Abstract
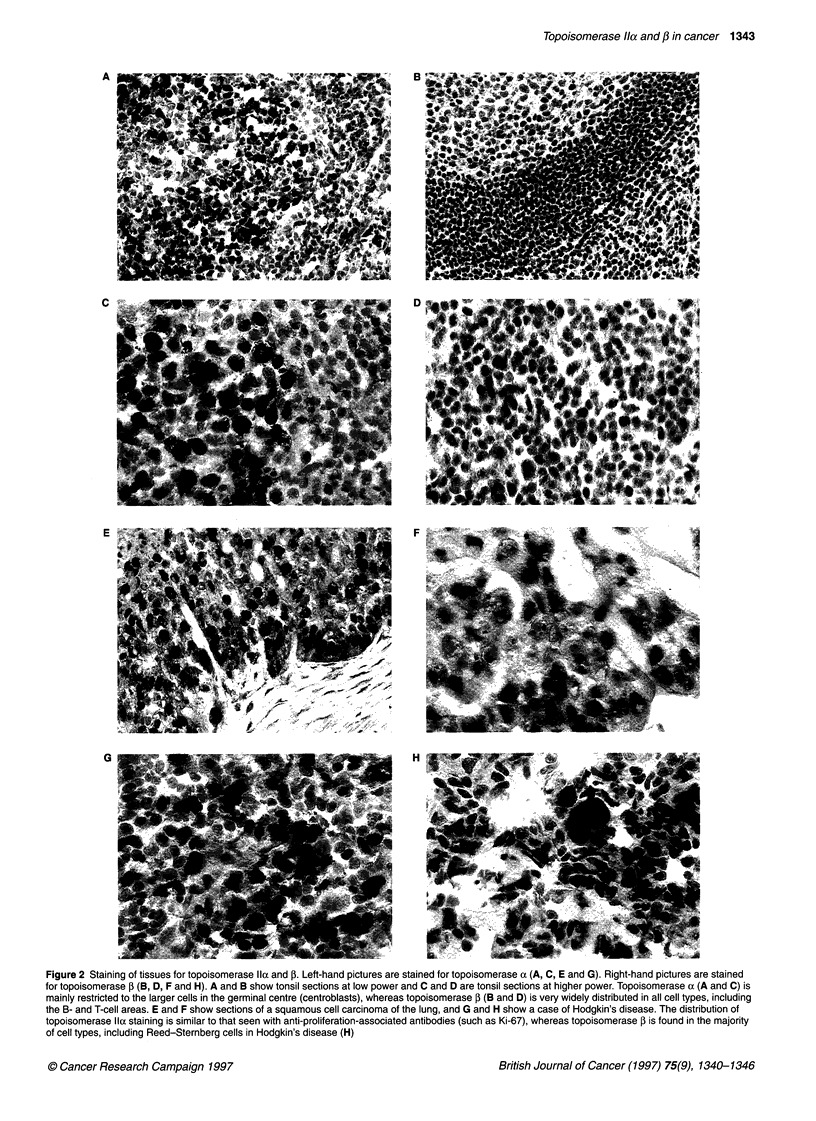
In mammalian cells, there are two isoforms of DNA topoisomerase II, designated alpha (170-kDa form) and beta (180-kDa form). Previous studies using cell lines have shown that the topoisomerase IIalpha and beta isoforms are differentially regulated during the cell cycle and in response to changes in growth state. Moreover, both isoforms can act as targets for a range of anti-tumour drugs. Here, we have analysed the normal tissue distribution in humans of topoisomerase IIalpha and beta using isoform-specific antibodies. In addition, we have studied expression of these isoforms in 69 primary tumour biopsies, representative either of tumours that are responsive to topoisomerase II-targeting drugs (breast, lung, lymphoma and seminoma) or of those that show de novo drug resistance (colon). Topoisomerase IIalpha was expressed exclusively in the proliferating compartments of all normal tissues, and was detectable in both the cell nucleus and cytoplasm. In biologically aggressive or rapidly proliferating tumours (e.g. high-grade lymphomas and seminomas), there was a high level of topoisomerase IIalpha, although expression was still detectable in colon tumours, indicating that expression of this isoform is not sufficient to explain the intrinsic drug resistance of colon tumours. Topoisomerase IIbeta was expressed ubiquitously in vivo and was localized in both the nucleoli and the nucleoplasm. This isoform was present in quiescent cell populations, but was expressed at a generally higher level in all tumours and proliferating cells than in normal quiescent tissues. We conclude that topoisomerase IIalpha is a strict proliferation marker in normal and neoplastic cells in vivo, but that topoisomerase IIbeta has a much more general cell and tissue distribution than has topoisomerase IIalpha. The apparent up-regulation of topoisomerase IIbeta in neoplastic cells has implications for the response of patients to anti-tumour therapies that include topoisomerase II-targeting drugs.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin C. A., Sng J. H., Patel S., Fisher L. M. Novel HeLa topoisomerase II is the II beta isoform: complete coding sequence and homology with other type II topoisomerases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Mar 20;1172(3):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90215-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck W. T., Danks M. K., Wolverton J. S., Kim R., Chen M. Drug resistance associated with altered DNA topoisomerase II. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1993;33:113–127. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(93)90012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies S. M., Robson C. N., Davies S. L., Hickson I. D. Nuclear topoisomerase II levels correlate with the sensitivity of mammalian cells to intercalating agents and epipodophyllotoxins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17724–17729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry A. M., Chresta C. M., Davies S. M., Walker M. C., Harris A. L., Hartley J. A., Masters J. R., Hickson I. D. Relationship between topoisomerase II level and chemosensitivity in human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 15;51(24):6592–6595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellemans P., van Dam P. A., Geyskens M., van Oosterom A. T., Buytaert P., Van Marck E. Immunohistochemical study of topoisomerase II-alpha expression in primary ductal carcinoma of the breast. J Clin Pathol. 1995 Feb;48(2):147–150. doi: 10.1136/jcp.48.2.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden J. A., Snow G. W., Perkins S. L., Jolles C. J., Kjeldsberg C. R. Immunohistochemical staining for DNA topoisomerase II in frozen and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human tissues. Mod Pathol. 1994 Oct;7(8):829–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houlbrook S., Addison C. M., Davies S. L., Carmichael J., Stratford I. J., Harris A. L., Hickson I. D. Relationship between expression of topoisomerase II isoforms and intrinsic sensitivity to topoisomerase II inhibitors in breast cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer. 1995 Dec;72(6):1454–1461. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1995.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs R. J., Harris A. L., Hickson I. D. Regulation of the human topoisomerase IIalpha gene promoter in confluence-arrested cells. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jul 12;271(28):16741–16747. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.28.16741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jans D. A. The regulation of protein transport to the nucleus by phosphorylation. Biochem J. 1995 Nov 1;311(Pt 3):705–716. doi: 10.1042/bj3110705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Ayton P., Jones T., Davies S. L., Simmons D. L., Harris A. L., Sheer D., Hickson I. D. