Abstract
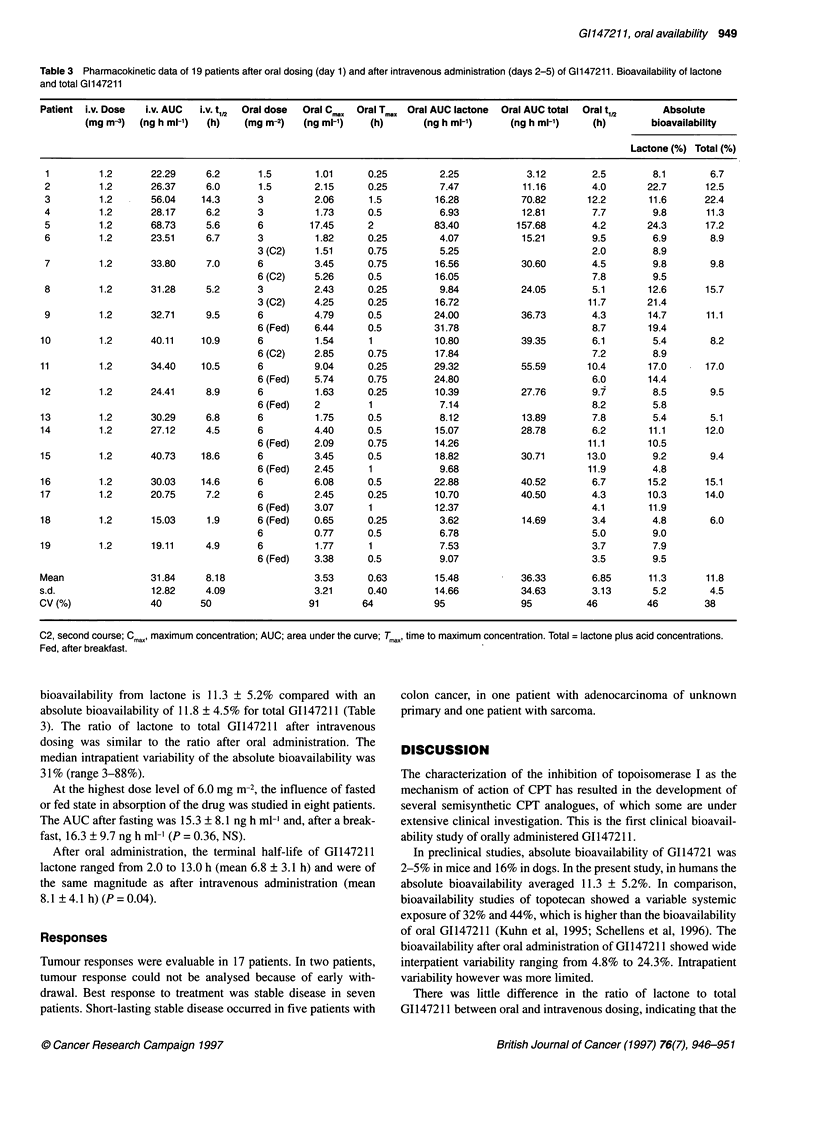
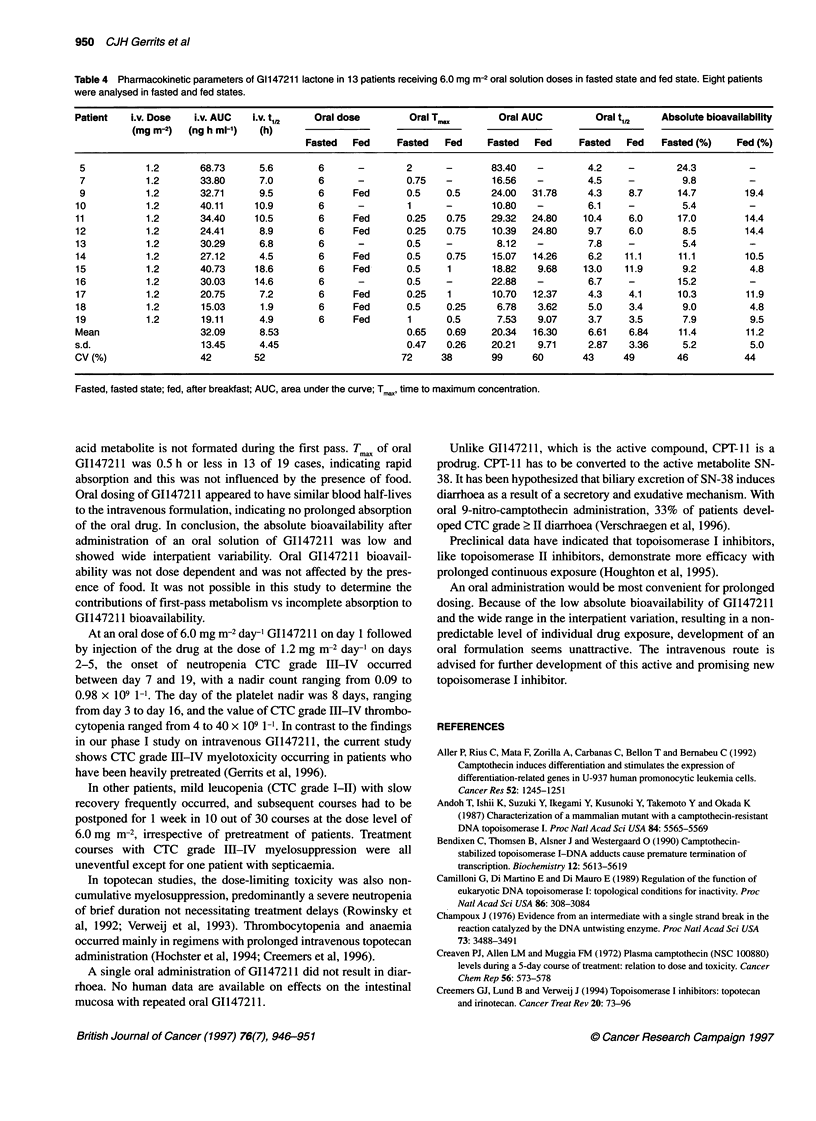
Topoisomerase I inhibitors are new compounds of interest for cancer chemotherapy. We performed a study with GI147211, a new semisynthetic camptothecin analogue, to determine the absolute bioavailability of the drug given orally. Patients with a histologically confirmed diagnosis of a solid tumour refractory to standard forms of therapy were eligible for the study. GI147211 was given orally on day 1 and as a 30-min infusion daily on days 2-5. The treatment course was repeated every 3 weeks. In subsequent patient cohorts, the dose of the oral formulation was escalated from 1.5 mg m(-2) to 6.0 mg m(-2); the dose for i.v. administration was fixed at 1.2 mg m(-2). Plasma pharmacokinetics was performed on day 1 and 2 of the first course and on day 1 of the second course using a validated high-performance liquid chromatographic assay. Nineteen patients were entered into the study; one patient was not evaluable because the treatment course was stopped prematurely. Eighteen patients received a total of 47 treatment courses. The absolute bioavailability of GI147211 averaged 1.3 +/- 5.2%. Drug appeared quickly in plasma with a median Tmax at 0.5 h. Fasting or fed state had no significant influence on the bioavailability of GI147211. The terminal half-life after administration of oral GI147211 was 6.85 +/- 3.13 h, similar to the half-life after intravenous administration. The major toxicities were neutropenia and thrombocytopenia. Nadirs for neutropenia and thrombocytopenia occurred on day 8 and day 15 respectively. Other toxicities predominantly consisted of mild and infrequent nausea and vomiting, and fatigue. The oral administration of the drug is well tolerated. Oral administration of topoisomerase I inhibitor GI147211 results in a low bioavailability with relatively wide interpatient variation. The intravenous route of administration is advised for further development of this promising topoisomerase I inhibitor.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aller P., Rius C., Mata F., Zorrilla A., Cabañas C., Bellón T., Bernabeu C. Camptothecin induces differentiation and stimulates the expression of differentiation-related genes in U-937 human promonocytic leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 1992 Mar 1;52(5):1245–1251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andoh T., Ishii K., Suzuki Y., Ikegami Y., Kusunoki Y., Takemoto Y., Okada K. Characterization of a mammalian mutant with a camptothecin-resistant DNA topoisomerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5565–5569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendixen C., Thomsen B., Alsner J., Westergaard O. Camptothecin-stabilized topoisomerase I-DNA adducts cause premature termination of transcription. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 12;29(23):5613–5619. doi: 10.1021/bi00475a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilloni G., Di Martino E., Di Mauro E., Caserta M. Regulation of the function of eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase I: topological conditions for inactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3080–3084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J. Evidence for an intermediate with a single-strand break in the reaction catalyzed by the DNA untwisting enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3488–3491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creaven P. J., Allen L. M., Muggia F. M. Plasma camptothecin (NSC-100880) levels during a 5-day course of treatment: relation to dose and toxicity. Cancer Chemother Rep. 1972 Oct;56(5):573–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creemers G. J., Gerrits C. J., Schellens J. H., Planting A. S., van der Burg M. E., van Beurden V. M., de Boer-Dennert M., Harteveld M., Loos W., Hudson I. Phase II and pharmacologic study of topotecan administered as a 21-day continuous infusion to patients with colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1996 Sep;14(9):2540–2545. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1996.14.9.2540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creemers G. J., Lund B., Verweij J. Topoisomerase I inhibitors: topotecan and irenotecan. Cancer Treat Rev. 1994 Jan;20(1):73–96. doi: 10.1016/0305-7372(94)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day F. A., Demko G. J. Population distribution problems and policies in Asia. Popul Geogr. 1981 Jun-Dec;3(1-2):16–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson D. L., Besterman J. M., Brown H. R., Evans M. G., Leitner P. P., Luzzio M. J., Shaffer J. E., Sternbach D. D., Uehling D., Vuong A. In vivo antitumor activity of two new seven-substituted water-soluble camptothecin analogues. Cancer Res. 1995 Feb 1;55(3):603–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng W. K., McCabe F. L., Tan K. B., Mattern M. R., Hofmann G. A., Woessner R. D., Hertzberg R. P., Johnson R. K. Development of a stable camptothecin-resistant subline of P388 leukemia with reduced topoisomerase I content. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;38(4):471–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerrits C. J., Creemers G. J., Schellens J. H., Wissel P., Planting A. S., Kunka R., Selinger K., de Boer-Dennert M., Marijnen Y., Harteveld M. Phase I and pharmacological study of the new topoisomerase I inhibitor GI147211, using a daily x 5 intravenous administration. Br J Cancer. 1996 Mar;73(6):744–750. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1996.130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanella B. C., Stehlin J. S., Wall M. E., Wani M. C., Nicholas A. W., Liu L. F., Silber R., Potmesil M. DNA topoisomerase I--targeted chemotherapy of human colon cancer in xenografts. Science. 