Abstract
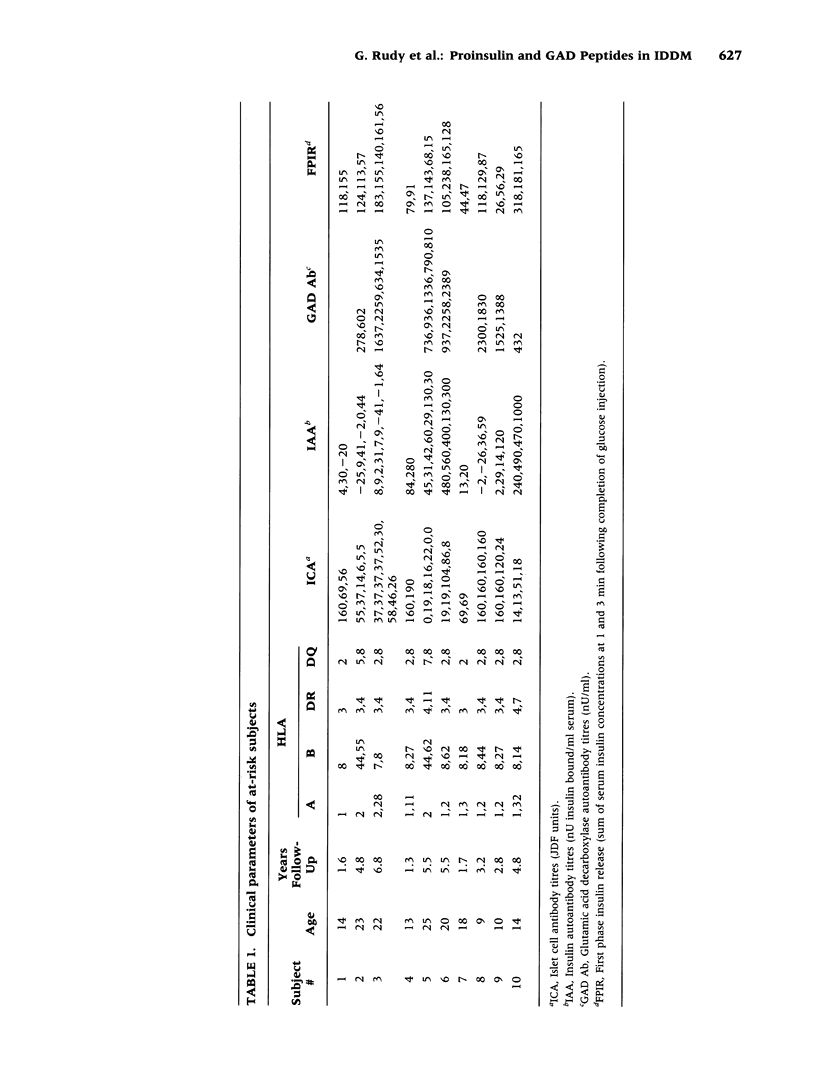
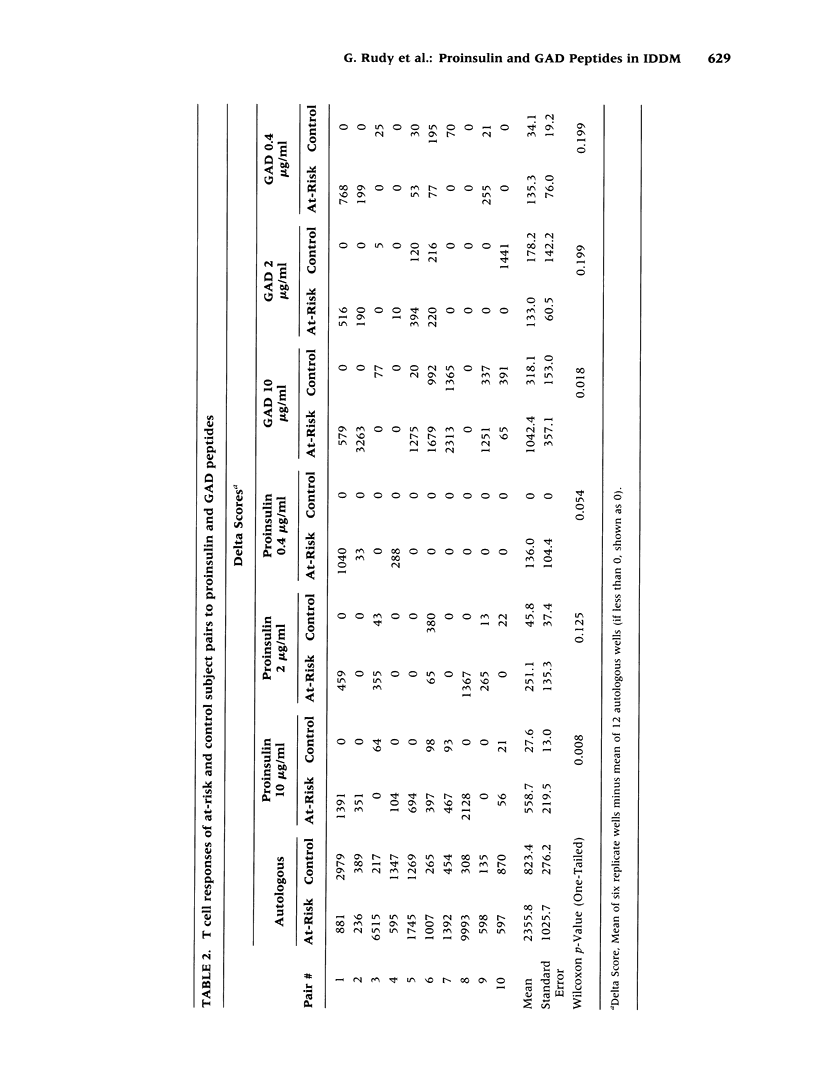
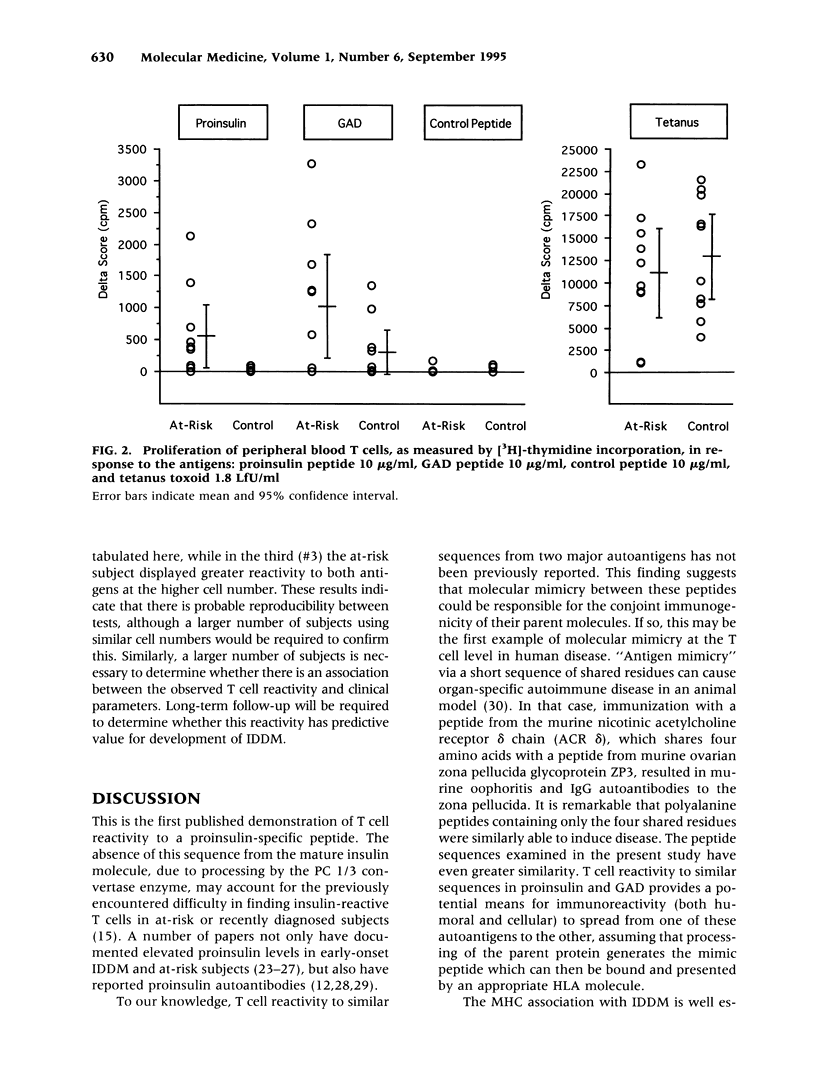
BACKGROUND: Insulin (1) and glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) (2) are both autoantigens in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM), but no molecular mechanism has been proposed for their association. We have identified a 13 amino acid peptide of proinsulin (amino acids 24-36) that bears marked similarity to a peptide of GAD65 (amino acids 506-518) (G. Rudy, unpublished). In order to test the hypothesis that this region of similarity is implicated in the pathogenesis of IDDM, we assayed T cell reactivity to these two peptides in subjects at risk for IDDM. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Subjects at risk for IDDM were islet cell antibody (ICA)-positive, first degree relatives of people with insulin-dependent diabetes. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from 10 pairs of at-risk and HLA-DR matched control subjects were tested in an in vitro proliferation assay. RESULTS: Reactivity to both proinsulin and GAD peptides was significantly greater among at-risk subjects than controls (proinsulin; p < 0.008; GAD; p < 0.018). In contrast to reactivity to the GAD peptide, reactivity to the proinsulin peptide was almost entirely confined to the at-risk subjects. CONCLUSIONS: This is the first demonstration of T cell reactivity to a proinsulin-specific peptide. In addition, it is the first example of reactivity to a minimal peptide region shared between two human autoimmune disease-associated self antigens. Mimicry between these similar peptides may provide a molecular basis for the conjoint autoantigenicity of proinsulin and GAD in IDDM.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson M. A., Bowman M. A., Campbell L., Darrow B. L., Kaufman D. L., Maclaren N. K. Cellular immunity to a determinant common to glutamate decarboxylase and coxsackie virus in insulin-dependent diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1994 Nov;94(5):2125–2129. doi: 10.1172/JCI117567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baekkeskov S., Aanstoot H. J., Christgau S., Reetz A., Solimena M., Cascalho M., Folli F., Richter-Olesen H., De Camilli P., Camilli P. D. Identification of the 64K autoantigen in insulin-dependent diabetes as the GABA-synthesizing enzyme glutamic acid decarboxylase. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):151–156. doi: 10.1038/347151a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo G. F., Dean B. M., McNally J. M., MacKay E. H., Swift P. G., Gamble D. R. In situ characterization of autoimmune phenomena and expression of HLA molecules in the pancreas in diabetic insulitis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Aug 8;313(6):353–360. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198508083130604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler M. H., Solimena M., Dirkx R., Jr, Hayday A., De Camilli P. Identification of a dominant epitope of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD-65) recognized by autoantibodies in stiff-man syndrome. J Exp Med. 1993 Dec 1;178(6):2097–2106. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.6.2097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhmer K., Keilacker H., Kuglin B., Hübinger A., Bertrams J., Gries F. A., Kolb H. Proinsulin autoantibodies are more closely associated with type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus than insulin autoantibodies. Diabetologia. 1991 Nov;34(11):830–834. doi: 10.1007/BF00408359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Cutri A., Wilkinson D., Boyd A. W., Harrison L. C. Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 is induced on isolated endocrine islet cells by cytokines but not by reovirus infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4282–4286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. L., Oxbrow L., West J., Harrison L. C. Regulation of MHC protein expression in pancreatic beta-cells by interferon-gamma and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Feb;2(2):101–107. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-2-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson H. W., Rhodes C. J., Hutton J. C. Intraorganellar calcium and pH control proinsulin cleavage in the pancreatic beta cell via two distinct site-specific endopeptidases. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):93–96. doi: 10.1038/333093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng H., Apple R., Clare-Salzler M., Trembleau S., Mathis D., Adorini L., Sercarz E. Determinant capture as a possible mechanism of protection afforded by major histocompatibility complex class II molecules in autoimmune disease. J Exp Med. 1993 Nov 1;178(5):1675–1680. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.5.1675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulis A. K., McGill M., Farquharson M. A. Insulitis in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in man--macrophages, lymphocytes, and interferon-gamma containing cells. J Pathol. 1991 Oct;165(2):97–103. doi: 10.1002/path.1711650203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham S., Wang E. C., Jenkins O., Borysiewicz L. K. Analysis of the human T-cell response to picornaviruses: identification of T-cell epitopes close to B-cell epitopes in poliovirus. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1627–1637. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1627-1637.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa T., Miyazaki A., Miyagawa J., Tamura S., Inada M., Yamada K., Shinji Y., Katsura H., Yamagata K., Itoh N. Examination of islets in the pancreas biopsy specimens from newly diagnosed type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1990 Feb;33(2):105–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00401048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., Chu S. X., DeAizpurua H. J., Graham M., Honeyman M. C., Colman P. G. Islet-reactive T cells are a marker of preclinical insulin-dependent diabetes. J Clin Invest. 