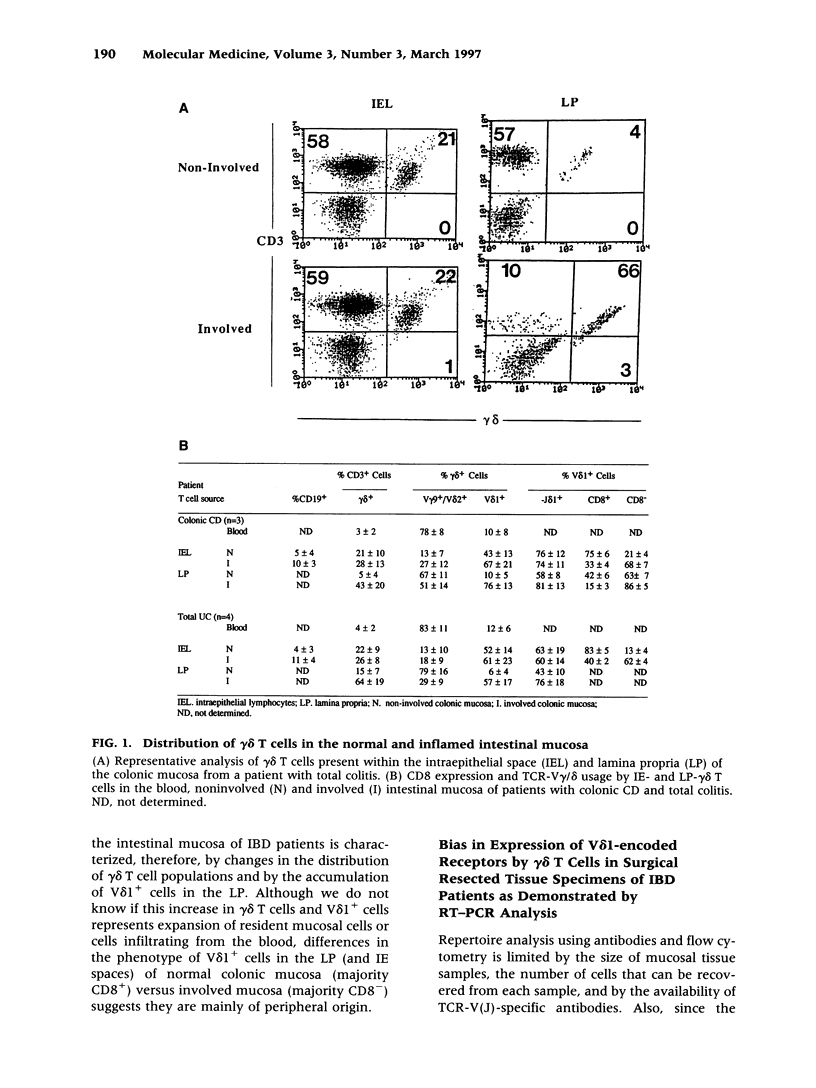
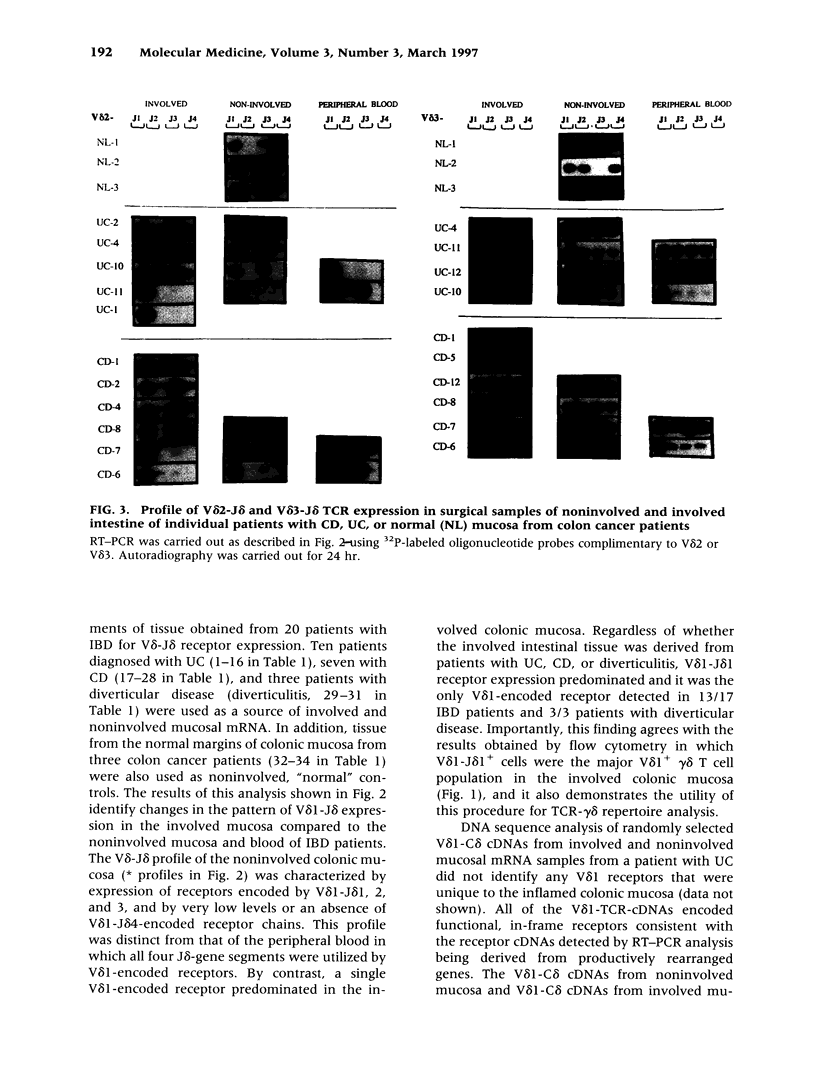
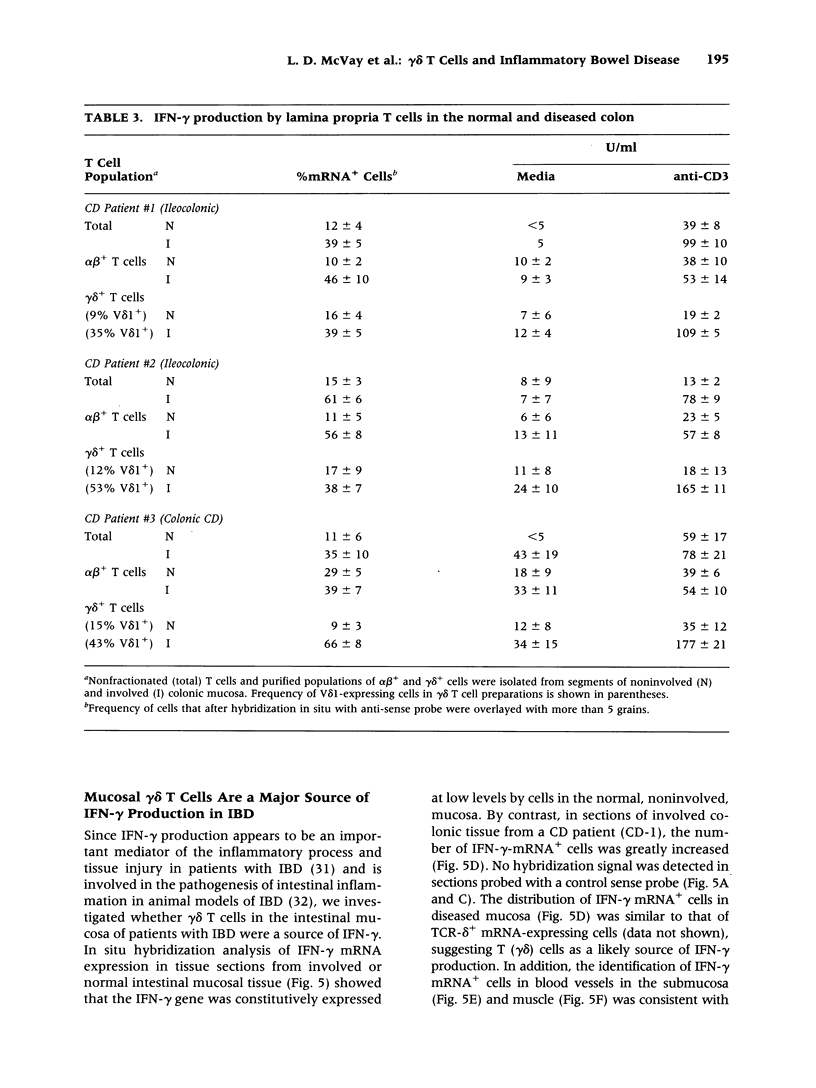
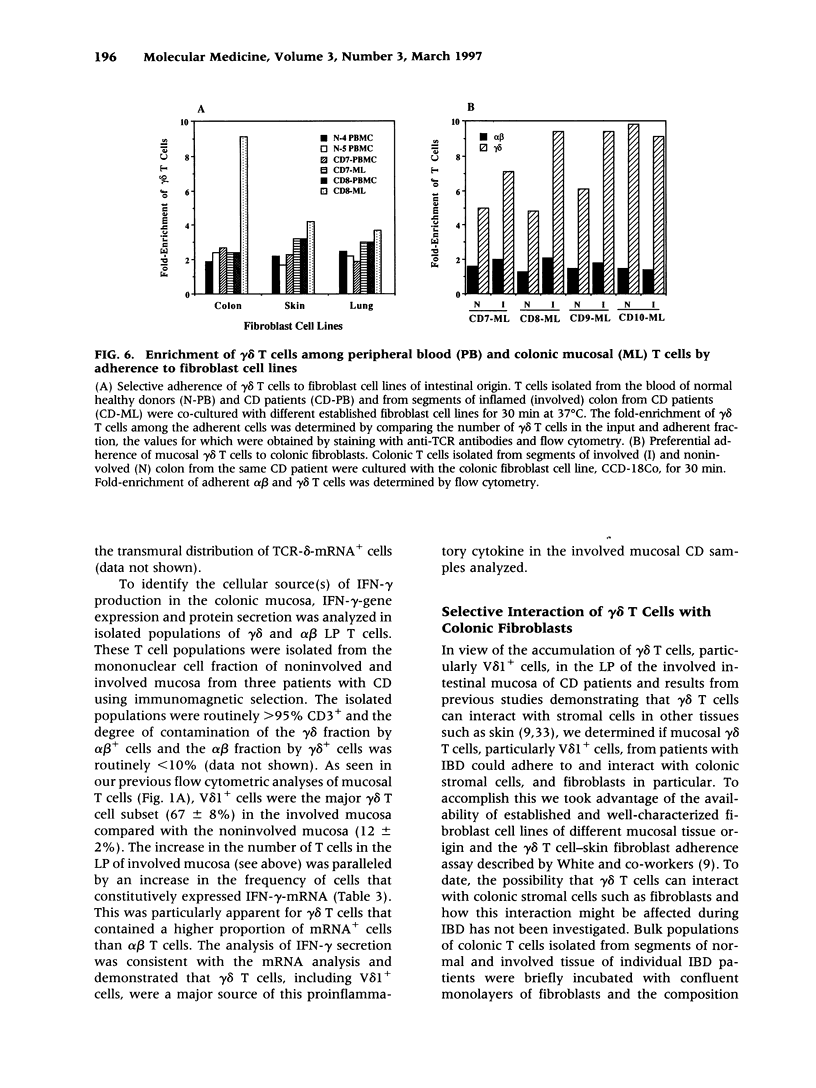
Abstract
BACKGROUND: Although gamma delta T cells are a major component of the human intestinal mucosa, it is not clear what role they play in mucosal immunity or if they are involved in the disease process of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). MATERIALS AND METHODS: Flow cytometry and reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assays were used to identify quantitative and qualitative changes in the repertoire of gamma delta T cells present in surgical and/or biopsy samples or normal and inflamed colon from individual patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) or Crohn's disease (CD). Cytokine production and the ability to adhere to and interact with colonic fibroblasts were used to compare the functional properties of gamma delta T cells isolated from the normal and diseased colonic mucosa. RESULTS: Increased numbers of gamma delta T cells localized in areas of inflammation and tissue injury were found in the majority of patients, irrespective of the type of IBD present. This expansion was attributable to an increase in V delta 1+ cells expressing a V delta 1-(D delta 3)-J delta 1-encoded T cell receptor and was seen in patients with severe disease as well as those with newly diagnosed or less severe forms of IBD. Among T cells present in the inflamed mucosa of patients with CD, gamma delta T cells, particularly V delta 1+ cells, were a major source of the proinflammatory cytokine interferon-gamma and could interact with colonic fibroblasts. CONCLUSIONS: Our results demonstrate that the chronic inflammatory immune response characteristic of IBD is associated with distinct changes in the number, distribution, composition, and function of mucosal gamma delta T cells. Through the production of cytokines and physical interaction with other cells, gamma delta T cells can perform an immunoregulatory function and contribute to the pathophysiology of IBDs.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boismenu R., Havran W. L. Modulation of epithelial cell growth by intraepithelial gamma delta T cells. Science. 1994 Nov 18;266(5188):1253–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.7973709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst J., van Dongen J. J., Bolhuis R. L., Peters P. J., Hafler D. A., de Vries E., van de Griend R. J. Distinct molecular forms of human T cell receptor gamma/delta detected on viable T cells by a monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1625–1644. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boullier S., Cochet M., Poccia F., Gougeon M. L. CDR3-independent gamma delta V delta 1+ T cell expansion in the peripheral blood of HIV-infected persons. J Immunol. 1995 Feb 1;154(3):1418–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brynskov J., Tvede N., Andersen C. B., Vilien M. Increased concentrations of interleukin 1 beta, interleukin-2, and soluble interleukin-2 receptors in endoscopical mucosal biopsy specimens with active inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 1992 Jan;33(1):55–58. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucht A., Söderström K., Hultman T., Uhlén M., Nilsson E., Kiessling R., Grönberg A. T cell receptor diversity and activation markers in the V delta 1 subset of rheumatoid synovial fluid and peripheral blood T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Feb;22(2):567–574. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull D. M., Bookman M. A. Isolation and functional characterization of human intestinal mucosal lymphoid cells. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):966–974. doi: 10.1172/JCI108719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschle M., Campana D., Carding S. R., Richard C., Hoffbrand A. V., Brenner M. K. Interferon gamma inhibits apoptotic cell death in B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Exp Med. 1993 Jan 1;177(1):213–218. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carding S. R., Allan W., McMickle A., Doherty P. C. Activation of cytokine genes in T cells during primary and secondary murine influenza pneumonia. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):475–482. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carding S. R., Kyes S., Jenkinson E. J., Kingston R., Bottomly K., Owen J. J., Hayday A. C. Developmentally regulated fetal thymic and extrathymic T-cell receptor gamma delta gene expression. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1304–1315. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carding S. R., McNamara J. G., Pan M., Bottomly K. Characterization of gamma/delta T cell clones isolated from human fetal liver and thymus. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jun;20(6):1327–1335. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chowers Y., Holtmeier W., Harwood J., Morzycka-Wroblewska E., Kagnoff M. F. The V delta 1 T cell receptor repertoire in human small intestine and colon. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):183–190. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Maria R., Fais S., Silvestri M., Frati L., Pallone F., Santoni A., Testi R. Continuous in vivo activation and transient hyporesponsiveness to TcR/CD3 triggering of human gut lamina propria lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Dec;23(12):3104–3108. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830231209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deem R. L., Shanahan F., Targan S. R. Triggered human mucosal T cells release tumour necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma which kill human colonic epithelial cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jan;83(1):79–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05592.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deusch K., Lüling F., Reich K., Classen M., Wagner H., Pfeffer K. A major fraction of human intraepithelial lymphocytes simultaneously expresses the gamma/delta T cell receptor, the CD8 accessory molecule and preferentially uses the V delta 1 gene segment. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Apr;21(4):1053–1059. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Allan W., Eichelberger M., Carding S. R. Roles of alpha beta and gamma delta T cell subsets in viral immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:123–151. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.001011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchmann R., Kaiser I., Hermann E., Mayet W., Ewe K., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. Tolerance exists towards resident intestinal flora but is broken in active inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) Clin Exp Immunol. 