Abstract
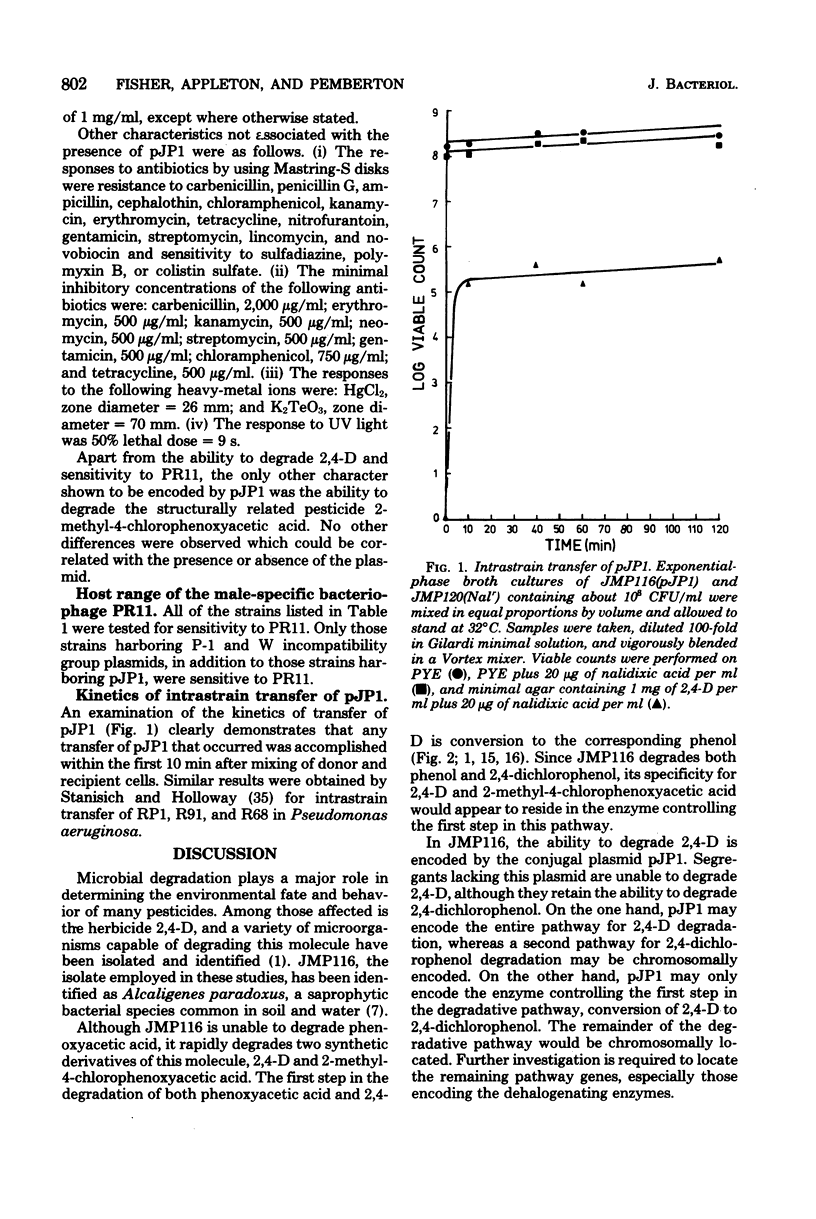
A strain of Alcaligenes paradoxus, unable to degrade phenoxyacetic acid, was shown to degrade two synthetic derivatives of this molecule, the herbicides 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid. The ability to degrade these pesticides is encoded by a 58-megadalton conjugal plasmid, pJP1.
Full text
PDF



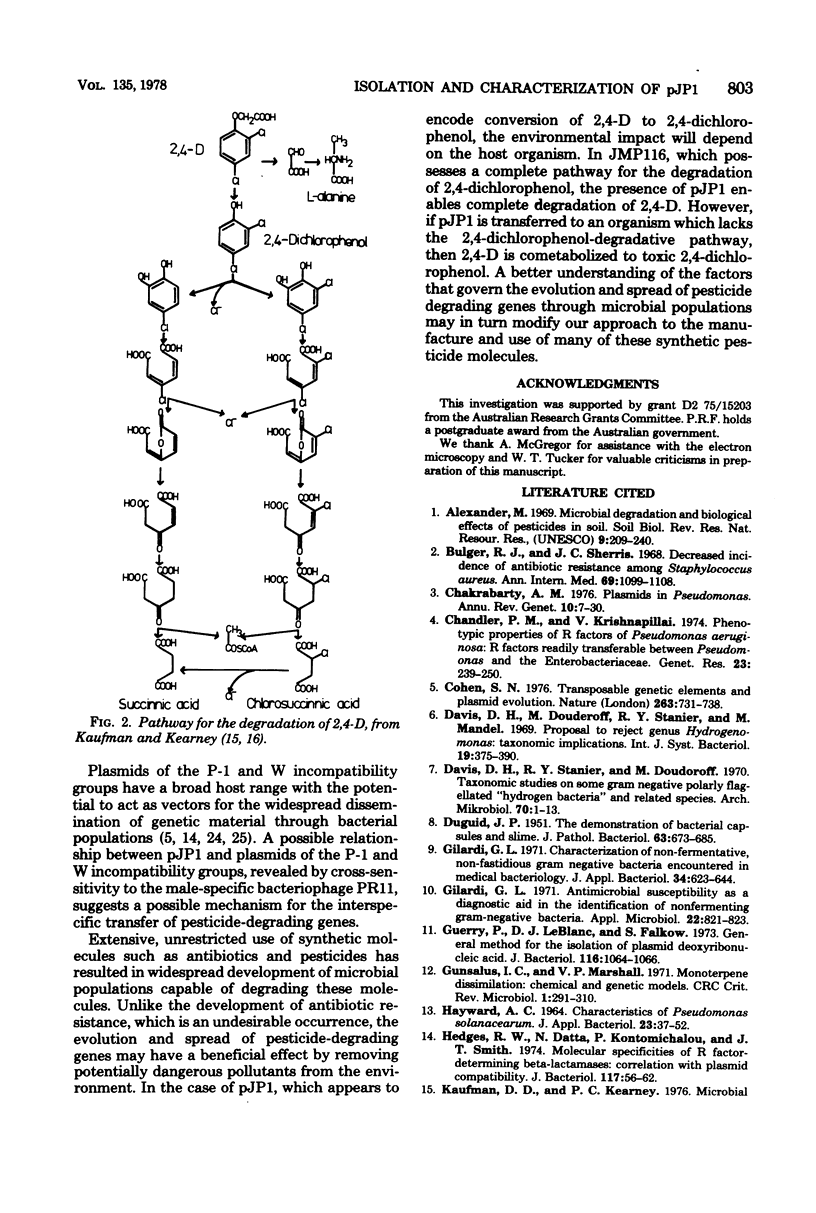

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bulger R. J., Sherris J. C. Decreased incidence of antibiotic resistance among Staphylococcus aureus. A study in a university hospital over a 9-year period. Ann Intern Med. 1968 Dec;69(6):1099–1108. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-69-6-1099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cain W. S. Bilateral interaction in olfaction. Nature. 1977 Jul 7;268(5615):50–52. doi: 10.1038/268050a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M. Plasmids in Pseudomonas. Annu Rev Genet. 1976;10:7–30. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.10.120176.000255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler P. M., Krishnapillai V. Phenotypic properties of R factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: R factors readily transferable between Pseudomonas and the Enterobacteriaceae. Genet Res. 1974 Jun;23(3):239–250. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300014890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N. Transposable genetic elements and plasmid evolution. Nature. 1976 Oct 28;263(5580):731–738. doi: 10.1038/263731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUGUID J. P. The demonstration of bacterial capsules and slime. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1951 Oct;63(4):673–685. doi: 10.1002/path.1700630413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis D. H., Stanier R. Y., Doudoroff M., Mandel M. Taxonomic studies on some gram negative polarly flagellated "hydrogen bacteria" and related species. Arch Mikrobiol. 1970;70(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00691056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi G. L. Antimicrobial susceptibility as a diagnostic aid in the identification of nonfermenting gram-negative bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Nov;22(5):821–823. doi: 10.1128/am.22.5.821-823.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi G. L. Characterization of nonfermentative nonfastidious gram negative bacteria encountered in medical bacteriology. J Appl Bacteriol. 1971 Sep;34(3):623–644. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1971.tb02326.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., LeBlanc D. J., Falkow S. General method for the isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1064-1066.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges R. W., Datta N., Kontomichalou P., Smith J. T. Molecular specificities of R factor-determined beta-lactamases: correlation with plasmid compatibility. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):56–62. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.56-62.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. Molecular weights of coliphages and coliphage DNA. 3. Contour length and molecular weight of DNA from bacteriophages T4, T5 and T7, and from bovine papilloma virus. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 28;54(3):557–565. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos M. A. Indicator media for microorganisms degrading chlorinated pesticides. Can J Microbiol. 1975 Jan;21(1):104–107. doi: 10.1139/m75-016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. A., Sanchez D., Elwell L. P., Falkow S. Simple agarose gel electrophoretic method for the identification and characterization of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1529-1537.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. V., Pemberton J. M., Richards K. E. F116, D3 and G101: temperate bacteriophages of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Virology. 