1992 Apr;89(4):1161–1165. doi: 10.1172/JCI115698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C., De Aizpurua H., Loudovaris T., Campbell I. L., Cebon J. S., Tait B. D., Colman P. G. Reactivity to human islets and fetal pig proislets by peripheral blood mononuclear cells from subjects with preclinical and clinical insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1991 Sep;40(9):1128–1133. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.9.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison L. C. Islet cell antigens in insulin-dependent diabetes: Pandora's box revisited. Immunol Today. 1992 Sep;13(9):348–352. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90170-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartling S. G., Lindgren F., Dahlqvist G., Persson B., Binder C. Elevated proinsulin in healthy siblings of IDDM patients independent of HLA identity. Diabetes. 1989 Oct;38(10):1271–1274. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.10.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaton D. A., Millward B. A., Gray I. P., Tun Y., Hales C. N., Pyke D. A., Leslie R. D. Increased proinsulin levels as an early indicator of B-cell dysfunction in non-diabetic twins of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1988 Mar;31(3):182–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00276853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honeyman M. C., Cram D. S., Harrison L. C. Glutamic acid decarboxylase 67-reactive T cells: a marker of insulin-dependent diabetes. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):535–540. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honeyman M. C., Harrison L. C. The immunologic insult in type 1 diabetes. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1993;14(3):253–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00195977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtenbach U., Lier E., Adorini L., Nagy Z. A. Prevention of autoimmune diabetes in non-obese diabetic mice by treatment with a class II major histocompatibility complex-blocking peptide. J Exp Med. 1993 May 1;177(5):1499–1504. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.5.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänninen A., Jalkanen S., Salmi M., Toikkanen S., Nikolakaros G., Simell O. Macrophages, T cell receptor usage, and endothelial cell activation in the pancreas at the onset of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):1901–1910. doi: 10.1172/JCI116067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh N., Hanafusa T., Miyazaki A., Miyagawa J., Yamagata K., Yamamoto K., Waguri M., Imagawa A., Tamura S., Inada M. Mononuclear cell infiltration and its relation to the expression of major histocompatibility complex antigens and adhesion molecules in pancreas biopsy specimens from newly diagnosed insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients. J Clin Invest. 1993 Nov;92(5):2313–2322. doi: 10.1172/JCI116835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. L., Clare-Salzler M., Tian J., Forsthuber T., Ting G. S., Robinson P., Atkinson M. A., Sercarz E. E., Tobin A. J., Lehmann P. V. Spontaneous loss of T-cell tolerance to glutamic acid decarboxylase in murine insulin-dependent diabetes. Nature. 