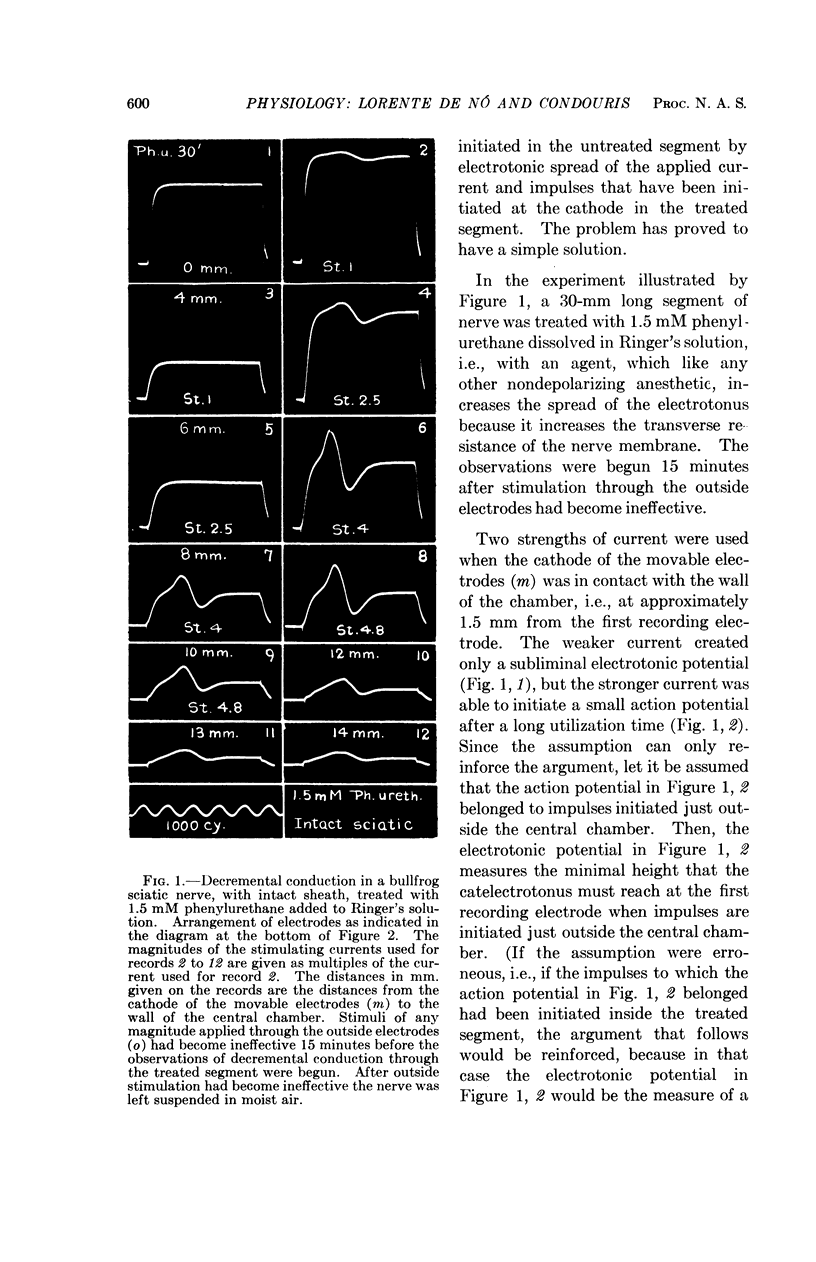
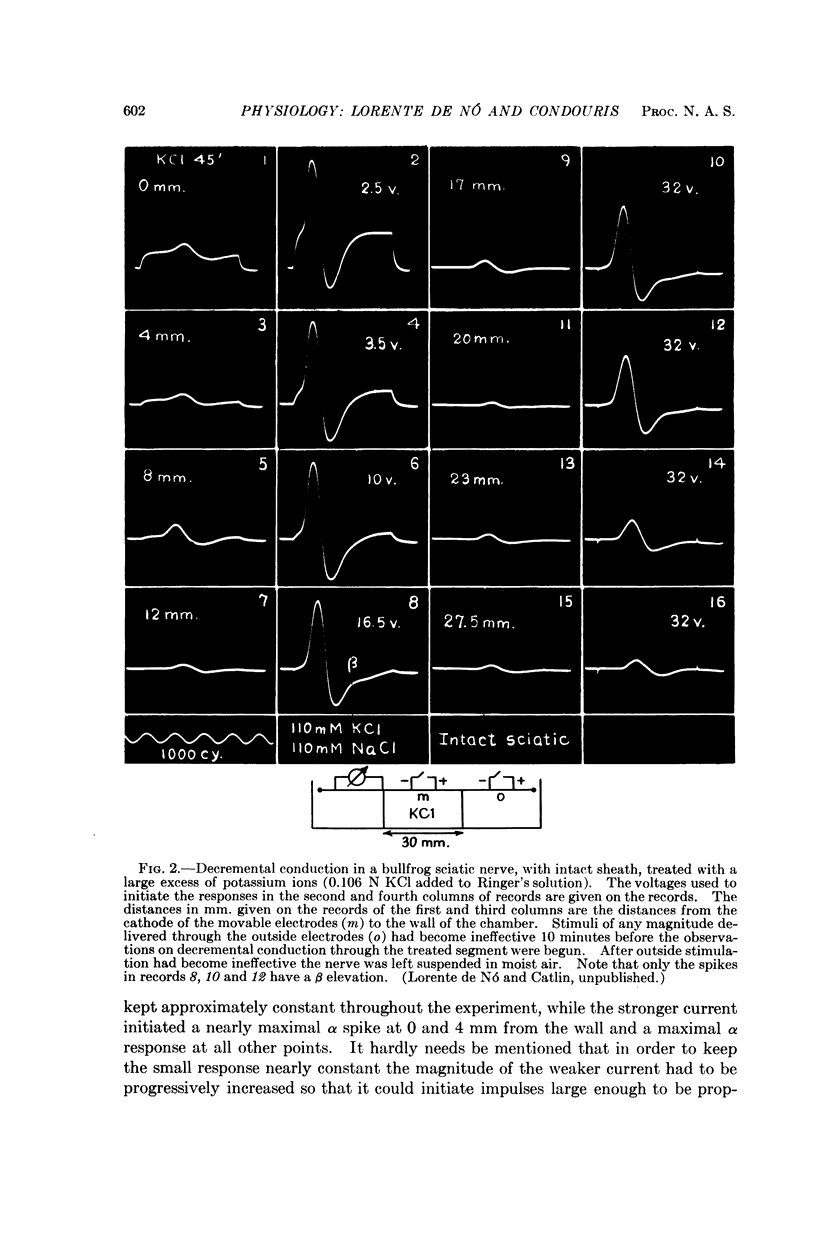
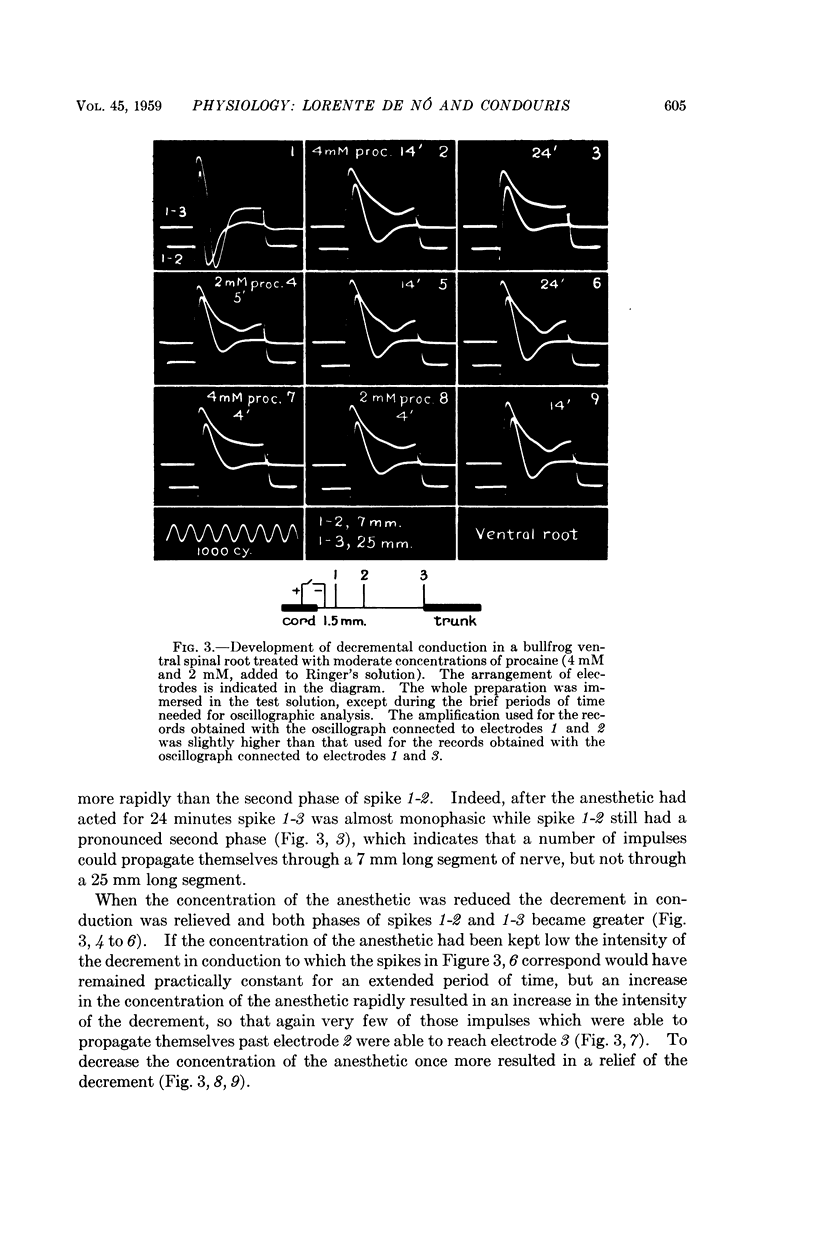
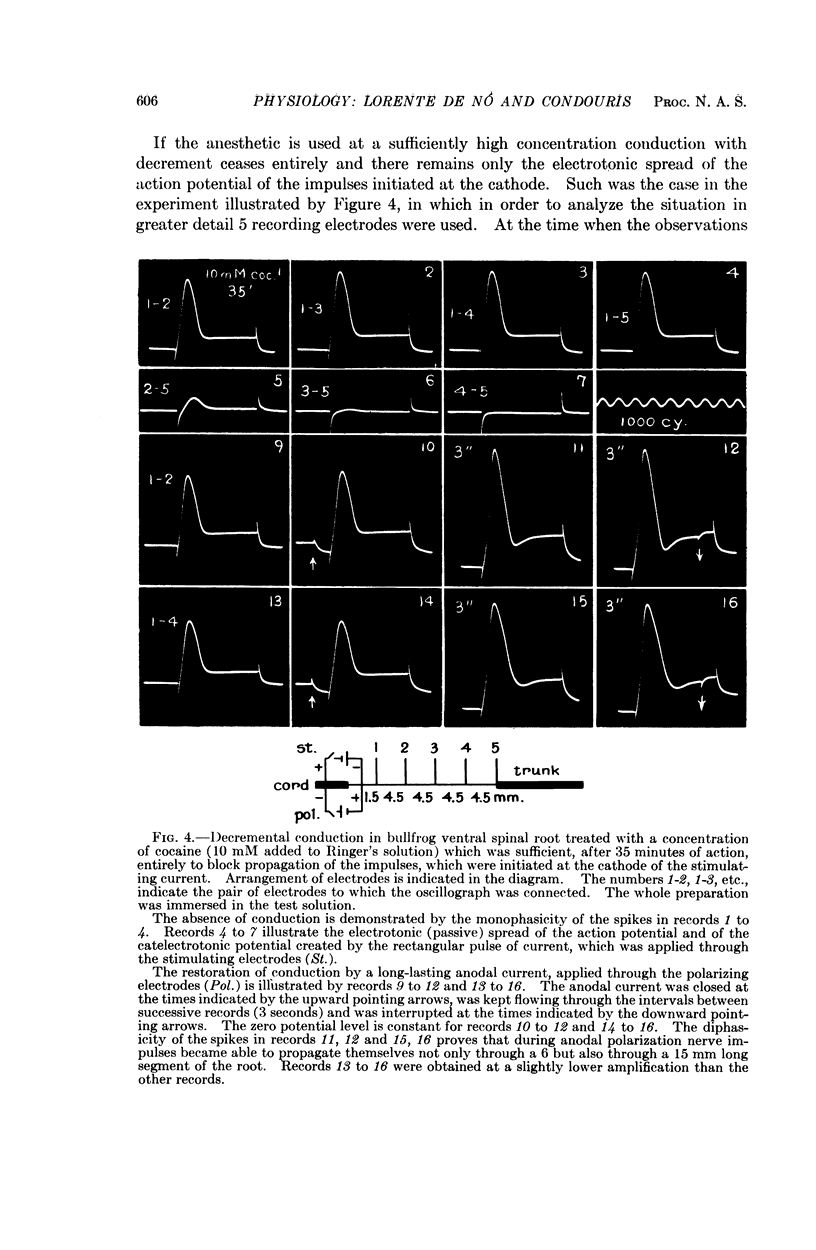
Full text
PDF

















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALTAMIRANO M., COATES C. W., GRUNDFEST H. Mechanisms of direct and neural excitability in electroplaques of electric eel. J Gen Physiol. 1955 Jan 20;38(3):319–360. doi: 10.1085/jgp.38.3.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian E. D. On the conduction of subnormal disturbances in normal nerve. J Physiol. 1912 Dec 9;45(5):389–412. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1912.sp001560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian E. D. On the summation of propagated disturbances in nerve and muscle. J Physiol. 1912 Mar 29;44(1-2):68–124. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1912.sp001503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian E. D. The all-or-none principle in nerve. J Physiol. 1914 Feb 27;47(6):460–474. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1914.sp001637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adrian E. D. Wedensky inhibition in relation to the ;all-or-none' principle in nerve. J Physiol. 1913 Jul 18;46(4-5):384–412. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1913.sp001598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISHOP G. H. Natural history of the nerve impulse. Physiol Rev. 1956 Jul;36(3):376–399. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1956.36.3.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BREMER F. Cerebral and cerebellar potentials. Physiol Rev. 1958 Jul;38(3):357–388. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1958.38.3.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOMBS J. S., CURTIS D. R., ECCLES J. C. The generation of impulses in motoneurones. J Physiol. 1957 Dec 3;139(2):232–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECCLES J. C., LIBET B., YOUNG R. R. The behaviour of chromatolysed motoneurones studied by intracellular recording. J Physiol. 1958 Aug 29;143(1):11–40. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L. Ionic movements and electrical activity in giant nerve fibres. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1958 Jan 1;148(930):1–37. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1958.0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G., Teruuchi D. Is there "transitional decrement" in narcotised nerve? J Physiol. 1927 Nov 21;64(2):193–198. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1927.sp002429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LLOYD D. P. Early and late post-tetanic potentiation, and post-tetanic block in a monosynaptic reflex pathway. J Gen Physiol. 1959 Jan 20;42(3):475–488. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.3.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas K. The effect of alcohol on the excitation, conduction and recovery processes in nerve. J Physiol. 1913 Aug 18;46(6):470–505. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1913.sp001601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUELLER P. Effects of external currents on duration and amplitude of normal and prolonged action potentials from single nodes of Ranvier. J Gen Physiol. 1958 Sep 20;42(1):163–191. doi: 10.1085/jgp.42.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUDOLPH G. Zur Physiologie der Impulsentstehung und Impulsfortleitung im peripheren Nerven; Untersuchungen an einzelnen aktiven Fasern im intakten Nervenstamm. Ann Univ Sarav Med. 1956;4(1):1–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