1989 Nov 24;246(4933):1046–1048. doi: 10.1126/science.2555920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb J. A., Guarino A. M., Call J. B., Oliverio V. T., Block J. B. Preliminary pharmacologic and clinical evaluation of camptothecin sodium (NSC-100880). Cancer Chemother Rep. 1970 Dec;54(6):461–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta R. S., Gupta R., Eng B., Lock R. B., Ross W. E., Hertzberg R. P., Caranfa M. J., Johnson R. K. Camptothecin-resistant mutants of Chinese hamster ovary cells containing a resistant form of topoisomerase I. Cancer Res. 1988 Nov 15;48(22):6404–6410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochster H., Liebes L., Speyer J., Sorich J., Taubes B., Oratz R., Wernz J., Chachoua A., Raphael B., Vinci R. Z. Phase I trial of low-dose continuous topotecan infusion in patients with cancer: an active and well-tolerated regimen. J Clin Oncol. 1994 Mar;12(3):553–559. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1994.12.3.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton P. J., Cheshire P. J., Hallman J. D., 2nd, Lutz L., Friedman H. S., Danks M. K., Houghton J. A. Efficacy of topoisomerase I inhibitors, topotecan and irinotecan, administered at low dose levels in protracted schedules to mice bearing xenografts of human tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1995;36(5):393–403. doi: 10.1007/BF00686188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang Y. H., Hertzberg R., Hecht S., Liu L. F. Camptothecin induces protein-linked DNA breaks via mammalian DNA topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14873–14878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang Y. H., Liu L. F. Identification of mammalian DNA topoisomerase I as an intracellular target of the anticancer drug camptothecin. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1722–1726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann W. K., Boyer J. C., Estabrooks L. L., Wilson S. J. Inhibition of replicon initiation in human cells following stabilization of topoisomerase-DNA cleavable complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3711–3718. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharbanda S., Rubin E., Gunji H., Hinz H., Giovanella B., Pantazis P., Kufe D. Camptothecin and its derivatives induce expression of the c-jun protooncogene in human myeloid leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 15;51(24):6636–6642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F. DNA topoisomerase poisons as antitumor drugs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:351–375. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muggia F. M., Creaven P. J., Hansen H. H., Cohen M. H., Selawry O. S. Phase I clinical trial of weekly and daily treatment with camptothecin (NSC-100880): correlation with preclinical studies. Cancer Chemother Rep. 1972 Aug;56(4):515–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller M. T., Pfund W. P., Mehta V. B., Trask D. K. Eukaryotic type I topoisomerase is enriched in the nucleolus and catalytically active on ribosomal DNA. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1237–1243. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03766.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller M. T. Quantitation of eukaryotic topoisomerase I reactivity with DNA. Preferential cleavage of supercoiled DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Mar 20;824(3):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(85)90057-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaya K., Chou S., Kaneko M., Nakamura Y. Topoisomerase inhibitors have potent differentiation-inducing activity for human and mouse myeloid leukemia cells. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1991 Feb;82(2):184–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1991.tb01827.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potmesil M. Camptothecins: from bench research to hospital wards. Cancer Res. 1994 Mar 15;54(6):1431–1439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potmesil M., Hsiang Y. H., Liu L. F., Bank B., Grossberg H., Kirschenbaum S., Forlenza T. J., Penziner A., Kanganis D., Forlenzar T. J. Resistance of human leukemic and normal lymphocytes to drug-induced DNA cleavage and low levels of DNA topoisomerase II. Cancer Res. 1988 Jun 15;48(12):3537–3543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowinsky E. K., Grochow L. B., Hendricks C. B., Ettinger D. S., Forastiere A. A., Hurowitz L. A., McGuire W. P., Sartorius S. E., Lubejko B. G., Kaufmann S. H. Phase I and pharmacologic study of topotecan: a novel topoisomerase I inhibitor. J Clin Oncol. 1992 Apr;10(4):647–656. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1992.10.4.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellens J. H., Creemers G. J., Beijnen J. H., Rosing H., de Boer-Dennert M., McDonald M., Davies B., Verweij J. Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of oral topotecan: a new topoisomerase I inhibitor. Br J Cancer. 1996 May;73(10):1268–1271. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1996.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slichenmyer W. J., Rowinsky E. K., Donehower R. C., Kaufmann S. H. The current status of camptothecin analogues as antitumor agents. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1993 Feb 17;85(4):271–291. doi: 10.1093/jnci/85.4.271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafford C. G., St Claire R. L., 3rd High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of the lactone and carboxylate forms of a topoisomerase I inhibitor (the antitumor drug GI147211) in plasma. J Chromatogr B Biomed Appl. 1995 Jan 6;663(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(94)00430-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Tsukahara S., Oh-hara T., Isoe T., Tsuruo T. Decreased expression of DNA topoisomerase I in camptothecin-resistant tumor cell lines as determined by a monoclonal antibody. Cancer Res. 1990 Nov 1;50(21):6925–6930. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanizawa A., Pommier Y. Topoisomerase I alteration in a camptothecin-resistant cell line derived from Chinese hamster DC3F cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 1;52(7):1848–1854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verweij J., Lund B., Beijnen J., Planting A., de Boer-Dennert M., Koier I., Rosing H., Hansen H. Phase I and pharmacokinetics study of topotecan, a new topoisomerase I inhibitor. Ann Oncol. 1993 Sep;4(8):673–678. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.annonc.a058623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