1993 Nov 4;366(6450):69–72. doi: 10.1038/366069a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuglin B., Gries F. A., Kolb H. Evidence of IgG autoantibodies against human proinsulin in patients with IDDM before insulin treatment. Diabetes. 1988 Jan;37(1):130–132. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.1.130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuglin B., Halder B., Bertrams J., Grüneklee D., Gries F. A., Kolb H. Proinsulin autoantibodies: association with type I diabetes but not with islet cell antibodies, insulin autoantibodies or HLA-DR type. J Autoimmun. 1990 Oct;3(5):573–577. doi: 10.1016/s0896-8411(05)80023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R. H., Mamula M. J., Hardin J. A., Janeway C. A., Jr Induction of autoreactive B cells allows priming of autoreactive T cells. J Exp Med. 1991 Jun 1;173(6):1433–1439. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindgren F. A., Hartling S. G., Persson B. E., Röder M. E., Snellman K., Binder C., Dahlquist G. Proinsulin levels in newborn siblings of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic children and their mothers. Diabetologia. 1993 Jun;36(6):560–563. doi: 10.1007/BF02743274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmann T., Leslie R. D., Hawa M., Geysen M., Rodda S., Londei M. Immunodominant epitopes of glutamic acid decarboxylase 65 and 67 in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Lancet. 1994 Jun 25;343(8913):1607–1608. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)93061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo A. M., Garza K. M., Hunt D., Tung K. S. Antigen mimicry in autoimmune disease sharing of amino acid residues critical for pathogenic T cell activation. J Clin Invest. 1993 Nov;92(5):2117–2123. doi: 10.1172/JCI116812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. P., Asplin C. M., Clemons P., Lyen K., Tatpati O., Raghu P. K., Paquette T. L. Insulin antibodies in insulin-dependent diabetics before insulin treatment. Science. 1983 Dec 23;222(4630):1337–1339. doi: 10.1126/science.6362005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich E. P., von Grafenstein H., Barlow A., Swenson K. E., Williams K., Janeway C. A., Jr Self peptides isolated from MHC glycoproteins of non-obese diabetic mice. J Immunol. 1994 Mar 1;152(5):2279–2288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter W., Shi Y., Baekkeskov S. Autoreactive epitopes defined by diabetes-associated human monoclonal antibodies are localized in the middle and C-terminal domains of the smaller form of glutamate decarboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2832–2836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero P., Corradin G., Luescher I. F., Maryanski J. L. H-2Kd-restricted antigenic peptides share a simple binding motif. J Exp Med. 1991 Sep 1;174(3):603–612. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.3.