A 14-year old boy presented with a 10-year history of recurring episodes of fever and productive cough. Ten years previously he had been treated for pneumonia, and subsequently he had also received antituberculous therapy, with little effect. A chest radiograph was performed (Figure 1A), which led to the need for computed tomography of the chest (Figure 1B). Sputum analysis for acid-fast bacilli and workup for allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis were negative. The patient was reassured and discharged with a diagnosis of bronchiectasis with a destroyed left lung.
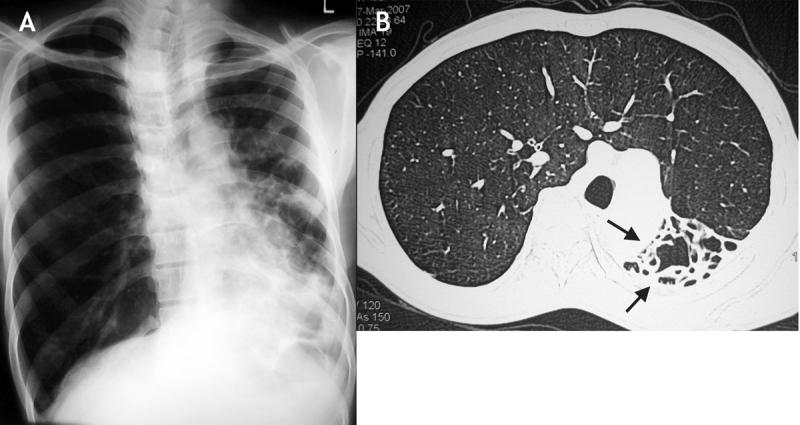
Figure 1: A: Chest radiograph showing volume loss on the left side with bronchiectasis in the left lower lobe and changes on the right consistent with hyperinflation. B: Computed tomography scan of the chest showing the right lung, which has herniated across to the left side in a horseshoe shape, and the destroyed left lung (arrows).
Destroyed lung, or pseudohorseshoe lung, results from inflammatory conditions such as necrotizing pneumonia. It is often associated with compensatory hyperinflation of the other lung. In contrast, horseshoe lung is a rare congenital anomaly characterized by the presence of a midline isthmus of pulmonary parenchyma bridging the lungs. Pseudohorseshoe lung usually affects the pediatric population; however, asymptomatic cases may be diagnosed in adults.
Navneet Singh MD DM Ritesh Agarwal MD DM Dheeraj Gupta MD DM Department of Pulmonary Medicine Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research Chandigarh, India
Footnotes
CMAJ invites contributions to Interesting Images, a new column with a very brief but clear description of the case, the images and the main teaching point. Submit manuscripts online at http://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/cmaj.


