Abstract
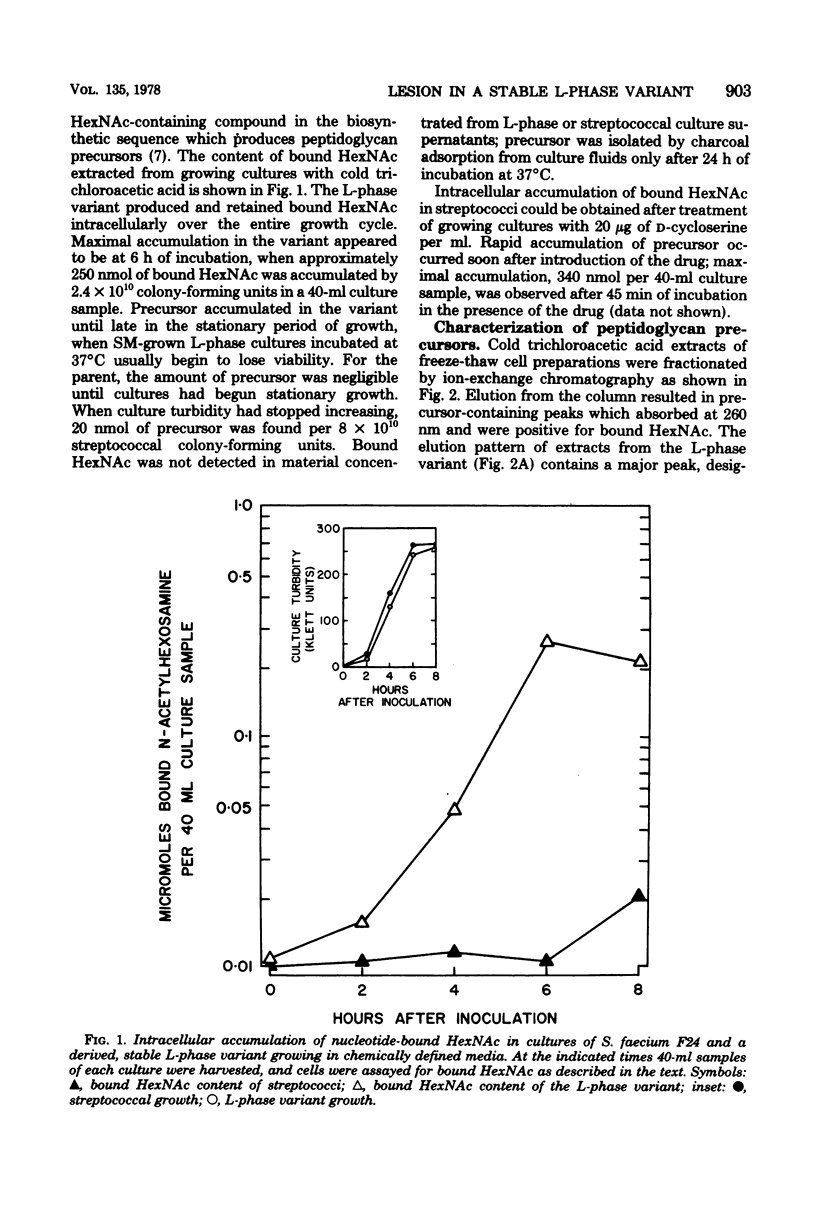
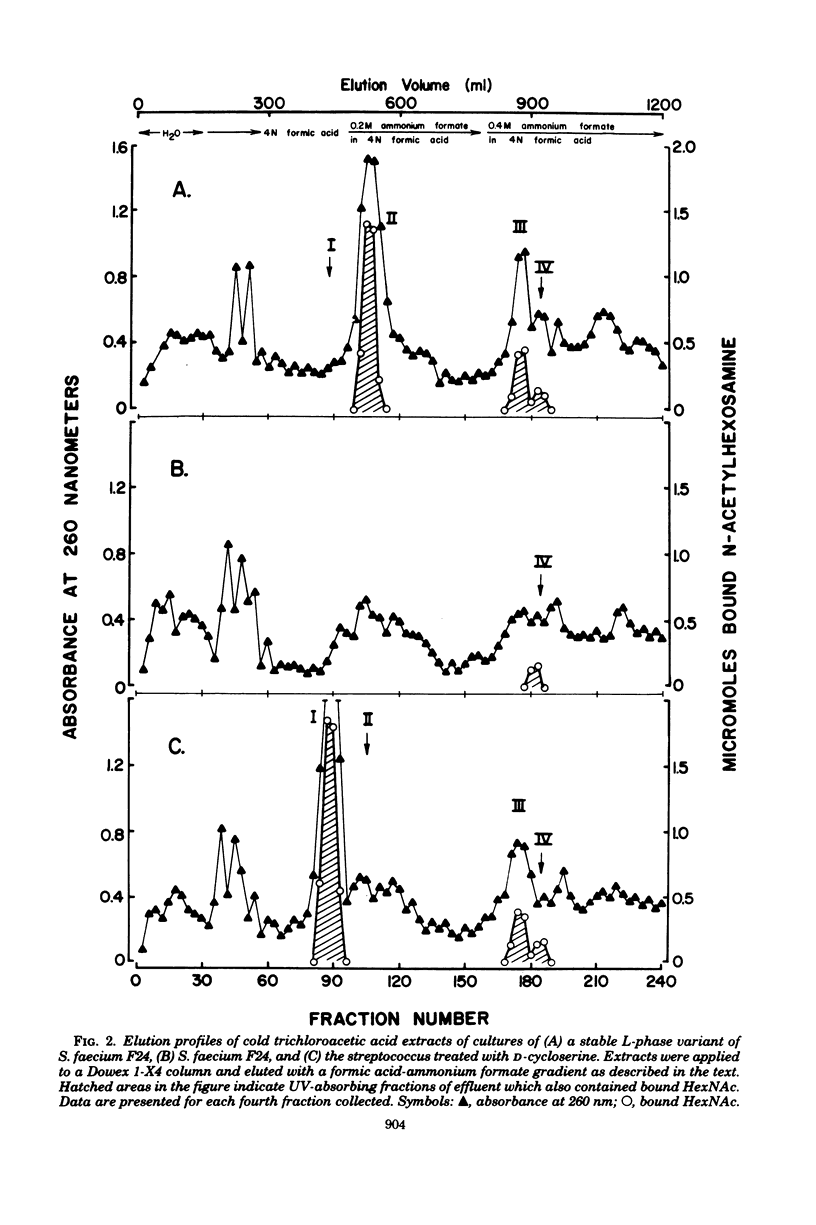
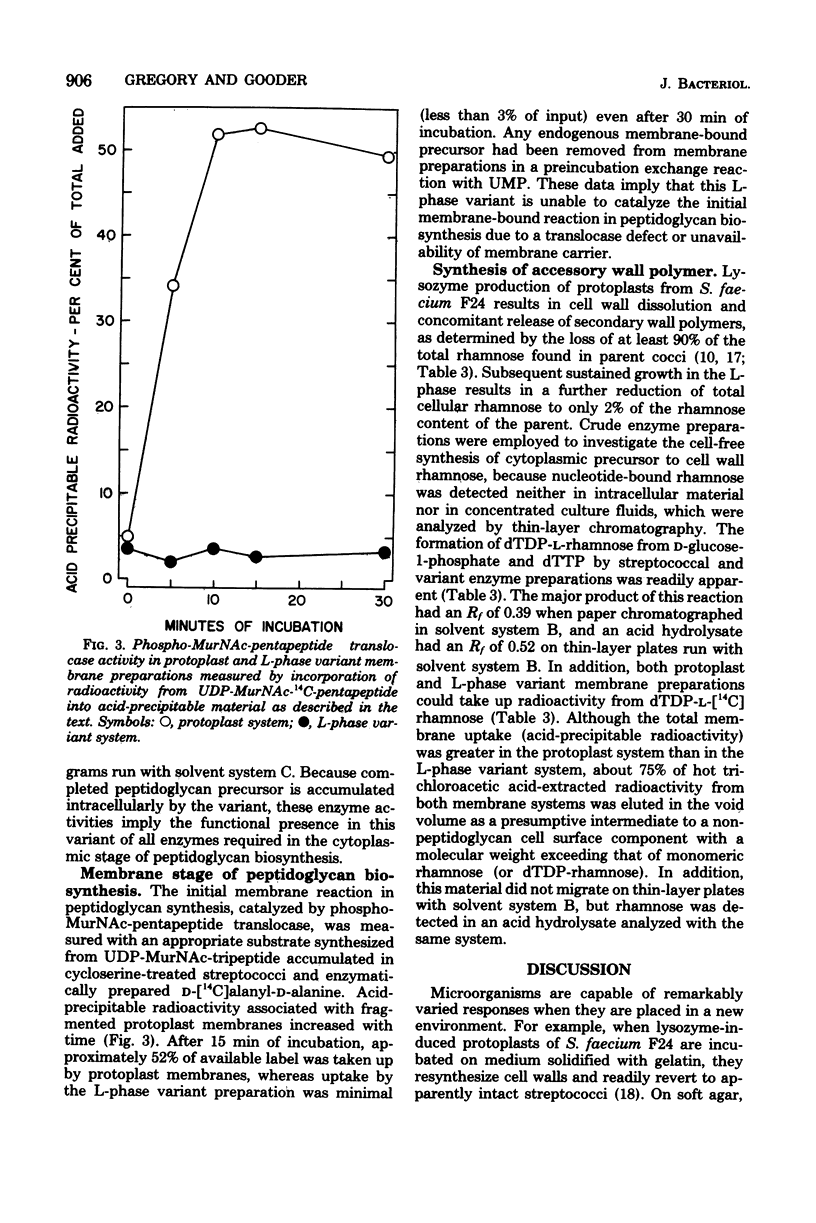
Cultures of a stable L-phase variant of Streptococcus faecium F24 produced and retained peptidoglycan precursors intracellularly over the entire growth cycle in a chemically defined medium. The identity of the most abundant precursor, UDP N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamyl-L-lysyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine (UDP-MurNAc-pentapeptide), was confirmed by demonstrating in vitro the presence of enzymes required for the cytoplasmic stage of peptidoglycan biosynthesis. The initial membrane-bound reaction in peptidoglycan biosynthesis involving phospho-MurNAc-pentapeptide translocase and undecaprenyl-phosphate membrane carrier was catalyzed by protoplast membrane preparations but not by L-phase membrane preparations. However, both protoplast and L-phase membranes incorporated radioactivity from dTDP-L-[14C]rhamnose, the presumed precursor to a non-peptidoglycan cell surface component, into high-molecular-weight material. dTDP-L-rhamnose did not accumulate in growing cultures but was synthesized from D-glucose-1-phosphate and dTTP by cell-free extracts of the streptococcus and L-phase variant. Neither rhamnose- nor muramic acid-containing compounds were detected in culture fluids. It is suggested that continued inhibition of cell wall biosynthesis in this stable L-phase variant is the result of a defect expressed at the membrane stage of peptidoglycan biosynthesis specifically involving the translocation step.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chatterjee A. N., Ward J. B., Perkins H. R. Synthesis of mucopeptide by L-form membranes. Nature. 1967 Jun 24;214(5095):1311–1314. doi: 10.1038/2141311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCastro-Costa M. R., Landman O. E. Inhibitory protein controls the reversion of protoplasts and L forms of Bacillus subtilis to the walled state. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):678–689. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.678-689.