Abstract
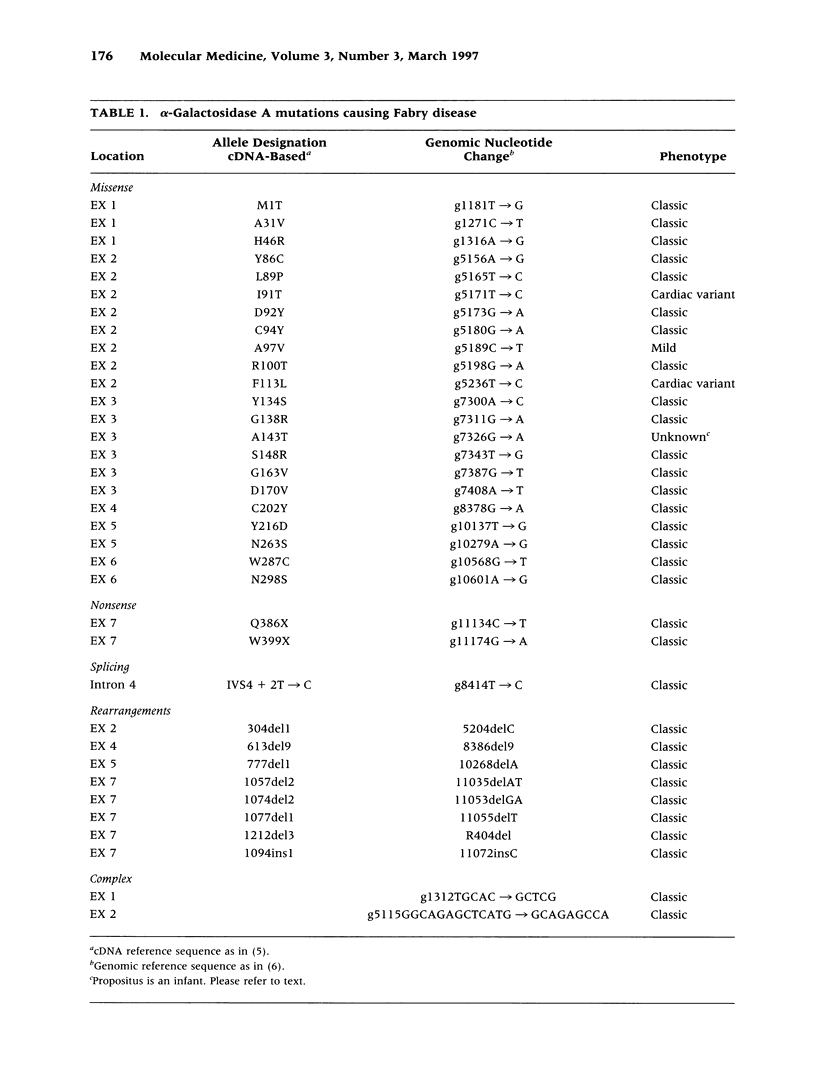
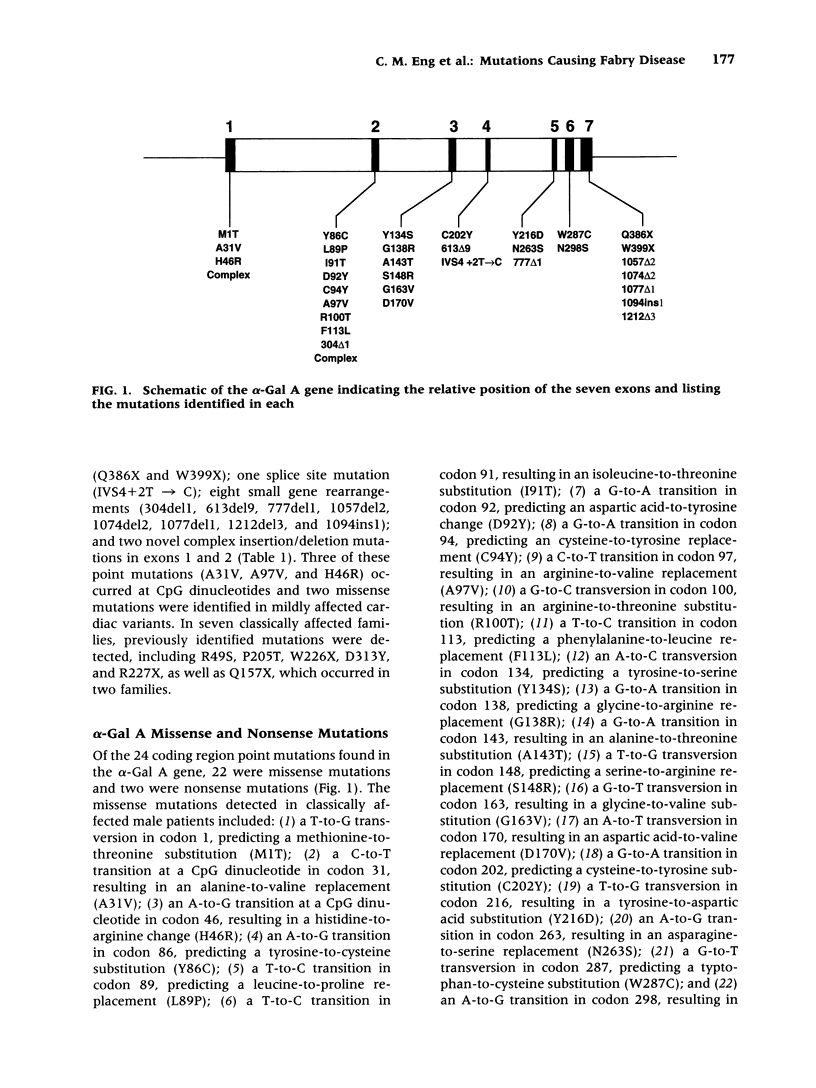
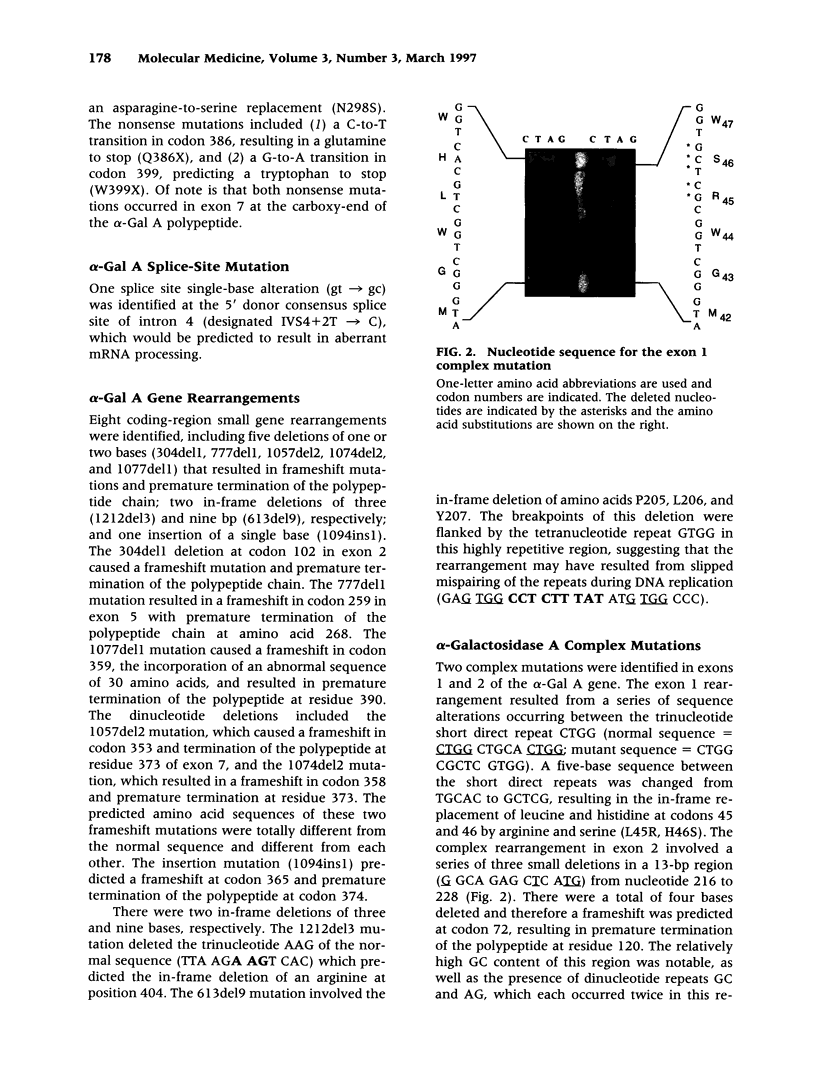
BACKGROUND: Fabry disease, an X-linked inborn error of glycosphingolipid catabolism, results from mutations in the alpha-galactosidase A (alpha-Gal A) gene located at Xq22.1. To determine the nature and frequency of the molecular lesions causing the classical and milder variant Fabry phenotypes and for precise carrier detection, the alpha-Gal A lesions in 42 unrelated Fabry hemizygotes were determined. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Genomic DNA was isolated from affected probands and their family members. The seven alpha-galactosidase A exons and flanking intronic sequences were PCR amplified and the nucleotide sequence was determined by solid-phase direct sequencing. RESULTS: Two patients with the mild cardiac phenotype had missense mutations, I9IT and F113L, respectively. In 38 classically affected patients, 33 new mutations were identified including 20 missense (MIT, A31V, H46R, Y86C, L89P, D92Y, C94Y, A97V, R100T, Y134S, G138R, A143T, S148R, G163V, D170V, C202Y, Y216D, N263S, W287C, and N298S), two nonsense (Q386X, W399X), one splice site mutation (IVS4 + 2T-->C), and eight small exonic insertions or deletions (304del1, 613del9, 777del1, 1057del2, 1074del2, 1077del1, 1212del3, and 1094ins1), which identified exon 7 as a region prone to gene rearrangements. In addition, two unique complex rearrangements consisting of contiguous small insertions and deletions were found in exons 1 and 2 causing L45R/H46S and L120X, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: These studies further define the heterogeneity of mutations causing Fabry disease, permit precise carrier identification and prenatal diagnosis in these families, and facilitate the identification of candidates for enzyme replacement therapy.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker D. F., Hostikka S. L., Zhou J., Chow L. T., Oliphant A. R., Gerken S. C., Gregory M. C., Skolnick M. H., Atkin C. L., Tryggvason K. Identification of mutations in the COL4A5 collagen gene in Alport syndrome. Science. 