Abstract
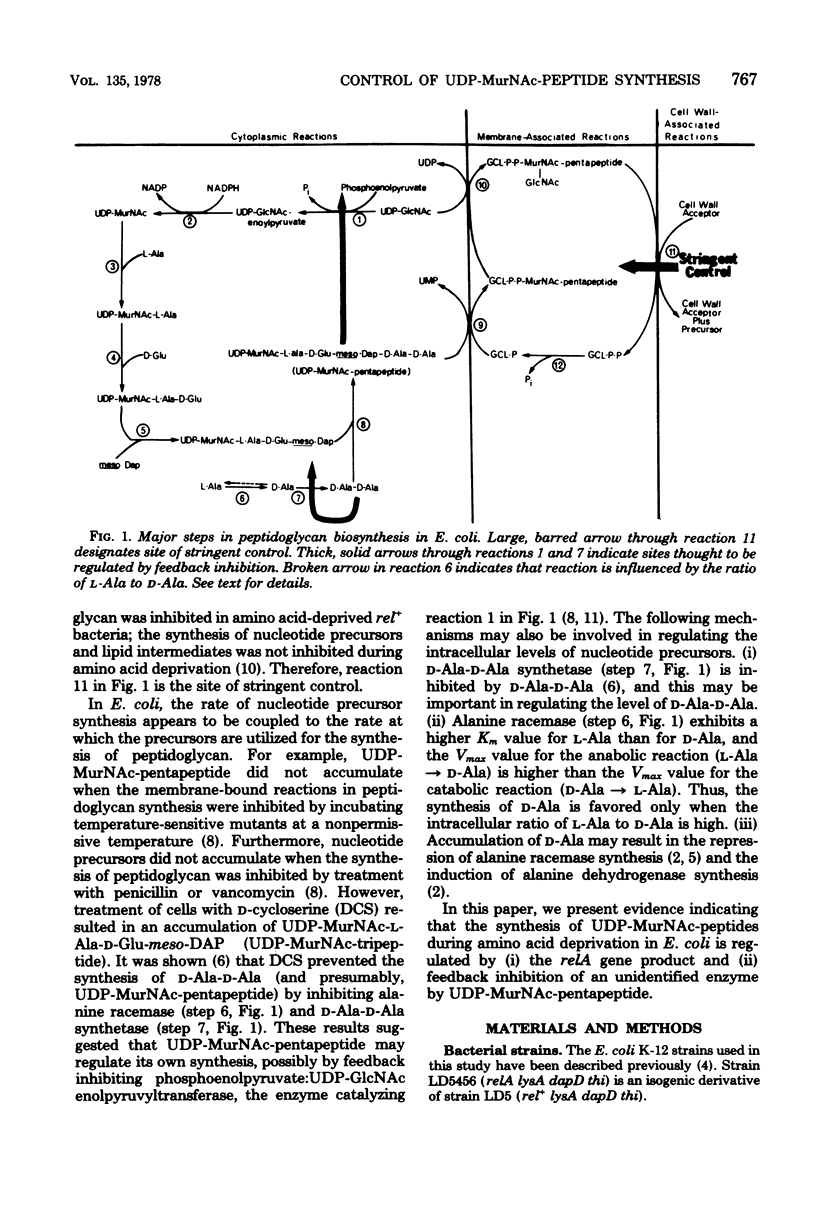
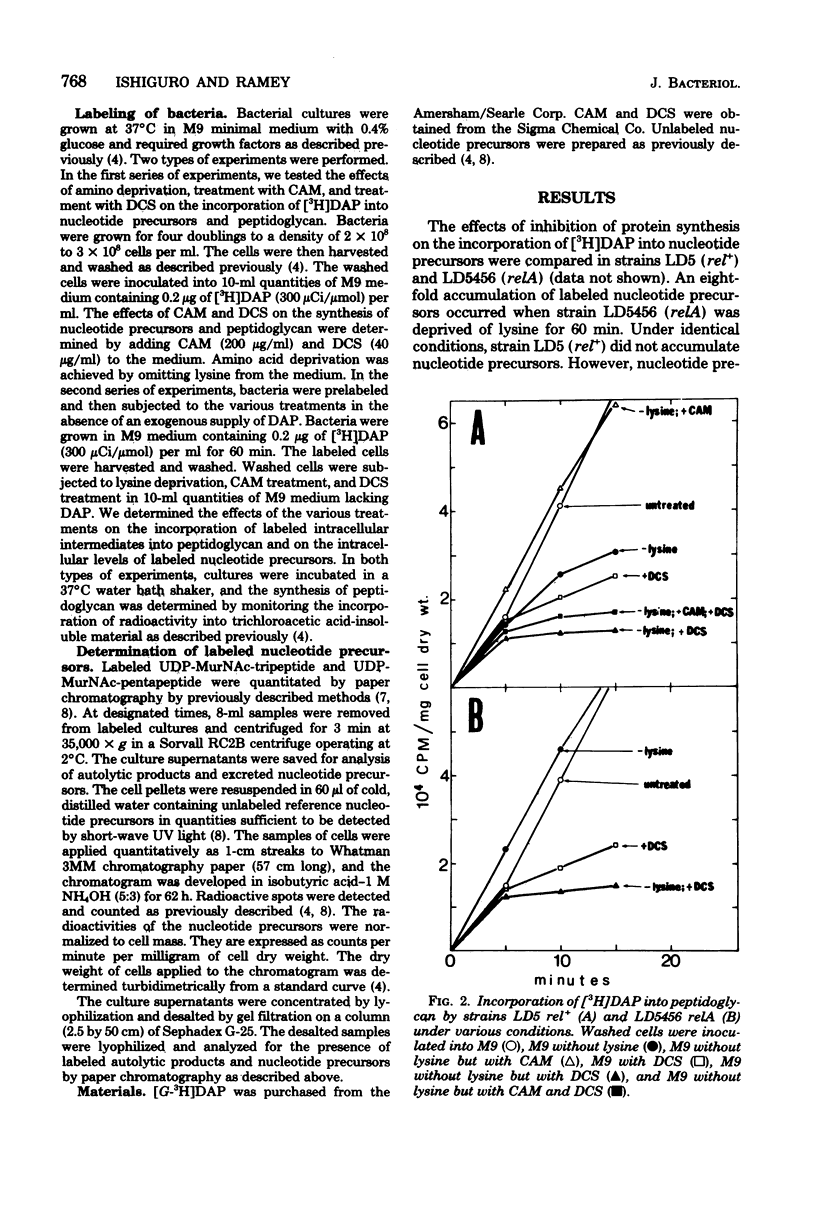
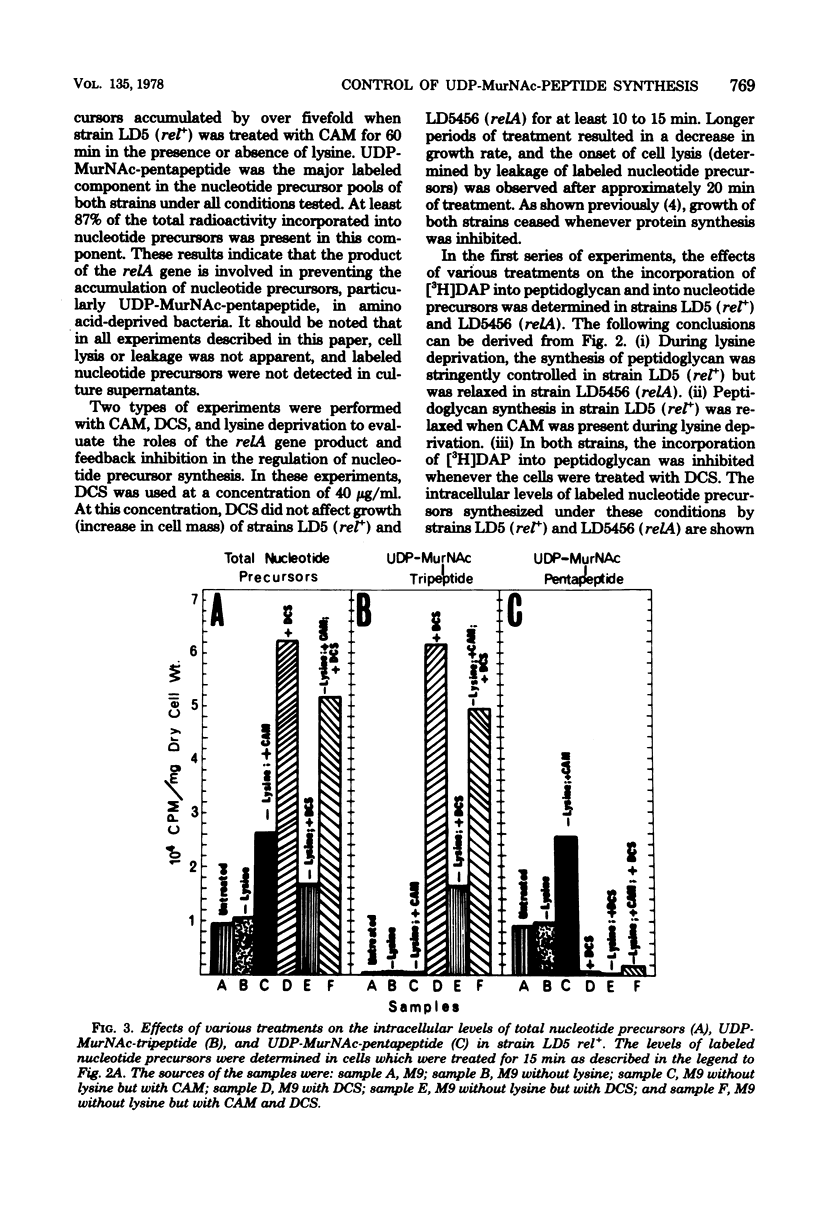
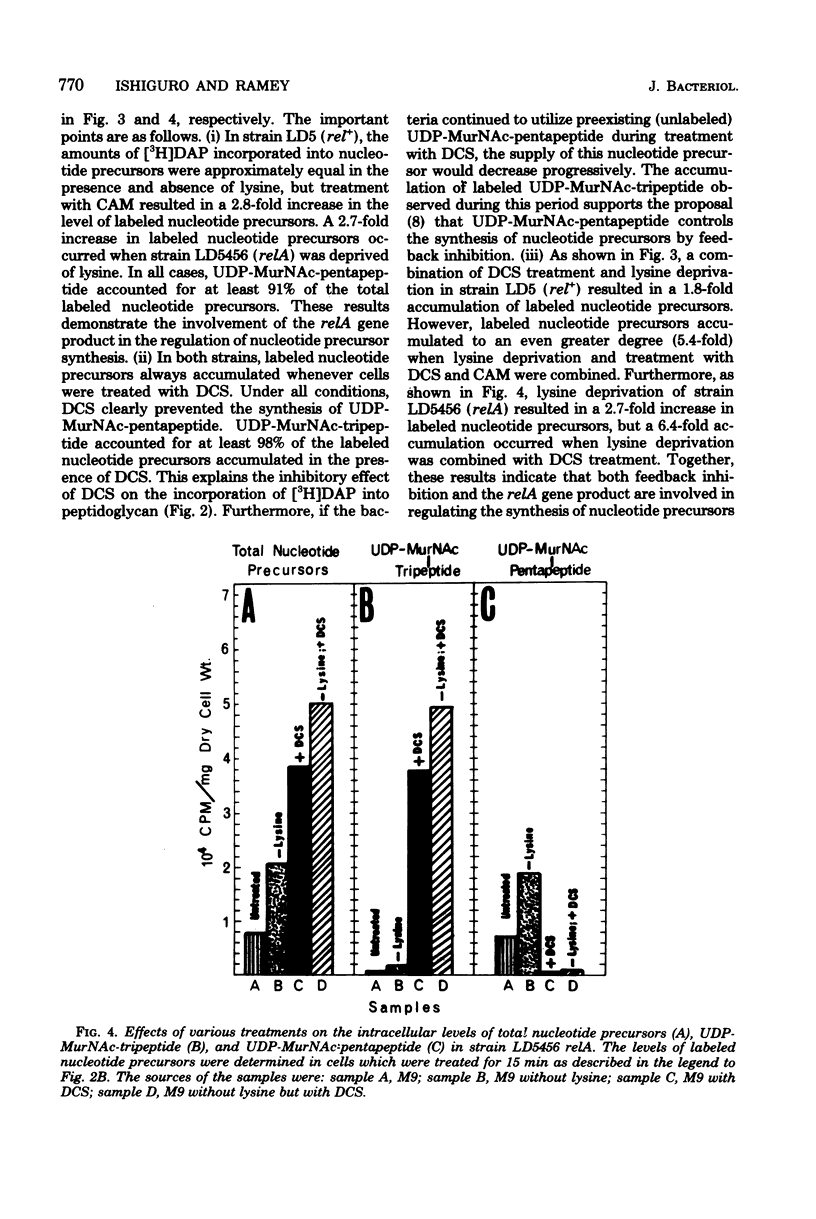
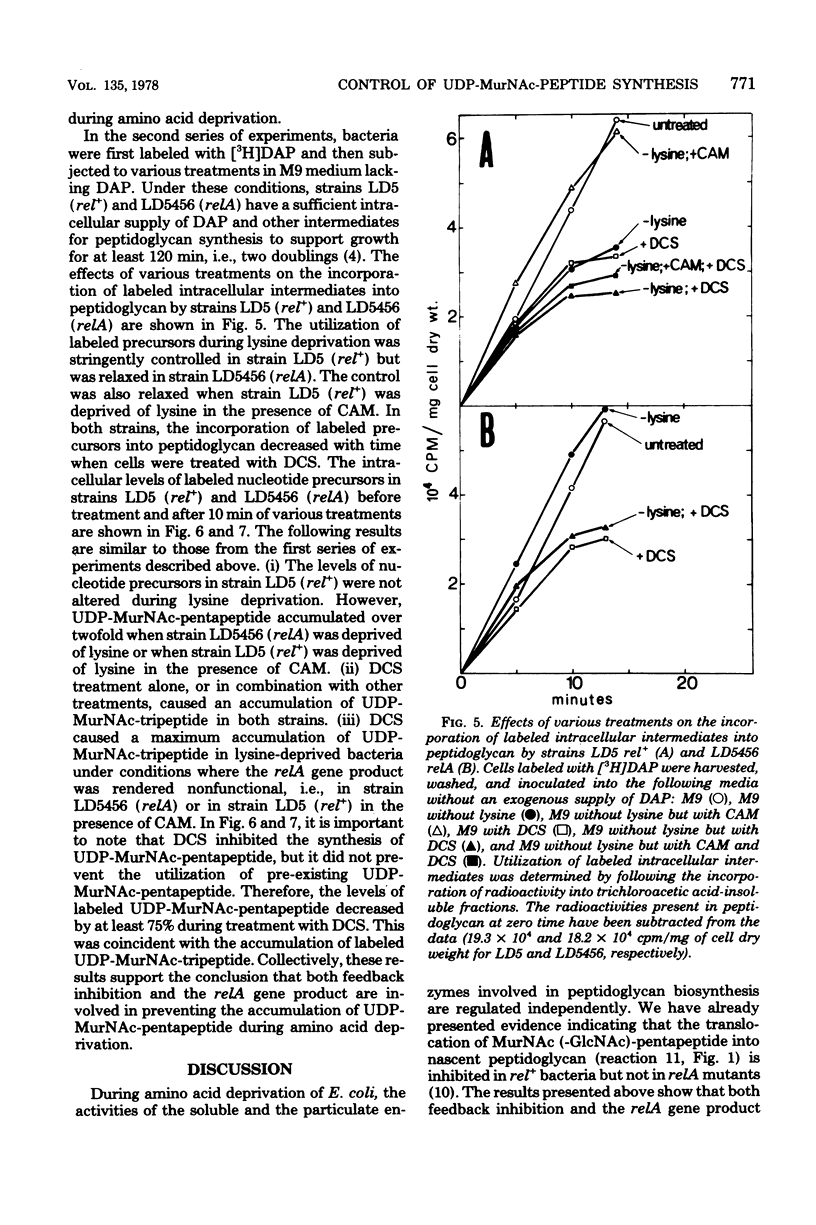
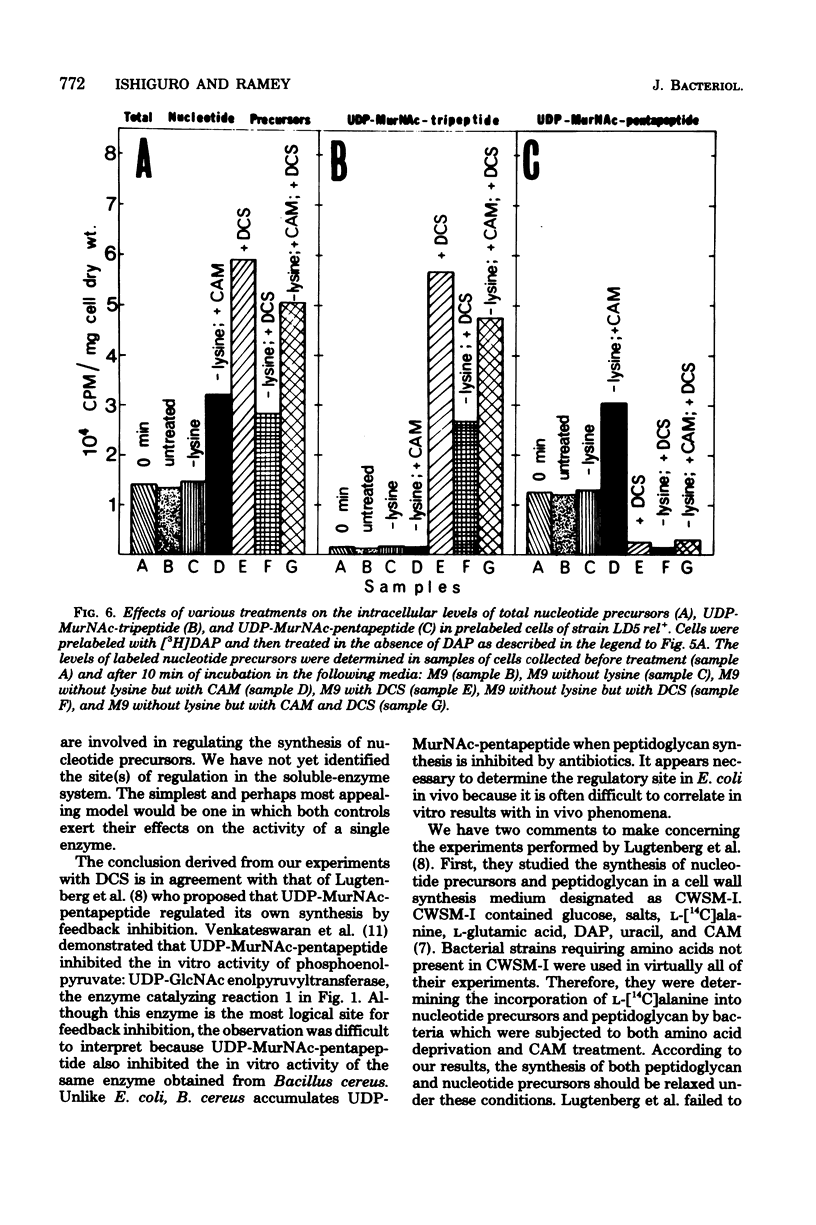
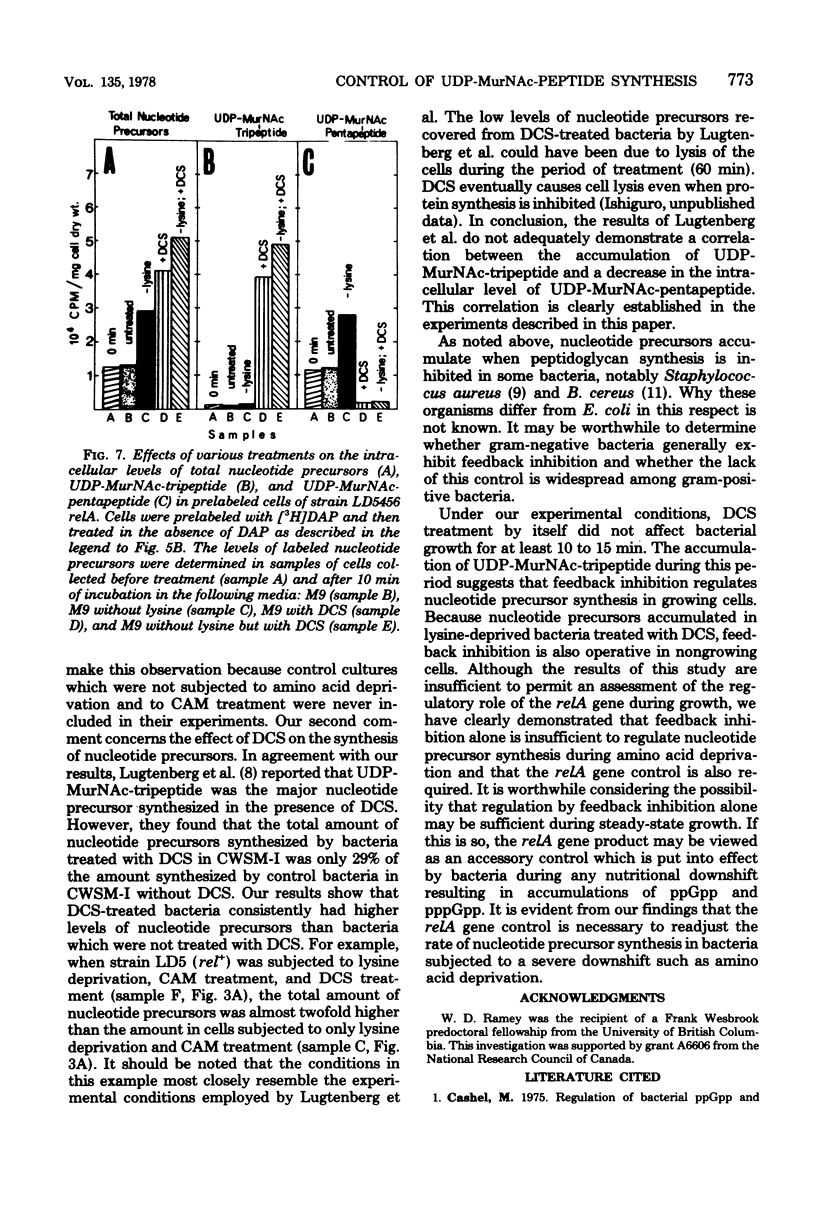
The regulation of uridine diphosphate-N-acetylmuramyl-peptide (UDP-MurNAc-peptide) synthesis was studied by labeling Escherichia coli strains auxotrophic for lysine and diaminopimelate with [3H]diaminopimelate for 15 min under various conditions. The amounts of [3H]diaminopimelate incorporated into UDP-MurNAc-tripeptide and -pentapeptide by a stringent (rel+) strain were the same in the presence or absence of