1995 Dec;102(3):448–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb03836.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert E. C. Proliferative responses of human intraepithelial lymphocytes to various T-cell stimuli. Gastroenterology. 1989 Dec;97(6):1372–1381. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)90379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima K., Masuda T., Ohtani H., Sasaki I., Funayama Y., Matsuno S., Nagura H. Immunohistochemical characterization, distribution, and ultrastructure of lymphocytes bearing T-cell receptor gamma/delta in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 1991 Sep;101(3):670–678. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90524-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuss I. J., Neurath M., Boirivant M., Klein J. S., de la Motte C., Strong S. A., Fiocchi C., Strober W. Disparate CD4+ lamina propria (LP) lymphokine secretion profiles in inflammatory bowel disease. Crohn's disease LP cells manifest increased secretion of IFN-gamma, whereas ulcerative colitis LP cells manifest increased secretion of IL-5. J Immunol. 1996 Aug 1;157(3):1261–1270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galéa P., Brezinschek R., Lipsky P. E., Oppenheimer-Marks N. Phenotypic characterization of CD4-/alpha beta TCR+ and gamma delta TCR+ T cells with a transendothelial migratory capacity. J Immunol. 1994 Jul 15;153(2):529–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham M. F., Diegelmann R. F., Elson C. O., Lindblad W. J., Gotschalk N., Gay S., Gay R. Collagen content and types in the intestinal strictures of Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1988 Feb;94(2):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(88)90411-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groh V., Porcelli S., Fabbi M., Lanier L. L., Picker L. J., Anderson T., Warnke R. A., Bhan A. K., Strominger J. L., Brenner M. B. Human lymphocytes bearing T cell receptor gamma/delta are phenotypically diverse and evenly distributed throughout the lymphoid system. J Exp Med. 1989 Apr 1;169(4):1277–1294. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.4.1277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas W., Pereira P., Tonegawa S. Gamma/delta cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:637–685. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.11.040193.003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halstensen T. S., Scott H., Brandtzaeg P. Intraepithelial T cells of the TcR gamma/delta+ CD8- and V delta 1/J delta 1+ phenotypes are increased in coeliac disease. Scand J Immunol. 1989 Dec;30(6):665–672. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1989.tb02474.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromatsu K., Yoshikai Y., Matsuzaki G., Ohga S., Muramori K., Matsumoto K., Bluestone J. A., Nomoto K. A protective role of gamma/delta T cells in primary infection with Listeria monocytogenes in mice. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):49–56. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagnoff M. F. Mucosal immunology: new frontiers. Immunol Today. 1996 Feb;17(2):57–59. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(96)80579-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kersten C. M., McCluskey R. T., Boyle L. A., Kurnick J. T. Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa induce expansion of V delta 2 cells in adult peripheral blood, but of V delta 1 cells in cord blood. J Immunol. 1996 Aug 15;157(4):1613–1619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen-Kragh J., Quayle A., Kalvenes C., Førre O., Sørskaar D., Vinje O., Thoen J., Natvig J. B. T gamma delta cells in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. In the juvenile rheumatoid arthritis synovium the T gamma delta cells express activation antigens and are predominantly V delta 1+, and a significant proportion of these patients have elevated percentages of T gamma delta cells. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Dec;32(6):651–659. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb03207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li B., Rossman M. D., Imir T., Oner-Eyuboglu A. F., Lee C. W., Biancaniello R., Carding S. R. Disease-specific changes in gammadelta T cell repertoire and function in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. J Immunol. 1996 Nov 1;157(9):4222–4229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald T. T., Spencer J. Evidence that activated mucosal T cells play a role in the pathogenesis of enteropathy in human small intestine. J Exp Med. 1988 Apr 1;167(4):1341–1349. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.4.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McVay L. D., Carding S. R., Bottomly K., Hayday A. C. Regulated expression and structure of T cell receptor gamma/delta transcripts in human thymic ontogeny. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):83–91. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07923.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mombaerts P., Mizoguchi E., Grusby M. J., Glimcher L. H., Bhan A. K., Tonegawa S. Spontaneous development of inflammatory bowel disease in T cell receptor mutant mice. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):274–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80069-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullin G. E., Lazenby A. J., Harris M. L., Bayless T. M., James S. P. Increased interleukin-2 messenger RNA in the intestinal mucosal lesions of Crohn's disease but not ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1992 May;102(5):1620–1627. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91722-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munk M. E., Schoel B., Modrow S., Karr R. W., Young R. A., Kaufmann S. H. T lymphocytes from healthy individuals with specificity to self-epitopes shared by the mycobacterial and human 65-kilodalton heat shock protein. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):2844–2849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima S., Roswit W. T., Look D. C., Holtzman M. J. A hierarchy for integrin expression and adhesiveness among T cell subsets that is linked to TCR gene usage and emphasizes V delta 1+ gamma delta T cell adherence and tissue retention. J Immunol. 1995 Aug 1;155(3):1117–1131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirzer U. C., Schürmann G., Post S., Betzler M., Meuer S. C. Differential responsiveness to CD3-Ti vs. CD2-dependent activation of human intestinal T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Oct;20(10):2339–2342. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porcelli S., Brenner M. B., Band H. Biology of the human gamma delta T-cell receptor. Immunol Rev. 1991 Apr;120:137–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1991.tb00591.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powrie F., Leach M. W., Mauze S., Menon S., Caddle L. B., Coffman R. L. Inhibition of Th1 responses prevents inflammatory bowel disease in scid mice reconstituted with CD45RBhi CD4+ T cells. Immunity. 1994 Oct;1(7):553–562. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiao L., Schürmann G., Betzler M., Meuer S. C. Activation and signaling status of human lamina propria T lymphocytes. Gastroenterology. 1991 Dec;101(6):1529–1536. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90388-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosat J. P., MacDonald H. R., Louis J. A. A role for gamma delta + T cells during experimental infection of mice with Leishmania major. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):550–555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rust C., Peña S., Kluin P., Koning F. Gamma delta T cells in coeliac disease. Res Immunol. 1990 Sep;141(7):668–671. doi: 10.1016/0923-2494(90)90079-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadlack B., Merz H., Schorle H., Schimpl A., Feller A. C., Horak I. Ulcerative colitis-like disease in mice with a disrupted interleukin-2 gene. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80067-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartor R. B. Cytokines in intestinal inflammation: pathophysiological and clinical considerations. Gastroenterology. 1994 Feb;106(2):533–539. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90614-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott S., Pandolfi F., Kurnick J. T. Fibroblasts mediate T cell survival: a proposed mechanism for retention of primed T cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1873–1876. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby W. S., Janossy G., Bofill M., Jewell D. P. Intestinal lymphocyte subpopulations in inflammatory bowel disease: an analysis by immunohistological and cell isolation techniques. Gut. 1984 Jan;25(1):32–40. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.1.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sioud M., Kjeldsen-Kragh J., Quayle A., Kalvenes C., Waalen K., Førre O., Natvig J. B. The V delta gene usage by freshly isolated T lymphocytes from synovial fluids in rheumatoid synovitis: a preliminary report. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Apr;31(4):415–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb02787.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeen M. J., Ziegler H. K. Induction of murine peritoneal gamma/delta T cells and their role in resistance to bacterial infection. J Exp Med. 1993 Sep 1;178(3):971–984. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.3.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. D., Bröker B., Moretta L., Ciccone E., Grossi C. E., Edwards J. C., Yüksel F., Colaco B., Worman C., Mackenzie L. T gamma delta cells and their subsets in blood and synovial tissue from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Dec;32(6):585–593. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb03200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer J., Isaacson P. G., Diss T. C., MacDonald T. T. Expression of disulfide-linked and non-disulfide-linked forms of the T cell receptor gamma/delta heterodimer in human intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jul;19(7):1335–1338. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer J., Isaacson P. G., MacDonald T. T., Thomas A. J., Walker-Smith J. A. Gamma/delta T cells and the diagnosis of coeliac disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jul;85(1):109–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb05690.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallmach A., Schuppan D., Riese H. H., Matthes H., Riecken E. O. Increased collagen type III synthesis by fibroblasts isolated from strictures of patients with Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1992 Jun;102(6):1920–1929. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90314-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strober W., Ehrhardt R. O. Chronic intestinal inflammation: an unexpected outcome in cytokine or T cell receptor mutant mice. Cell. 1993 Oct 22;75(2):203–205. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)80062-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strober W., James S. P. The immunologic basis of inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Immunol. 1986 Nov;6(6):415–432. doi: 10.1007/BF00915248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söderström K., Halapi E., Nilsson E., Grönberg A., van Embden J., Klareskog L., Kiessling R. Synovial cells responding to a 65-kDa mycobacterial heat shock protein have a high proportion of a TcR gamma delta subtype uncommon in peripheral blood. Scand J Immunol. 1990 Nov;32(5):503–515. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1990.tb03191.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Targan S. R., Deem R. L., Liu M., Wang S., Nel A. Definition of a lamina propria T cell responsive state. Enhanced cytokine responsiveness of T cells stimulated through the CD2 pathway. J Immunol. 1995 Jan 15;154(2):664–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trejdosiewicz L. K., Calabrese A., Smart C. J., Oakes D. J., Howdle P. D., Crabtree J. E., Losowsky M. S., Lancaster F., Boylston A. W. Gamma delta T cell receptor-positive cells of the human gastrointestinal mucosa: occurrence and V region gene expression in Heliobacter pylori-associated gastritis, coeliac disease and inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Jun;84(3):440–444. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji M., Mombaerts P., Lefrancois L., Nussenzweig R. S., Zavala F., Tonegawa S. Gamma delta T cells contribute to immunity against the liver stages of malaria in alpha beta T-cell-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):345–349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vroom T. M., Scholte G., Ossendorp F., Borst J. Tissue distribution of human gamma delta T cells: no evidence for general epithelial tropism. J Clin Pathol. 1991 Dec;44(12):1012–1017. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.12.1012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B., Korn J. H., Piela-Smith T. H. Preferential adherence of human gamma delta, CD8+, and memory T cells to fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1994 May 15;152(10):4912–4918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]