Abstract
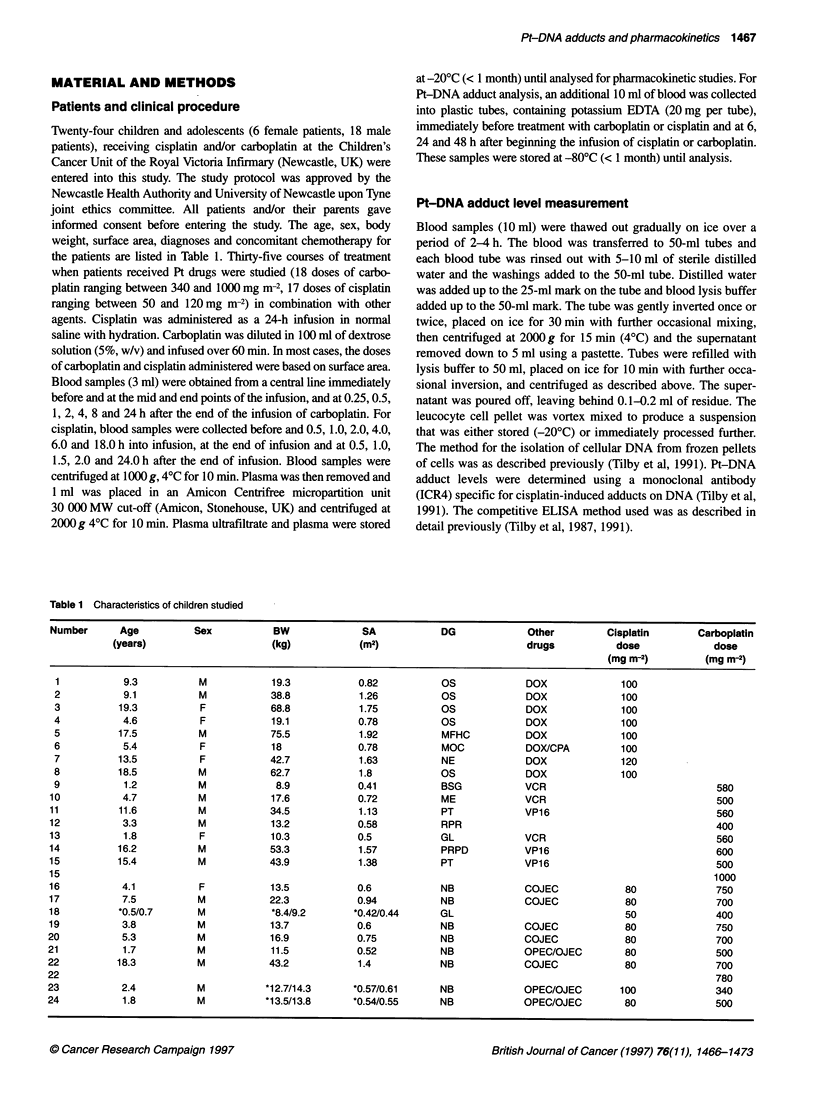
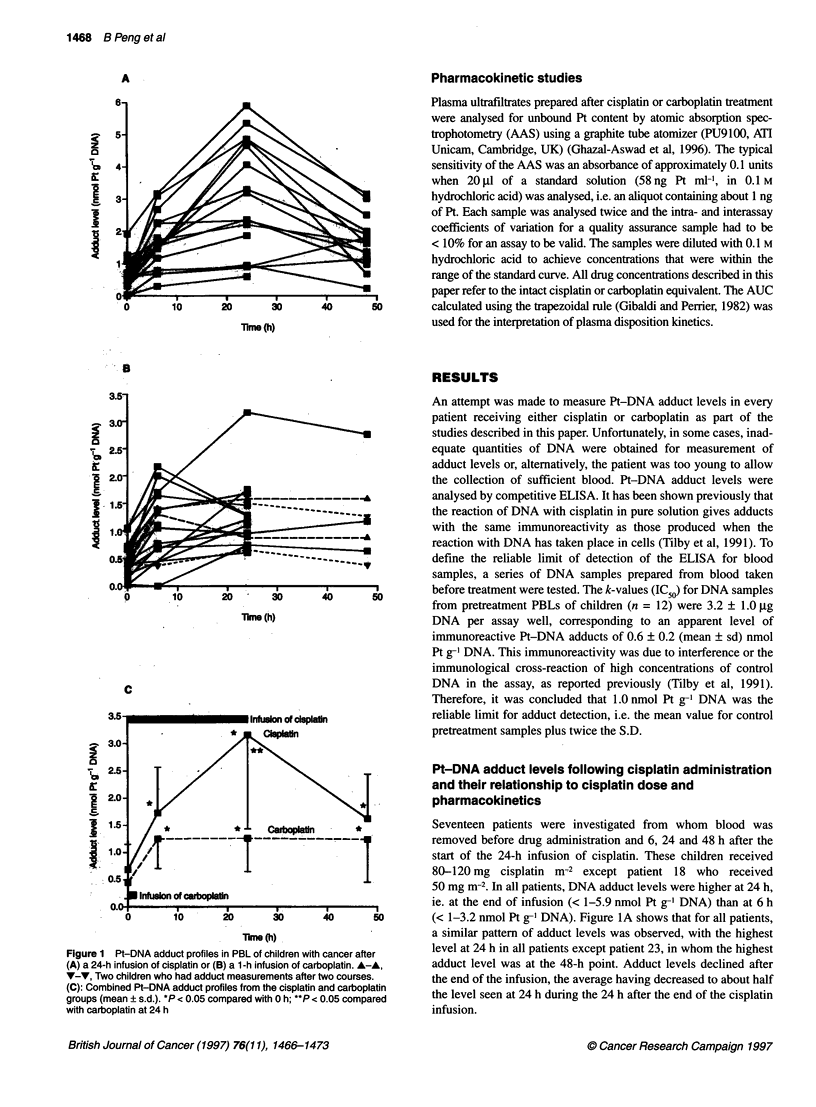
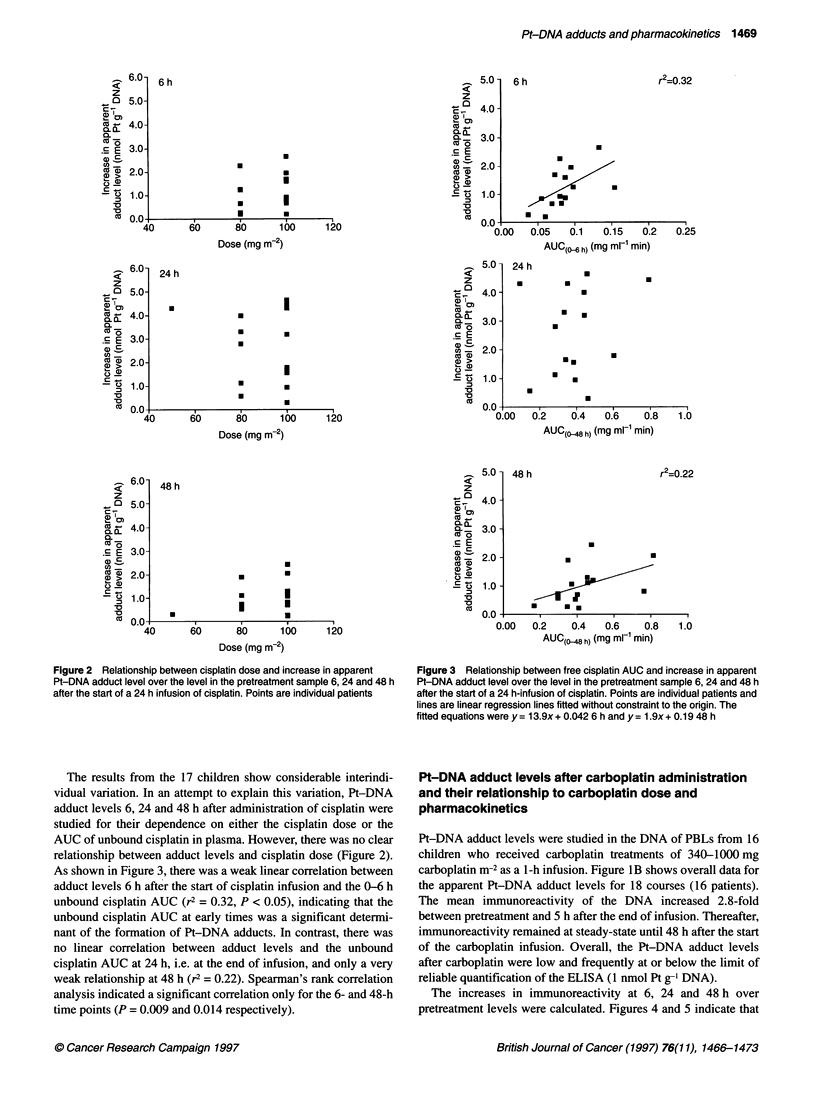
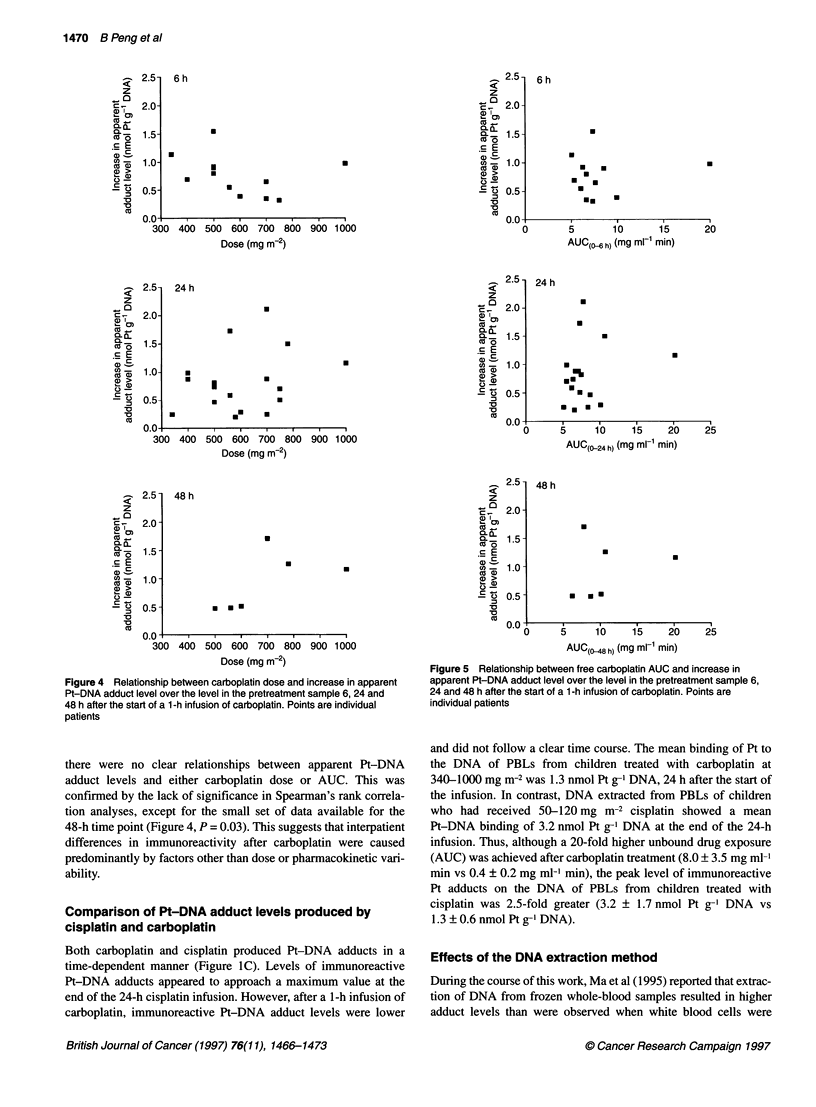
Platinum (Pt)-DNA adducts were measured in peripheral blood leucocytes (PBLs) from 24 children with solid tumours after standard cisplatin and/or carboplatin treatment. The relationship between Pt-DNA adduct levels and pharmacokinetics of cisplatin and carboplatin was investigated. Adduct measurements were performed by competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and plasma unbound Pt concentrations were measured by atomic absorption spectrophotometry (AAS). There was considerable interindividual variation in Pt-DNA adduct level that was weakly correlated (r2 = 0.32) with the area under the unbound drug concentration vs time curve (AUC) at 6 h after the start of cisplatin infusion, indicating that the variation in Pt-DNA adduct levels was primarily determined by factors other than AUC. No clear relationship between AUC and adduct levels was seen at 24 and 48 h after cisplatin or at 6, 24 or 48 h after carboplatin. Carboplatin produced lower levels of immunoreactive adducts than did cisplatin (1.3 +/- 0.6 nmol Pt g-1 DNA vs 3.2 +/- 1.7 nmol Pt g-1 DNA), despite a 20-fold higher unbound drug AUC for carboplatin (8.0 +/- 3.5 mg ml-1 min vs 0.4 +/- 0.2 mg ml-1 min). This study demonstrates that, after cisplatin and carboplatin treatment the drug-target interaction is determined by both pharmacokinetic and, predominantly, cellular factors. Intrinsic differences between the two complexes, primarily reactivity, probably explain the lower adduct levels observed after carboplatin treatment.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blommaert F. A., Michael C., Terheggen P. M., Muggia F. M., Kortes V., Schornagel J. H., Hart A. A., den Engelse L. Drug-induced DNA modification in buccal cells of cancer patients receiving carboplatin and cisplatin combination chemotherapy, as determined by an immunocytochemical method: interindividual variation and correlation with disease response. Cancer Res. 1993 Dec 1;53(23):5669–5675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer M. J., Horn I., Firestone R. A., Steele-Norwood D., Tannock I. F. pH dependent cytotoxicity of N-dodecylimidazole: a compound that acquires detergent properties under acidic conditions. Br J Cancer. 