lysine. Chloramphenicol-treated rel+ cells showed a 2.8-fold increase in labeled UDP-MurNAc-pentapeptide. An isogenic relaxed (relA) strain deprived of lysine showed a 2.7-fold increase in UDP-MurNAc-pentapeptide. Thus, UDP-MurNAc-pentapeptide synthesis is regulated by the relA gene. D-Cycloserine treatment of rel+ and relA strains caused a depletion of intracellular UDP-MurNAc-pentapeptide. Labeled UDP-MurNAc-tripeptide accumulated in D-cycloserine-treated cells of the rel+ and relA strains, suggesting that UDP-MurNAc-pentapeptide is a feedback inhibitor of UDP-MurNAc-peptide synthesis. In lysine-deprived cells, D-cycloserine treatment caused 41- and 71-fold accumulations of UDP-MurNAc-tripeptide in rel+ and relA strains, respectively. A 124-fold increase in UDP-MurNAc-tripeptide occurred in lysine-deprived rel+ cells treated with both chloramphenicol and D-cycloserine. These results indicate that both the relA gene product and feedback inhibition are involved in regulating UDP-MurNAc-peptide synthesis during amino acid deprivation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cashel M. Regulation of bacterial ppGpp and pppGpp. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:301–318. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin F. C., Venables W. A. Biochemical, genetic, and regulatory studies of alanine catabolism in Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Dec 8;149(2):229–237. doi: 10.1007/BF00332894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishiguro E. E., Ramey W. D. Stringent control of peptidoglycan biosynthesis in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1119–1126. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1119-1126.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M. P., Neuhaus F. C. Factors affecting the level of alanine racemase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Mar;109(3):1156–1161. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.3.1156-1161.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg E. J., De Haas-Menger L., Ruyters W. H. Murein synthesis and identification of cell wall precursors of temperature-sensitive lysis mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jan;109(1):326–335. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.1.326-335.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg E. J. Studies on Escherichia coli enzymes involved in the synthesis of uridine diphosphate-N-acetyl-muramyl-pentapeptide. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):26–34. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.26-34.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg E. J., de Haan P. G. A simple method for following the fate of alanine-containing components in murein synthesis in Escherichia coli. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1971;37(4):537–552. doi: 10.1007/BF02218524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramey W. D., Ishiguro E. E. Site of inhibition of peptidoglycan biosynthesis during the stringent response in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):71–77. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.71-77.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkateswaran P. S., Lugtenberg E. J., Wu H. C. Inhibition of phosphoenolpyruvate:uridine diphosphate N-acetylglucosamine enolpyruvyltransferase by uridine diphosphate N-acetylmuramyl peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 15;293(2):570–574. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90367-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