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J., Panos C. STREPTOCOCCAL L FORMS V. : Acid-Soluble Nucleotides of a Group A Streptococcus and Derived L Form. J Bacteriol. 1962 Dec;84(6):1202–1208. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.6.1202-1208.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott T. S., Ward J. B., Rogers H. J. Formation of cell wall polymers by reverting protoplasts of Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):623–632. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.623-632.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor M. Cell wall mucopeptide synthesis during the growth of staphylococcal L forms. Naturwissenschaften. 1966 Jun;53(11):282–283. doi: 10.1007/BF00621664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilpin R. W., Young F. E., Chatterjee A. N. Characterization of a stable L-form of Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):486–499. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.486-499.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory W. W., Gooder H. Identical nutritional requirements of Streptococcus faecium f24 and a derived stable L-phase variant. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):1151–1153. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.1151-1153.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURLBERT R. B., SCHMITZ H., BRUMM A. F., POTTER V. R. Nucleotide metabolism. II. Chromatographic separation of acid-soluble nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1954 Jul;209(1):23–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammes W. P., Neuhaus F. C. On the specificity of phospho-N-acetylmuramyl-pentapeptide translocase. The peptide subunit of uridine diphosphate-N-actylmuramyl-pentapeptide. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3140–3150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne D., Hakenbeck R., Tomasz A. Secretion of lipids induced by inhibition of peptidoglycan synthesis in streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):704–717. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.704-717.