1993 Jan;67(1):81–87. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell A. B., Kalman S. M., Jacobs C. Plasma platinum levels: relationship to cisplatin dose and nephrotoxicity. Cancer Treat Rep. 1983 Feb;67(2):169–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatelut E., Boddy A. V., Peng B., Rubie H., Lavit M., Dezeuze A., Pearson A. D., Roché H., Robert A., Newell D. R. Population pharmacokinetics of carboplatin in children. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1996 Apr;59(4):436–443. doi: 10.1016/S0009-9236(96)90113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doz F., Pinkerton R. What is the place of carboplatin in paediatric oncology? Eur J Cancer. 1994;30A(2):194–201. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(94)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egorin M. J., Van Echo D. A., Tipping S. J., Olman E. A., Whitacre M. Y., Thompson B. W., Aisner J. Pharmacokinetics and dosage reduction of cis-diammine(1,1-cyclobutanedicarboxylato)platinum in patients with impaired renal function. Cancer Res. 1984 Nov;44(11):5432–5438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichtinger-Schepman A. M., Baan R. A., Luiten-Schuite A., van Dijk M., Lohman P. H. Immunochemical quantitation of adducts induced in DNA by cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II) and analysis of adduct-related DNA-unwinding. Chem Biol Interact. 1985 Nov;55(3):275–288. doi: 10.1016/s0009-2797(85)80135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichtinger-Schepman A. M., van Dijk-Knijnenburg H. C., van der Velde-Visser S. D., Berends F., Baan R. A. Cisplatin- and carboplatin-DNA adducts: is PT-AG the cytotoxic lesion? Carcinogenesis. 1995 Oct;16(10):2447–2453. doi: 10.1093/carcin/16.10.2447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichtinger-Schepman A. M., van der Velde-Visser S. D., van Dijk-Knijnenburg H. C., van Oosterom A. T., Baan R. A., Berends F. Kinetics of the formation and removal of cisplatin-DNA adducts in blood cells and tumor tissue of cancer patients receiving chemotherapy: comparison with in vitro adduct formation. Cancer Res. 1990 Dec 15;50(24):7887–7894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazal-Aswad S., Calvert A. H., Newell D. R. A single-sample assay for the estimation of the area under the free carboplatin plasma concentration versus time curve. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1996;37(5):429–434. doi: 10.1007/s002800050408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland S. J., Gumbrell L. A., Horwich A. Carboplatin dose in combination chemotherapy for testicular cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1991;27(6):691–695. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(91)90167-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwich A., Dearnaley D. P., Nicholls J., Jay G., Mason M., Harland S., Peckham M. J., Hendry W. F. Effectiveness of carboplatin, etoposide, and bleomycin combination chemotherapy in good-prognosis metastatic testicular nonseminomatous germ cell tumors. J Clin Oncol. 1991 Jan;9(1):62–69. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1991.9.1.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jodrell D. I., Egorin M. J., Canetta R. M., Langenberg P., Goldbloom E. P., Burroughs J. N., Goodlow J. L., Tan S., Wiltshaw E. Relationships between carboplatin exposure and tumor response and toxicity in patients with ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1992 Apr;10(4):520–528. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1992.10.4.520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox R. J., Friedlos F., Lydall D. A., Roberts J. J. Mechanism of cytotoxicity of anticancer platinum drugs: evidence that cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) and cis-diammine-(1,1-cyclobutanedicarboxylato)platinum(II) differ only in the kinetics of their interaction with DNA. Cancer Res. 1986 Apr;46(4 Pt 2):1972–1979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Verweij J., Planting A. S., de Boer-Dennert M., van Ingen H. E., van der Burg M. E., Stoter G., Schellens J. H. Current sample handling methods for measurement of platinum-DNA adducts in leucocytes in man lead to discrepant results in DNA adduct levels and DNA repair. Br J Cancer. 