1974 Jun;59(2):566–569. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90466-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P., Clowes R. C., Cohen S. N., Curtiss R., 3rd, Datta N., Falkow S. Uniform nomenclature for bacterial plasmids: a proposal. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):168–189. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.168-189.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P. Extrachromosomal inheritance in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Jun;33(2):210–263. doi: 10.1128/br.33.2.210-263.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H., Shipley P. L. RP1 properties and fertility inhibition among P, N, W, and X incompatibility group plasmids. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):28–35. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.28-35.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H., Shipley P. Host range and properties of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa R factor R1822. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):772–780. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.772-780.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palchaudhuri S., Chakrabarty A. Isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid from Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):410–416. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.410-416.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton J. M., Clark A. J. Detection and characterization of plasmids in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):424–433. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.424-433.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton J. M. F116: a DNA bacteriophage specific for the pili of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAO. Virology. 1973 Oct;55(2):558–560. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90203-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton J. M., Holloway B. W. A new sex factor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genet Res. 1973 Jun;21(3):263–272. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300013458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton J. M. Size of the chromosome of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):748–752. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.748-752.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARR M. P., STEPHENS W. L. PIGMENTATION AND TAXONOMY OF THE GENUS XANTHOMONAS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Feb;87:293–302. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.2.293-302.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanier R. Y., Palleroni N. J., Doudoroff M. The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol. 1966 May;43(2):159–271. doi: 10.1099/00221287-43-2-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanisich V. A., Holloway B. W. Chromosome transfer in Pseudomonas aeruginosa mediated by R factors. Genet Res. 1971 Apr;17(2):169–172. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300012179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanisich V. A. The properties and host range of male-specific bacteriophages of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Oct;84(2):332–342. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-2-332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers A. O., Jacoby G. A. Plasmid-determined resistance to tellurium compounds. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):276–281. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.276-281.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. C., Fisher H. W. Electron microscopy of tobacco mosaic virus under conditions of minimal beam exposure. J Mol Biol. 1970 Aug 28;52(1):121–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



