Abstract
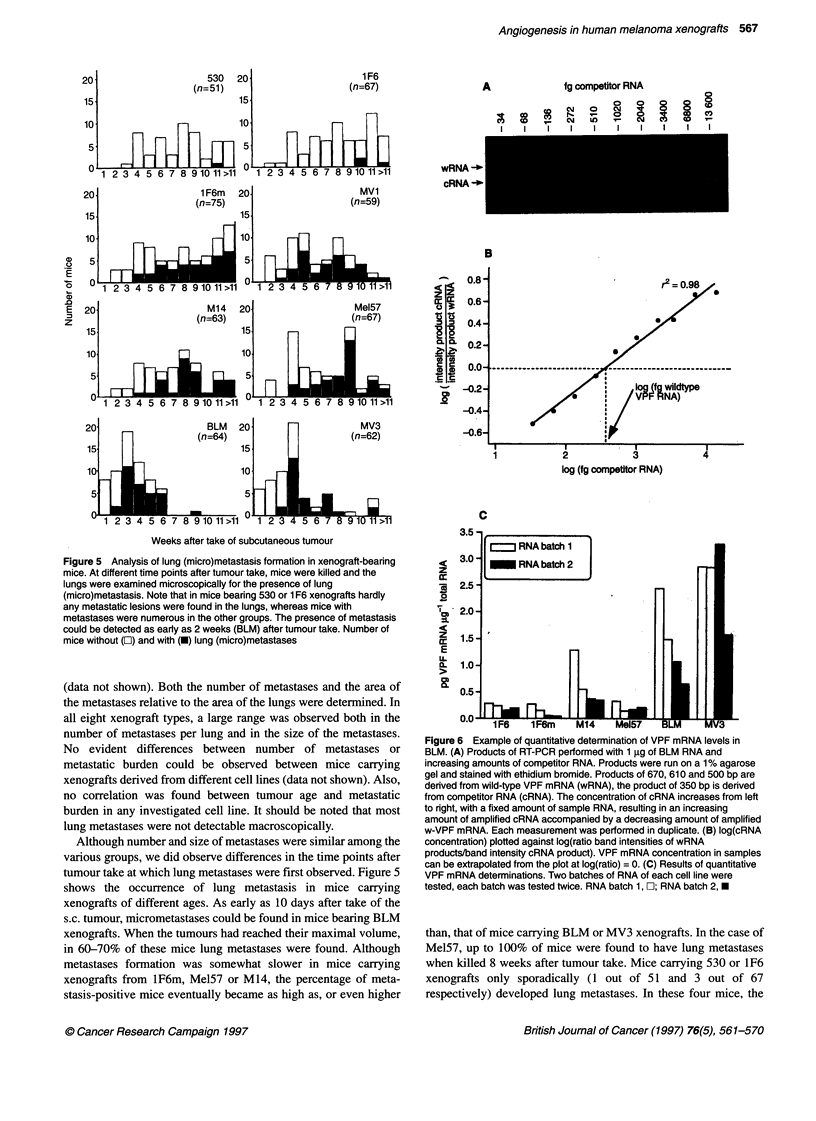
We studied the relation between tumour vascular density and tumour growth rate, metastatic incidence and vascular permeability factor (VPF) mRNA levels in a human xenograft model described previously. Vascular density was determined by automated image analysis. Xenografts derived from cell lines BLM and MV3 showed the highest mean vascular density (MVD), the highest in vivo growth rate, high VPF mRNA levels and rapid development of lung metastases. Xenografts of cell lines M14, Mel57 and MV1 showed a significantly lower degree of vascularization, lower in vivo growth rates and lower levels of VPF mRNA, but formed lung metastases with a similar incidence as those of BLM and MV3. Xenografts from cell line 1F6 did not form lung metastases, whereas tumours derived from a spontaneous mutant of 1F6, designated 1F6m, gave rise to lung metastases to the same extent as Mel57, M14 and MV1 tumours. MVD values in 1F6 and 1F6m xenografts, VPF mRNA levels and in vivo growth rates of 1F6 and 1 F6m xenografts, however, were similar. In conclusion, in the melanoma xenograft model vascular density is correlated with in vivo growth rate and with in vitro VPF mRNA levels, but not with the ability to metastasize.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albelda S. M. Role of integrins and other cell adhesion molecules in tumor progression and metastasis. Lab Invest. 1993 Jan;68(1):4–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnhill R. L., Busam K. J., Berwick M., Blessing K., Cochran A. J., Elder D. E., Fandrey K., Karaoli T., White W. L. Tumour vascularity is not a prognostic factor for cutaneous melanoma. Lancet. 1994 Oct 29;344(8931):1237–1238. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)90557-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnhill R. L., Fandrey K., Levy M. A., Mihm M. C., Jr, Hyman B. Angiogenesis and tumor progression of melanoma. Quantification of vascularity in melanocytic nevi and cutaneous malignant melanoma. Lab Invest. 1992 Sep;67(3):331–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigler S. A., Deering R. E., Brawer M. K. Comparison of microscopic vascularity in benign and malignant prostate tissue. Hum Pathol. 1993 Feb;24(2):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(93)90304-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busam K. J., Berwick M., Blessing K., Fandrey K., Kang S., Karaoli T., Fine J., Cochran A. J., White W. L., Rivers J. Tumor vascularity is not a prognostic factor for malignant melanoma of the skin. Am J Pathol. 1995 Oct;147(4):1049–1056. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnochan P., Briggs J. C., Westbury G., Davies A. J. The vascularity of cutaneous melanoma: a quantitative histological study of lesions 0.85-1.25 mm in thickness. Br J Cancer. 1991 Jul;64(1):102–107. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claffey K. P., Brown L. F., del Aguila L. F., Tognazzi K., Yeo K. T., Manseau E. J., Dvorak H. F. Expression of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor by melanoma cells increases tumor growth, angiogenesis, and experimental metastasis. Cancer Res. 1996 Jan 1;56(1):172–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danen E. H., Van Muijen G. N., Ruiter D. J. Role of integrins as signal transducing cell adhesion molecules in human cutaneous melanoma. Cancer Surv. 1995;24:43–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danen E. H., van Muijen G. N., van de Wiel-van Kemenade E., Jansen K. F., Ruiter D. J., Figdor C. G. Regulation of integrin-mediated adhesion to laminin and collagen in human melanocytes and in non-metastatic and highly metastatic human melanoma cells. Int J Cancer. 1993 May 8;54(2):315–321. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910540225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med. 1995 Jan;1(1):27–31. doi: 10.1038/nm0195-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Seminars in Medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. Clinical applications of research on angiogenesis. N Engl J Med. 1995 Dec 28;333(26):1757–1763. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199512283332608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Shing Y. Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 5;267(16):10931–10934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med. 1971 Nov 18;285(21):1182–1186. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197111182852108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham C. H., Rivers J., Kerbel R. S., Stankiewicz K. S., White W. L. Extent of vascularization as a prognostic indicator in thin (< 0.76 mm) malignant melanomas. Am J Pathol. 1994 Sep;145(3):510–514. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak E. R., Leek R., Klenk N., LeJeune S., Smith K., Stuart N., Greenall M., Stepniewska K., Harris A. L. Angiogenesis, assessed by platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule antibodies, as indicator of node metastases and survival in breast cancer. Lancet. 1992 Nov 7;340(8828):1120–1124. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93150-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., D'Amore P. A. Regulators of angiogenesis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:217–239. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung D. W., Cachianes G., Kuang W. J., Goeddel D. V., Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a secreted angiogenic mitogen. Science. 1989 Dec 8;246(4935):1306–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.2479986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Steeg P. S., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90642-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macchiarini P., Fontanini G., Hardin M. J., Squartini F., Angeletti C. A. Relation of neovascularisation to metastasis of non-small-cell lung cancer. Lancet. 1992 Jul 18;340(8812):145–146. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)93217-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelen M. R., Van der Burgt C. J., Nillesen W. N., Vis A., Smeets H. J. Familial Angelman syndrome with a crossover in the critical deletion region. Am J Med Genet. 1994 Sep 1;52(3):352–357. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320520320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pötgens A. J., Lubsen N. H., van Altena M. C., Schoenmakers J. G., Ruiter D. J., de Waal R. M. Vascular permeability factor expression influences tumor angiogenesis in human melanoma lines xenografted to nude mice. Am J Pathol. 1995 Jan;146(1):197–209. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pötgens A. J., Westphal H. R., de Waal R. M., Ruiter D. J. The role of vascular permeability factor and basic fibroblast growth factor in tumor angiogenesis. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1995 Feb;376(2):57–70. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1995.376.2.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pötgens A. J., van Altena M. C., Lubsen N. H., Ruiter D. J., de Waal R. M. Analysis of the tumor vasculature and metastatic behavior of xenografts of human melanoma cell lines transfected with vascular permeability factor. Am J Pathol. 1996 Apr;148(4):1203–1217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax P. H., van Muijen G. N., Weening-Verhoeff E. J., Lund L. R., Danø K., Ruiter D. J., Verheijen J. H. Metastatic behavior of human melanoma cell lines in nude mice correlates with urokinase-type plasminogen activator, its type-1 inhibitor, and urokinase-mediated matrix degradation. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):191–199. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smolle J., Soyer H. P., Hofmann-Wellenhof R., Smolle-Juettner F. M., Kerl H. Vascular architecture of melanocytic skin tumors. A quantitative immunohistochemical study using automated image analysis. Pathol Res Pract. 1989 Nov;185(5):740–745. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(89)80230-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava A., Laidler P., Davies R. P., Horgan K., Hughes L. E. The prognostic significance of tumor vascularity in intermediate-thickness (0.76-4.0 mm thick) skin melanoma. A quantitative histologic study. Am J Pathol. 1988 Nov;133(2):419–423. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Muijen G. N., Cornelissen L. M., Jansen C. F., Figdor C. G., Johnson J. P., Bröcker E. B., Ruiter D. J. Antigen expression of metastasizing and non-metastasizing human melanoma cells xenografted into nude mice. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1991 May-Jun;9(3):259–272. doi: 10.1007/BF01753729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vecchi A., Garlanda C., Lampugnani M. G., Resnati M., Matteucci C., Stoppacciaro A., Schnurch H., Risau W., Ruco L., Mantovani A. Monoclonal antibodies specific for endothelial cells of mouse blood vessels. Their application in the identification of adult and embryonic endothelium. Eur J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;63(2):247–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakui S., Furusato M., Itoh T., Sasaki H., Akiyama A., Kinoshita I., Asano K., Tokuda T., Aizawa S., Ushigome S. Tumour angiogenesis in prostatic carcinoma with and without bone marrow metastasis: a morphometric study. J Pathol. 1992 Nov;168(3):257–262. doi: 10.1002/path.1711680303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Carroll P. R., Flax J., Blumenfeld W., Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis correlates with metastasis in invasive prostate carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1993 Aug;143(2):401–409. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N. Intratumor microvessel density as a prognostic factor in cancer. Am J Pathol. 1995 Jul;147(1):9–19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner N., Semple J. P., Welch W. R., Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis--correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jan 3;324(1):1–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199101033240101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstat-Saslow D., Steeg P. S. Angiogenesis and colonization in the tumor metastatic process: basic and applied advances. FASEB J. 1994 Apr 1;8(6):401–407. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.8.6.7513289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weterman M. A., Stoopen G. M., van Muijen G. N., Kuznicki J., Ruiter D. J., Bloemers H. P. Expression of calcyclin in human melanoma cell lines correlates with metastatic behavior in nude mice. Cancer Res. 1992 Mar 1;52(5):1291–1296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Muijen G. N., Danen E. H., de Vries T. J., Quax P. H., Verheijen J. H., Ruiter D. J. Properties of metastasizing and nonmetastasizing human melanoma cells. Recent Results Cancer Res. 1995;139:105–122. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-78771-3_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Muijen G. N., Jansen K. F., Cornelissen I. M., Smeets D. F., Beck J. L., Ruiter D. J. Establishment and characterization of a human melanoma cell line (MV3) which is highly metastatic in nude mice. Int J Cancer. 1991 Apr 22;48(1):85–91. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910480116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]