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito E., Strominger J. L. Enzymatic synthesis of the peptide in bacterial uridine nucleotides. VII. Comparative biochemistry. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3131–3136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J. R., Gooder H. Induction of enterococcal L-forms by the action of lysozyme. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):686–691. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.686-691.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J. R., Gooder H. Reversion to the streptococcal state of enterococcal protoplasts, spheroplasts, and L-forms. J Bacteriol. 1970 Sep;103(3):692–696. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.3.692-696.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J., ST CLAIR J. Protoplasts and L-type growth of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1958 Feb;75(2):143–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.2.143-160.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch J. L., Neuhaus F. C. On the mechanism of action of the antibiotic O-carbamyld-serine in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1966 Jan;91(1):449–460. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.1.449-460.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELO A., GLASER L. THE NUCLEOTIDE SPECIFICITY AND FEEDBACK CONTROL OF THYMIDINE DIPHOSPHATE D-GLUCOSE PYROPHOSPHORYLASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:398–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEUHAUS F. C., STRUVE W. G. ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF ANALOGS OF THE CELL-WALL PRECURSOR. I. KINETICS AND SPECIFICITY OF URIDINE DIPHOSPHO-N-ACETYLMURAMYL-L-ALANYL-D-GLUTAMYL-L-LYSINE:D-ALANYL-D-ALANINE LIGASE (ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE) FROM STREPTOCOCCUS FAECALIS R. Biochemistry. 1965 Jan;4:120–131. doi: 10.1021/bi00877a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandhi P. N., Panos C. Biosynthesis of D-alanyl-D-alanine from L-alanine by extracts of a stabilized L-form from Streptococcus pyogenes. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Aug;71(3):487–494. doi: 10.1099/00221287-71-3-487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panos C., Cohen M. Cell wall inhibition in a stable streptococcal L-form. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Mar 28;117(1):98–106. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90156-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISSIG J. L., STORMINGER J. L., LELOIR L. F. A modified colorimetric method for the estimation of N-acetylamino sugars. J Biol Chem. 1955 Dec;217(2):959–966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reusch V. M., Panos C. Defective synthesis of lipid intermediates for peptidoglycan formation in a stabilized L-form of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):300–311. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.300-311.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal R. S., Jungkind D., Daneo-Moore L., Shockman G. D. Evidence for the synthesis of soluble peptidoglycan fragments by protoplasts of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):398–409. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.398-409.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal R. S., Shockman G. D. Characterization of the presumed peptide cross-links in the soluble peptidoglycan fragments synthesized by protoplasts of Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):410–418. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.410-418.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struve W. G., Sinha R. K., Neuhaus F. C. On the initial stage in peptidoglycan synthesis. Phospho-N-acetylmuramyl-pentapeptide translocase (uridine monophosphate). Biochemistry. 1966 Jan;5(1):82–93. doi: 10.1021/bi00865a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. B. Peptidoglycan synthesis in L-phase variants of Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):668–678. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.668-678.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyrick P. B., McConnell M., Rogers H. J. Genetic transfer of the stable L form state to intact bacterial cells. Nature. 1973 Aug 24;244(5417):505–507. doi: 10.1038/244505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