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidli R. S., DeAizpurua H. J., Harrison L. C., Colman P. G. Antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase in at-risk and clinical insulin-dependent diabetic subjects: relationship to age, sex and islet cell antibody status, and temporal profile. J Autoimmun. 1994 Feb;7(1):55–66. doi: 10.1006/jaut.1994.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimoda S., Nakamura M., Ishibashi H., Hayashida K., Niho Y. HLA DRB4 0101-restricted immunodominant T cell autoepitope of pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in primary biliary cirrhosis: evidence of molecular mimicry in human autoimmune diseases. J Exp Med. 1995 May 1;181(5):1835–1845. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.5.1835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley R. K., Sutherland D. E., Goetz F., Michael A. F. Recurrent diabetes mellitus in the pancreas iso- and allograft. A light and electron microscopic and immunohistochemical analysis of four cases. Lab Invest. 1985 Aug;53(2):132–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snorgaard O., Hartling S. G., Binder C. Proinsulin and C-peptide at onset and during 12 months cyclosporin treatment of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 1990 Jan;33(1):36–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00586459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spinas G. A., Snorgaard O., Hartling S. G., Oberholzer M., Berger W. Elevated proinsulin levels related to islet cell antibodies in first-degree relatives of IDDM patients. Diabetes Care. 1992 May;15(5):632–637. doi: 10.2337/diacare.15.5.632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taki T., Nagata M., Ogawa W., Hatamori N., Hayakawa M., Hari J., Shii K., Baba S., Yokono K. Prevention of cyclophosphamide-induced and spontaneous diabetes in NOD/Shi/Kbe mice by anti-MHC class I Kd monoclonal antibody. Diabetes. 1991 Sep;40(9):1203–1209. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.9.1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian J., Lehmann P. V., Kaufman D. L. T cell cross-reactivity between coxsackievirus and glutamate decarboxylase is associated with a murine diabetes susceptibility allele. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1979–1984. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisch R., Yang X. D., Singer S. M., Liblau R. S., Fugger L., McDevitt H. O. Immune response to glutamic acid decarboxylase correlates with insulitis in non-obese diabetic mice. Nature. 1993 Nov 4;366(6450):72–75. doi: 10.1038/366072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegmann D. R., Norbury-Glaser M., Daniel D. Insulin-specific T cells are a predominant component of islet infiltrates in pre-diabetic NOD mice. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Aug;24(8):1853–1857. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler A. G., Hillebrand B., Rabl W., Mayrhofer M., Hummel M., Mollenhauer U., Vordemann J., Lenz A., Standl E. On the appearance of islet associated autoimmunity in offspring of diabetic mothers: a prospective study from birth. Diabetologia. 1993 May;36(5):402–408. doi: 10.1007/BF00402275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




