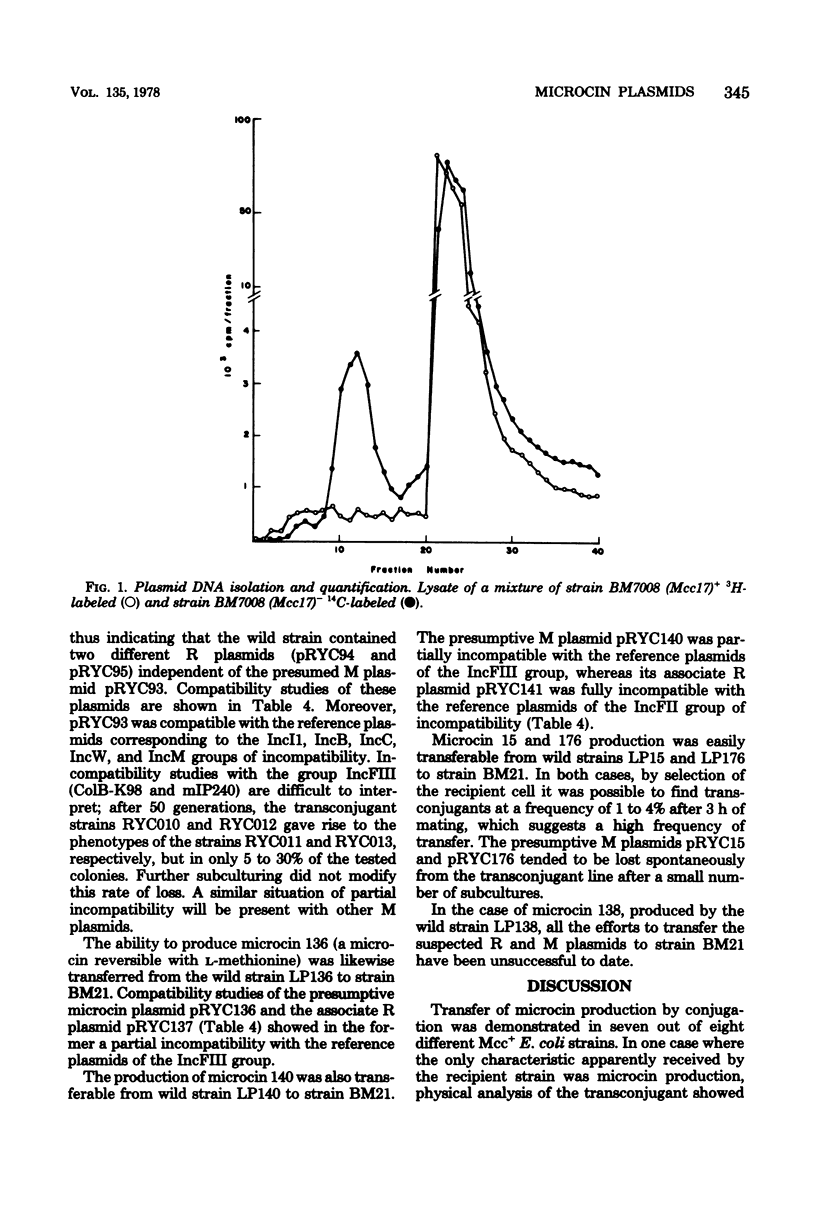
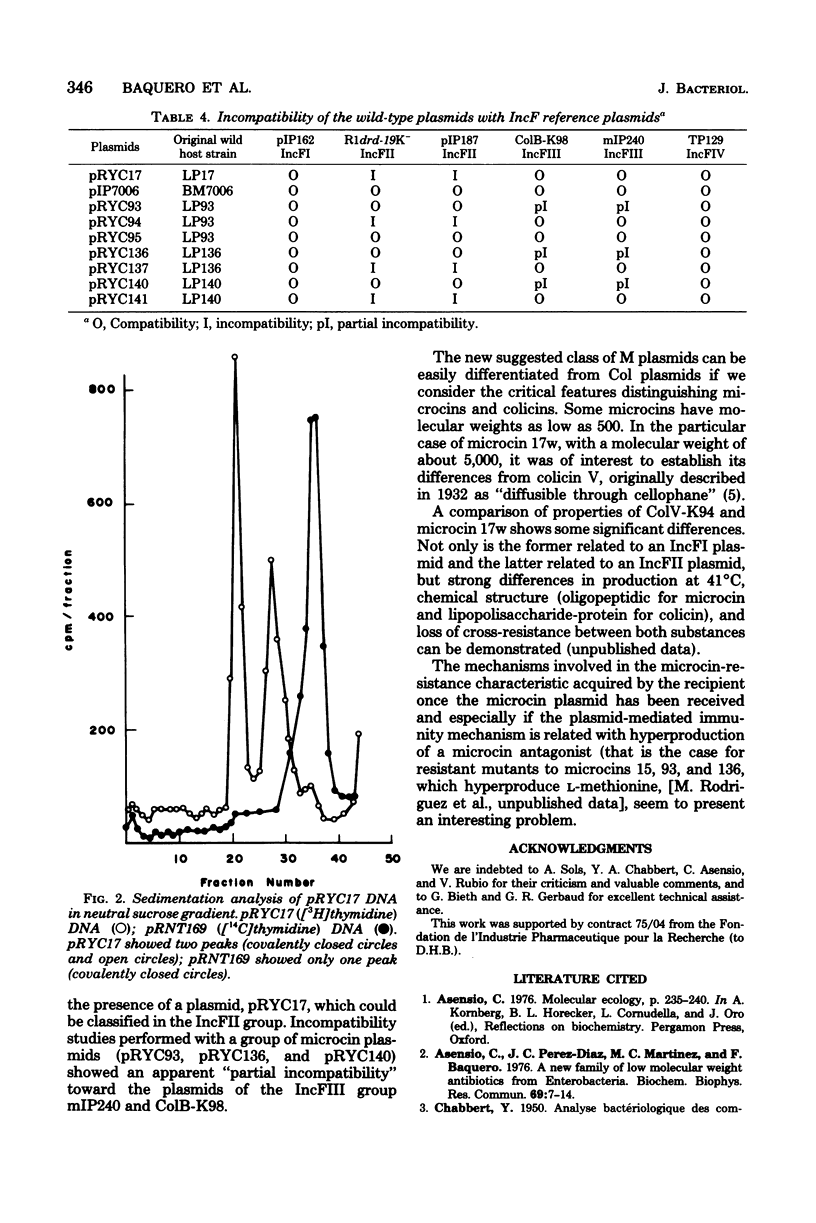
Abstract
Microcins are low-molecular-weight compounds produced and excreted by Enterobacteriaceae. They inhibit the growth of a wide spectrum of microorganisms. Microcin-synthesizing transconjugants were obtained in seven out of eight experiments of conjugational transfer between wild-type microcinogenic strains of Escherichia coli and E. coli strain BM21. The physical analysis of one of the transconjugant strains that has acquired the ability to produce microcin 17 showed the presence of extrachromosomal DNA as a plasmid (pRYC17) of molecular weight 36 X 10(6) (18.3-micron length), which is absent in the "microcincured" derivative strain. pRYC17 was incompatible with plasmids of the IncFII group. Other suspected plasmids containing the information for the synthesis of microcins have not been clearly classified. Strains producing microcins 93, 136, and 140 show a partial incompatibility with IncFIII group of plasmids.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asensio C., Pérez-Díaz J. C. A new family of low molecular weight antibiotics from enterobacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 8;69(1):7–14. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(76)80264-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDERICQ P. COLICINES ET AUTRES BACTERIOCINES. Ergeb Mikrobiol Immunitatsforsch Exp Ther. 1963;37:114–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingram L. C., Richmond M. H., Sykes R. B. Molecular characterization of the R factors implicated in the carbenicillin resistance of a sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from burns. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Feb;3(2):279–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.2.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Bouanchaud D. The problems of drug-resistant pathogenic bacteria. Extrachromosomal nature of drug resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1971 Jun 11;182:279–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb30664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Clowes R. C., Cohen S. N., Curtiss R., 3rd, Datta N., Falkow S. Uniform nomenclature for bacterial plasmids: a proposal. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):168–189. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.168-189.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE T., FUKASAWA T. Episome-mediated transfer of drug resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. I. Transfer of resistance factors by conjugation. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81:669–678. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.669-678.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