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding the beta isozyme of human DNA topoisomerase II and localisation of the gene to chromosome 3p24. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5587–5592. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Karp J. E., Jones R. J., Miller C. B., Schneider E., Zwelling L. A., Cowan K., Wendel K., Burke P. J. Topoisomerase II levels and drug sensitivity in adult acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood. 1994 Jan 15;83(2):517–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheroff N., Zechiedrich E. L., Gale K. C. Catalytic function of DNA topoisomerase II. Bioessays. 1991 Jun;13(6):269–273. doi: 10.1002/bies.950130603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrov P., Drake F. H., Loranger A., Huang W., Hancock R. Localization of DNA topoisomerase II in Chinese hamster fibroblasts by confocal and electron microscopy. Exp Cell Res. 1993 Jan;204(1):73–81. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pommier Y. DNA topoisomerase I and II in cancer chemotherapy: update and perspectives. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1993;32(2):103–108. doi: 10.1007/BF00685611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosperi E., Negri C., Marchese G., Ricotti G. C. Expression of the 170-kDa and 180-kDa isoforms of DNA topoisomerase II in resting and proliferating human lymphocytes. Cell Prolif. 1994 May;27(5):257–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1994.tb01423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swedlow J. R., Sedat J. W., Agard D. A. Multiple chromosomal populations of topoisomerase II detected in vivo by time-lapse, three-dimensional wide-field microscopy. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90163-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K. B., Dorman T. E., Falls K. M., Chung T. D., Mirabelli C. K., Crooke S. T., Mao J. Topoisomerase II alpha and topoisomerase II beta genes: characterization and mapping to human chromosomes 17 and 3, respectively. Cancer Res. 1992 Jan 1;52(1):231–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai-Pflugfelder M., Liu L. F., Liu A. A., Tewey K. M., Whang-Peng J., Knutsen T., Huebner K., Croce C. M., Wang J. C. Cloning and sequencing of cDNA encoding human DNA topoisomerase II and localization of the gene to chromosome region 17q21-22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7177–7181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuccari G., Rizzo A., Giuffrè G., Barresi G. Immunocytochemical detection of DNA topoisomerase type II in primary breast carcinomas: correlation with clinico-pathological features. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1993;423(1):51–55. doi: 10.1007/BF01606432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:665–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. DNA topoisomerases: why so many? J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6659–6662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt P. M., Hickson I. D. Structure and function of type II DNA topoisomerases. Biochem J. 1994 Nov 1;303(Pt 3):681–695. doi: 10.1042/bj3030681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells N. J., Addison C. M., Fry A. M., Ganapathi R., Hickson I. D. Serine 1524 is a major site of phosphorylation on human topoisomerase II alpha protein in vivo and is a substrate for casein kinase II in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 25;269(47):29746–29751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells N. J., Fry A. M., Guano F., Norbury C., Hickson I. D. Cell cycle phase-specific phosphorylation of human topoisomerase II alpha. Evidence of a role for protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1995 Nov 24;270(47):28357–28363. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.47.28357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells N. J., Hickson I. D. Human topoisomerase II alpha is phosphorylated in a cell-cycle phase-dependent manner by a proline-directed kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Jul 15;231(2):491–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20723.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner R. D., Mattern M. R., Mirabelli C. K., Johnson R. K., Drake F. H. Proliferation- and cell cycle-dependent differences in expression of the 170 kilodalton and 180 kilodalton forms of topoisomerase II in NIH-3T3 cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Apr;2(4):209–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zini N., Martelli A. M., Sabatelli P., Santi S., Negri C., Astaldi Ricotti G. C., Maraldi N. M. The 180-kDa isoform of topoisomerase II is localized in the nucleolus and belongs to the structural elements of the nucleolar remnant. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Jun;200(2):460–466. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90196-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]