1990 Jun 8;248(4960):1224–1227. doi: 10.1126/science.2349482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. S., Bishop D. F., Astrin K. H., Kornreich R., Eng C. M., Sakuraba H., Desnick R. J. Fabry disease: six gene rearrangements and an exonic point mutation in the alpha-galactosidase gene. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1390–1399. doi: 10.1172/JCI114027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. F., Calhoun D. H., Bernstein H. S., Hantzopoulos P., Quinn M., Desnick R. J. Human alpha-galactosidase A: nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone encoding the mature enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4859–4863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. F., Kornreich R., Desnick R. J. Structural organization of the human alpha-galactosidase A gene: further evidence for the absence of a 3' untranslated region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3903–3907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. N., Krawczak M. Mechanisms of insertional mutagenesis in human genes causing genetic disease. Hum Genet. 1991 Aug;87(4):409–415. doi: 10.1007/BF00197158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. N., Youssoufian H. The CpG dinucleotide and human genetic disease. Hum Genet. 1988 Feb;78(2):151–155. doi: 10.1007/BF00278187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. P., Eng C. M., Hill J. A., Malcolm S., MacDermot K., Winchester B., Desnick R. J. Fabry disease: fourteen alpha-galactosidase A mutations in unrelated families from the United Kingdom and other European countries. Eur J Hum Genet. 1996;4(4):219–224. doi: 10.1159/000472202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desnick R. J., Allen K. Y., Desnick S. J., Raman M. K., Bernlohr R. W., Krivit W. Fabry's disease: enzymatic diagnosis of hemizygotes and heterozygotes. Alpha-galactosidase activities in plasma, serum, urine, and leukocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Feb;81(2):157–171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng C. M., Desnick R. J. Molecular basis of Fabry disease: mutations and polymorphisms in the human alpha-galactosidase A gene. Hum Mutat. 1994;3(2):103–111. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380030204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng C. M., Niehaus D. J., Enriquez A. L., Burgert T. S., Ludman M. D., Desnick R. J. Fabry disease: twenty-three mutations including sense and antisense CpG alterations and identification of a deletional hot-spot in the alpha-galactosidase A gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Oct;3(10):1795–1799. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.10.1795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng C. M., Resnick-Silverman L. A., Niehaus D. J., Astrin K. H., Desnick R. J. Nature and frequency of mutations in the alpha-galactosidase A gene that cause Fabry disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1993 Dec;53(6):1186–1197. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs R. A., Nguyen P. N., McBride L. J., Koepf S. M., Caskey C. T. Identification of mutations leading to the Lesch-Nyhan syndrome by automated direct DNA sequencing of in vitro amplified cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1919–1923. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostikka S. L., Eddy R. L., Byers M. G., Höyhtyä M., Shows T. B., Tryggvason K. Identification of a distinct type IV collagen alpha chain with restricted kidney distribution and assignment of its gene to the locus of X chromosome-linked Alport syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1606–1610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornreich R., Desnick R. J., Bishop D. F. Nucleotide sequence of the human alpha-galactosidase A gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3301–3302. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornreich R., Desnick R. J. Fabry disease: detection of gene rearrangements in the human alpha-galactosidase A gene by multiplex PCR amplification. Hum Mutat. 1993;2(2):108–111. doi: 10.1002/humu.1380020208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao S., Takenaka T., Maeda M., Kodama C., Tanaka A., Tahara M., Yoshida A., Kuriyama M., Hayashibe H., Sakuraba H. An atypical variant of Fabry's disease in men with left ventricular hypertrophy. N Engl J Med. 1995 Aug 3;333(5):288–293. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199508033330504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira C. P., McGuire M. C., Graeser C., Bartels C. F., Arpagaus M., Van der Spek A. F., Lightstone H., Lockridge O., La Du B. N. Identification of a frameshift mutation responsible for the silent phenotype of human serum cholinesterase, Gly 117 (GGT----GGAG). Am J Hum Genet. 1990 May;46(5):934–942. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pease L. R., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., Yun T. J. Unusual mutation clusters provide insight into class I gene conversion mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4374–4381. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuraba H., Oshima A., Fukuhara Y., Shimmoto M., Nagao Y., Bishop D. F., Desnick R. J., Suzuki Y. Identification of point mutations in the alpha-galactosidase A gene in classical and atypical hemizygotes with Fabry disease. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Nov;47(5):784–789. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetrie D., Vorechovský I., Sideras P., Holland J., Davies A., Flinter F., Hammarström L., Kinnon C., Levinsky R., Bobrow M. The gene involved in X-linked agammaglobulinaemia is a member of the src family of protein-tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1993 Jan 21;361(6409):226–233. doi: 10.1038/361226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamakawa-Kobayashi K., Kobayashi T., Yanagi H., Shimakura Y., Satoh J., Hamaguchi H. A novel complex mutation in the LDL receptor gene probably caused by the simultaneous occurrence of deletion and insertion in the same region. Hum Genet. 1994 Jun;93(6):625–628. doi: 10.1007/BF00201560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Scheidt W., Eng C. M., Fitzmaurice T. F., Erdmann E., Hübner G., Olsen E. G., Christomanou H., Kandolf R., Bishop D. F., Desnick R. J. An atypical variant of Fabry's disease with manifestations confined to the myocardium. N Engl J Med. 1991 Feb 7;324(6):395–399. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199102073240607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