1995 Mar;71(3):512–517. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marina N. M., Rodman J., Shema S. J., Bowman L. C., Douglass E., Furman W., Santana V. M., Hudson M., Wilimas J., Meyer W. Phase I study of escalating targeted doses of carboplatin combined with ifosfamide and etoposide in children with relapsed solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 1993 Mar;11(3):554–560. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1993.11.3.554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell D. R., Pearson A. D., Balmanno K., Price L., Wyllie R. A., Keir M., Calvert A. H., Lewis I. J., Pinkerton C. R., Stevens M. C. Carboplatin pharmacokinetics in children: the development of a pediatric dosing formula. The United Kingdom Children's Cancer Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 1993 Dec;11(12):2314–2323. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1993.11.12.2314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell D. R., Siddik Z. H., Gumbrell L. A., Boxall F. E., Gore M. E., Smith I. E., Calvert A. H. Plasma free platinum pharmacokinetics in patients treated with high dose carboplatin. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1987 Sep;23(9):1399–1405. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(87)90126-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. J., Gill I., Tarone R., Vionnet J. A., Grunberg S., Muggia F. M., Reed E. Platinum-DNA damage in leukocyte DNA of patients receiving carboplatin and cisplatin chemotherapy, measured by atomic absorption spectrometry. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Jul;12(7):1253–1258. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.7.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson A. D., Craft A. W., Pinkerton C. R., Meller S. T., Reid M. M. High-dose rapid schedule chemotherapy for disseminated neuroblastoma. Eur J Cancer. 1992;28A(10):1654–1659. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(92)90062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkerton C. R., Pritchard J., Spitz L. High complete response rate in children with advanced germ cell tumors using cisplatin-containing combination chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 1986 Feb;4(2):194–199. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1986.4.2.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirier M. C., Lippard S. J., Zwelling L. A., Ushay H. M., Kerrigan D., Thill C. C., Santella R. M., Grunberger D., Yuspa S. H. Antibodies elicited against cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II)-modified DNA are specific for cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II)-DNA adducts formed in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6443–6447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reece P. A., Stafford I., Russell J., Khan M., Gill P. G. Creatinine clearance as a predictor of ultrafilterable platinum disposition in cancer patients treated with cisplatin: relationship between peak ultrafilterable platinum plasma levels and nephrotoxicity. J Clin Oncol. 1987 Feb;5(2):304–309. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1987.5.2.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed E., Ostchega Y., Steinberg S. M., Yuspa S. H., Young R. C., Ozols R. F., Poirier M. C. Evaluation of platinum-DNA adduct levels relative to known prognostic variables in a cohort of ovarian cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1990 Apr 15;50(8):2256–2260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed E., Ozols R. F., Tarone R., Yuspa S. H., Poirier M. C. Platinum-DNA adducts in leukocyte DNA correlate with disease response in ovarian cancer patients receiving platinum-based chemotherapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5024–5028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed E., Ozols R. F., Tarone R., Yuspa S. H., Poirier M. C. The measurement of cisplatin-DNA adduct levels in testicular cancer patients. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Oct;9(10):1909–1911. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.10.1909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed E., Yuspa S. H., Zwelling L. A., Ozols R. F., Poirier M. C. Quantitation of cis-diamminedichloroplatinum II (cisplatin)-DNA-intrastrand adducts in testicular and ovarian cancer patients receiving cisplatin chemotherapy. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):545–550. doi: 10.1172/JCI112335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. J., Thomson A. J. The mechanism of action of antitumor platinum compounds. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1979;22:71–133. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60799-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellens J. H., Ma J., Planting A. S., van der Burg M. E., van Meerten E., de Boer-Dennert M., Schmitz P. I., Stoter G., Verweij J. Relationship between the exposure to cisplatin, DNA-adduct formation in leucocytes and tumour response in patients with solid tumours. Br J Cancer. 1996 Jun;73(12):1569–1575. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1996.296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen B. T., Strömgren A., Jakobsen P., Jakobsen A. Dose-toxicity relationship of carboplatin in combination with cyclophosphamide in ovarian cancer patients. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1991;28(5):397–401. doi: 10.1007/BF00685696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terheggen P. M., Dijkman R., Begg A. C., Dubbelman R., Floot B. G., Hart A. A., den Engelse L. Monitoring of interaction products of cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) and cis-diammine(1,1-cyclobutanedicarboxylato)platinum(II) with DNA in cells from platinum-treated cancer patients. Cancer Res. 1988 Oct 1;48(19):5597–5603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilby M. J., Johnson C., Knox R. J., Cordell J., Roberts J. J., Dean C. J. Sensitive detection of DNA modifications induced by cisplatin and carboplatin in vitro and in vivo using a monoclonal antibody. Cancer Res. 1991 Jan 1;51(1):123–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilby M. J., Styles J. M., Dean C. J. Immunological detection of DNA damage caused by melphalan using monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res. 1987 Mar 15;47(6):1542–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graeff A., Slebos R. J., Rodenhuis S. Resistance to cisplatin and analogues: mechanisms and potential clinical implications. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1988;22(4):325–332. doi: 10.1007/BF00254240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]