Abstract
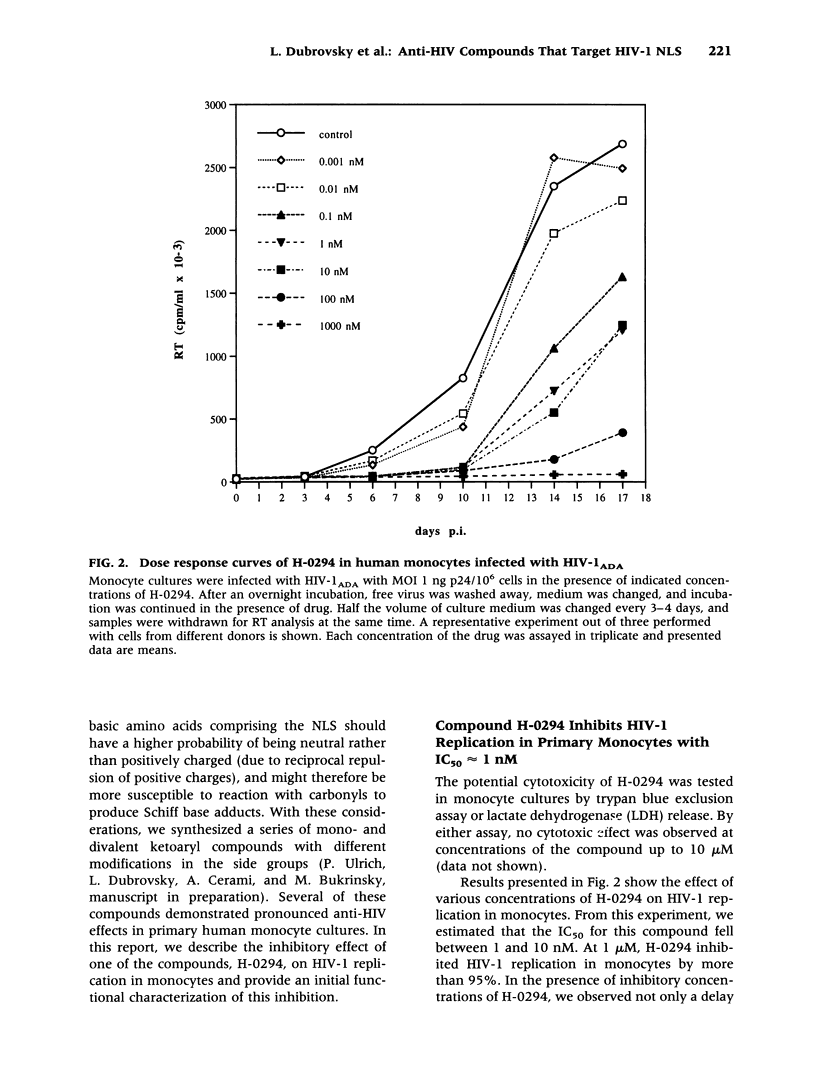
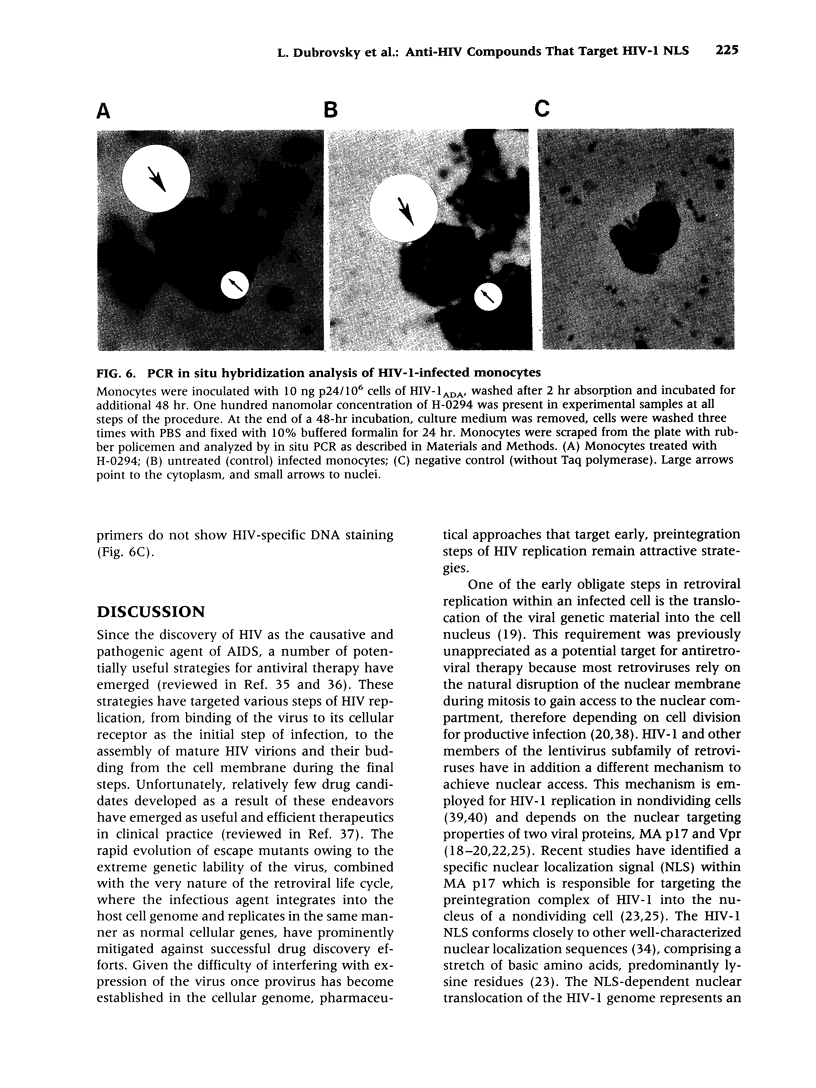
BACKGROUND: Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) is a lentivirus and shares with other members of this retroviral subfamily the ability to replicate in nondividing cells, in particular, cells of the monocyte/macrophage lineage. This feature relies on the presence of a specific nuclear localization signal (NLS) within the viral matrix protein (MA p17), which to some degree can be complemented by the activity of the viral vpr gene product. The MA p17 NLS ensures efficient transportation of the viral preintegration complex into the nucleus of an infected macrophage and confers persistence of HIV-1 in quiescent T cells, and therefore presents an attractive target for therapeutic intervention. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Nuclear localization signals (NLS) in general and the HIV-1 MA p17 NLS in particular are characterized by a stretch of positively charged amino acids including one or more lysine residues. A series of compounds potentially capable of binding and reacting with lysine by forming Schiff base adducts was synthesized. Our special consideration was to make compounds that would preferentially bind to two closely contiguous amino functions, as opposed to isolated single lysine residues. We assumed that this approach might specifically target the compound to NLS while affecting other regions less, thus reducing nonspecific cytotoxicity. Antiviral activity was assessed in primary monocytes and in peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) infected with HIV-1ADA strain. Viral replication was monitored by reverse transcriptase (RT) activity in the supernatant. Efficiency of nuclear importation of the viral preintegration complex was estimated by the formation of 2-LTR circle forms of HIV-1 DNA and also by in situ PCR techniques. RESULTS: Arylene bis(methyl ketone) compounds with a nitrogenous third subsituent, especially a pyrimidinic side-chain, inhibited HIV-1 replication in human monocytes at an IC50 as low as 1 nM. These compounds did not block HIV-1 replication in peripheral blood lymphocyte cultures. The inhibitory effect observed in monocyte cultures appeared in the context of markedly reduced nuclear importation of viral DNA in the presence of the drug. No cytotoxic effects of the compounds was observed in vitro at concentrations as high as 10 microM. An amidinohydrazone derivative of the most active compound was about 100 times less active than the parent, indicating that carbonyl groups were instrumental in the antiviral effect. CONCLUSIONS: These early results suggest that retroviral replication in nondividing cells is susceptible to pharmaceutical intervention targeted against the NLS activity of HIV-1 proteins in the viral preintegration complex. The compounds described efficiently block translocation of viral DNA to the nuclei of infected primary monocytes, and inhibit viral replication. This inhibition is effective only in nondividing cells and is not seen in proliferating cultures, such as activated PBLs. Thus, drugs that target HIV-1 NLS may be useful to specifically block the macrophage arm of HIV infection and could thereby be of value in treating macrophage-specific manifestations of HIV disease, such as HIV-1 dementia. In combination with other drugs, potential therapeutics exploiting this target may also help to control the progression of HIV-1 infection and disease.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bukrinsky M. I., Haggerty S., Dempsey M. P., Sharova N., Adzhubel A., Spitz L., Lewis P., Goldfarb D., Emerman M., Stevenson M. A nuclear localization signal within HIV-1 matrix protein that governs infection of non-dividing cells. Nature. 1993 Oct 14;365(6447):666–669. doi: 10.1038/365666a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukrinsky M. I., Sharova N., Dempsey M. P., Stanwick T. L., Bukrinskaya A. G., Haggerty S., Stevenson M. Active nuclear import of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 preintegration complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6580–6584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukrinsky M. I., Sharova N., McDonald T. L., Pushkarskaya T., Tarpley W. G., Stevenson M. Association of integrase, matrix, and reverse transcriptase antigens of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 with viral nucleic acids following acute infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6125–6129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukrinsky M. I., Stanwick T. L., Dempsey M. P., Stevenson M. Quiescent T lymphocytes as an inducible virus reservoir in HIV-1 infection. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):423–427. doi: 10.1126/science.1925601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T. M., Powell D., Lightfoote M., Koenig S., Fauci A. S., Benn S., Rabson A., Daugherty D., Gendelman H. E., Hoggan M. D. Biological and biochemical characterization of a cloned Leu-3- cell surviving infection with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome retrovirus. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):280–290. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner S., Markovits P., Markovitz D. M., Kaplan M. H., Gallo R. C., Popovic M. The role of mononuclear phagocytes in HTLV-III/LAV infection. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):215–219. doi: 10.1126/science.3014648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Baca L. M., Weiser B., Burger H., Kalter D. C., Meltzer M. S. The macrophage in the persistence and pathogenesis of HIV infection. AIDS. 1989 Aug;3(8):475–495. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198908000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Martin M. A., Ferrua C., Mitra R., Phipps T., Wahl L. A., Lane H. C., Fauci A. S., Burke D. S. Efficient isolation and propagation of human immunodeficiency virus on recombinant colony-stimulating factor 1-treated monocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1428–1441. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulizia J., Dempsey M. P., Sharova N., Bukrinsky M. I., Spitz L., Goldfarb D., Stevenson M. Reduced nuclear import of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 preintegration complexes in the presence of a prototypic nuclear targeting signal. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):2021–2025. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.2021-2025.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzinger N. K., Bukrinsky M. I., Haggerty S. A., Ragland A. M., Kewalramani V., Lee M. A., Gendelman H. E., Ratner L., Stevenson M., Emerman M. The Vpr protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 influences nuclear localization of viral nucleic acids in nondividing host cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):7311–7315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho W. Z., Cherukuri R., Douglas S. D. The macrophage and HIV-1. Immunol Ser. 1994;60:569–587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Dal Canto M. C., Pezeshkpour G. H., Yungbluth M., Janotta F., Aksamit A., Martin M. A., Fauci A. S. Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1089–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.3016903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyanagi Y., O'Brien W. A., Zhao J. Q., Golde D. W., Gasson J. C., Chen I. S. Cytokines alter production of HIV-1 from primary mononuclear phagocytes. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1673–1675. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layne S. P., Merges M. J., Dembo M., Spouge J. L., Conley S. R., Moore J. P., Raina J. L., Renz H., Gelderblom H. R., Nara P. L. Factors underlying spontaneous inactivation and susceptibility to neutralization of human immunodeficiency virus. Virology. 1992 Aug;189(2):695–714. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90593-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P. F., Emerman M. Passage through mitosis is required for oncoretroviruses but not for the human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):510–516. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.510-516.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G., Simm M., Potash M. J., Volsky D. J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 DNA synthesis, integration, and efficient viral replication in growth-arrested T cells. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):3969–3977. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.3969-3977.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer M. S., Kornbluth R. S., Hansen B., Dhawan S., Gendelman H. E. HIV infection of the lung. Role of virus-infected macrophages in the pathophysiology of pulmonary disease. Chest. 1993 Feb;103(2 Suppl):103S–108S. doi: 10.1378/chest.103.2.103s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. D., Warmerdam M. T., Gaston I., Greene W. C., Feinberg M. B. The human immunodeficiency virus-1 nef gene product: a positive factor for viral infection and replication in primary lymphocytes and macrophages. J Exp Med. 1994 Jan 1;179(1):101–113. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuya H., Yarchoan R., Kageyama S., Broder S. Targeted therapy of human immunodeficiency virus-related disease. FASEB J. 1991 Jul;5(10):2369–2381. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.10.1712326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia B. A., Jordan B. D., Price R. W. The AIDS dementia complex: I. Clinical features. Ann Neurol. 1986 Jun;19(6):517–524. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuovo G. J., Gallery F., MacConnell P., Becker J., Bloch W. An improved technique for the in situ detection of DNA after polymerase chain reaction amplification. Am J Pathol. 1991 Dec;139(6):1239–1244. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuovo G. J., Gallery F., MacConnell P., Braun A. In situ detection of polymerase chain reaction-amplified HIV-1 nucleic acids and tumor necrosis factor-alpha RNA in the central nervous system. Am J Pathol. 1994 Apr;144(4):659–666. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuovo G. J., Margiotta M., MacConnell P., Becker J. Rapid in situ detection of PCR-amplified HIV-1 DNA. Diagn Mol Pathol. 1992 Jun;1(2):98–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo G., Graziosi C., Demarest J. F., Butini L., Montroni M., Fox C. H., Orenstein J. M., Kotler D. P., Fauci A. S. HIV infection is active and progressive in lymphoid tissue during the clinically latent stage of disease. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):355–358. doi: 10.1038/362355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearce T. E., Nowakowski M., Eden E., Huang Z. B., Steiner P., Shahabuddin M., Potash M. J., Volsky D. J. Uniform detection of HIV-1 in alveolar macrophages of pediatric but not adult AIDS patients. J Leukoc Biol. 1993 Jun;53(6):722–726. doi: 10.1002/jlb.53.6.722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Gartner S. Isolation of HIV-1 from monocytes but not T lymphocytes. Lancet. 1987 Oct 17;2(8564):916–916. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91403-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe T., Reynolds T. C., Yu G., Brown P. O. Integration of murine leukemia virus DNA depends on mitosis. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2099–2108. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05858.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos M. T., Lange J. M., de Goede R. E., Coutinho R. A., Schellekens P. T., Miedema F., Tersmette M. Viral phenotype and immune response in primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;165(3):427–432. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.3.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg Z. F., Fauci A. S. Immunopathogenic mechanisms of HIV infection: cytokine induction of HIV expression. Immunol Today. 1990 May;11(5):176–180. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90070-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin S. Z., Rose R. M., Groopman J. E., Markham P. D., Gallo R. C. Human T lymphotropic virus type III infection of human alveolar macrophages. Blood. 1986 Jul;68(1):281–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuitemaker H., Koot M., Kootstra N. A., Dercksen M. W., de Goede R. E., van Steenwijk R. P., Lange J. M., Schattenkerk J. K., Miedema F., Tersmette M. Biological phenotype of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 clones at different stages of infection: progression of disease is associated with a shift from monocytotropic to T-cell-tropic virus population. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1354–1360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1354-1360.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuitemaker H., Kootstra N. A., Koppelman M. H., Bruisten S. M., Huisman H. G., Tersmette M., Miedema F. Proliferation-dependent HIV-1 infection of monocytes occurs during differentiation into macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1154–1160. doi: 10.1172/JCI115697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuitemaker H., Meyaard L., Kootstra N. A., Dubbes R., Otto S. A., Tersmette M., Heeney J. L., Miedema F. Lack of T cell dysfunction and programmed cell death in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected chimpanzees correlates with absence of monocytotropic variants. J Infect Dis. 1993 Nov;168(5):1140–1147. doi: 10.1093/infdis/168.5.1140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spina C. A., Kwoh T. J., Chowers M. Y., Guatelli J. C., Richman D. D. The importance of nef in the induction of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication from primary quiescent CD4 lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1994 Jan 1;179(1):115–123. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M., Bukrinsky M., Haggerty S. HIV-1 replication and potential targets for intervention. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Feb;8(2):107–117. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich P., Cerami A. Trypanocidal 1,3-arylene diketone bis(guanylhydrazone)s. Structure-activity relationships among substituted and heterocyclic analogues. J Med Chem. 1984 Jan;27(1):35–40. doi: 10.1021/jm00367a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins B. A., Dorn H. H., Kelly W. B., Armstrong R. C., Potts B. J., Michaels F., Kufta C. V., Dubois-Dalcq M. Specific tropism of HIV-1 for microglial cells in primary human brain cultures. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):549–553. doi: 10.1126/science.2200125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg J. B., Matthews T. J., Cullen B. R., Malim M. H. Productive human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection of nonproliferating human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Dec 1;174(6):1477–1482. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.6.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Nelson J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus: infection of the nervous system. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;160:157–172. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75267-4_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Schrier R. D., Nelson J. A., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Cellular localization of human immunodeficiency virus infection within the brains of acquired immune deficiency syndrome patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7089–7093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarchoan R., Pluda J. M., Perno C. F., Mitsuya H., Broder S. Anti-retroviral therapy of human immunodeficiency virus infection: current strategies and challenges for the future. Blood. 1991 Aug 15;78(4):859–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zack J. A., Arrigo S. J., Weitsman S. R., Go A. S., Haislip A., Chen I. S. HIV-1 entry into quiescent primary lymphocytes: molecular analysis reveals a labile, latent viral structure. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90802-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu T., Mo H., Wang N., Nam D. S., Cao Y., Koup R. A., Ho D. D. Genotypic and phenotypic characterization of HIV-1 patients with primary infection. Science. 1993 Aug 27;261(5125):1179–1181. doi: 10.1126/science.8356453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Schwedler U., Kornbluth R. S., Trono D. The nuclear localization signal of the matrix protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 allows the establishment of infection in macrophages and quiescent T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):6992–6996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.6992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]