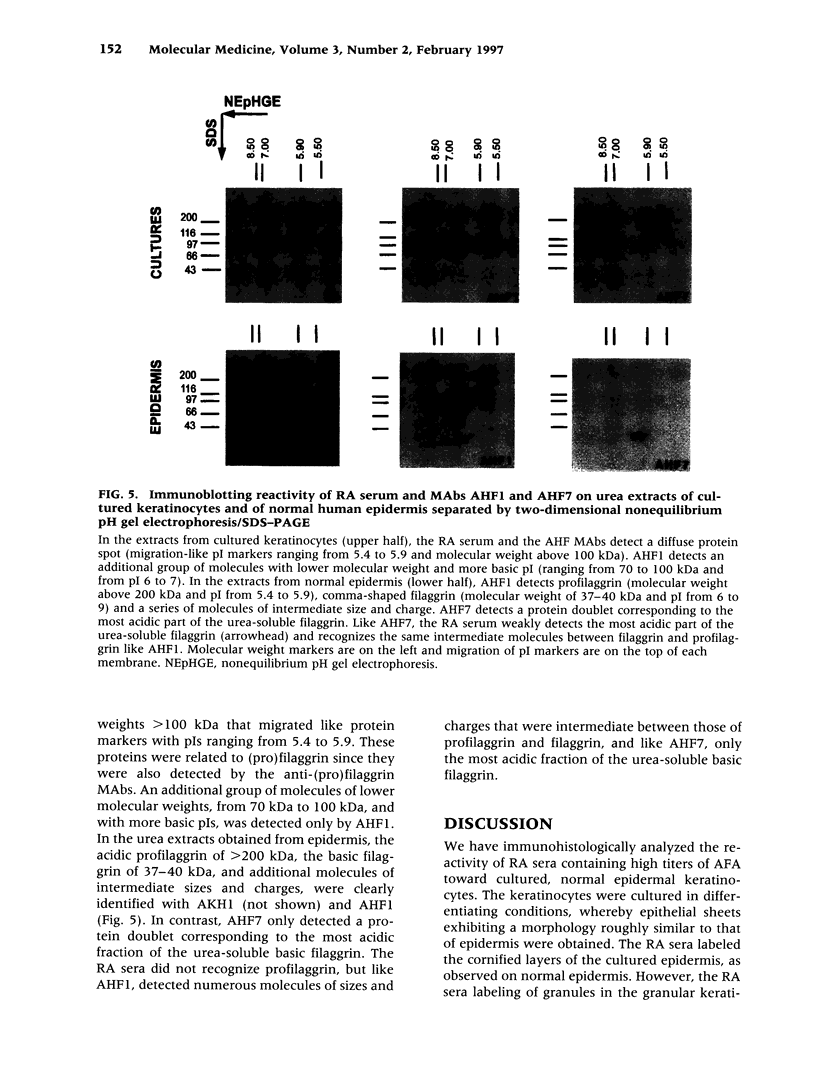
Abstract
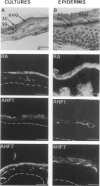
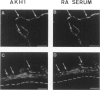
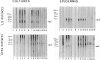
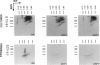
BACKGROUND: The so-called antikeratin antibodies and the antiperinuclear factor are the most specific serological markers of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). They were recently shown to be largely the same autoantibodies and to recognize human epidermal filaggrins and profilaggrin-related proteins of buccal epithelial cells (collectively referred to as (pro)filaggrin). MATERIALS AND METHODS: To further characterize the target antigens, we investigated their expression by normal human epidermal keratinocytes cultured in differentiating conditions, using immunofluorescence and immunoblotting with RA sera and three different monoclonal antibodies to (pro)filaggrin. RESULTS: On the cornified, stratified epithelial sheets obtained in vitro, RA sera with anti(pro)filaggrin autoantibodies (AFA) produced granular staining of the stratum granulosum and diffuse staining of the stratum corneum. The antigens recognized by RA sera strictly colocalized with (pro)filaggrin in keratohyalin granules. Following sequential extraction of the proteins from the epithelial sheets, the RA sera and the three monoclonal antibodies to (pro)filaggrin, recognized a series of low-salt-soluble molecules, including a neutral/acidic isoform of filaggrin and several proteins with sizes and pI intermediates between this isoform and profilaggrin. They also recognized urea-soluble high-molecular-weight profilaggrin-related molecules. CONCLUSIONS: These results show that in vitro epidermal keratinocytes express various molecular forms of (pro) filaggrin that bear epitopes targeted by AFA of RA sera, and that some of these are absent from epidermis. Moreover, these epitopes, which are present on the keratohyalin granules of buccal epithelial cells but not on those of epidermal cells, are present on the granules of the cultured keratinocytes. This work completes the molecular characterization of the proteins targeted by AFA.
Full text
PDF



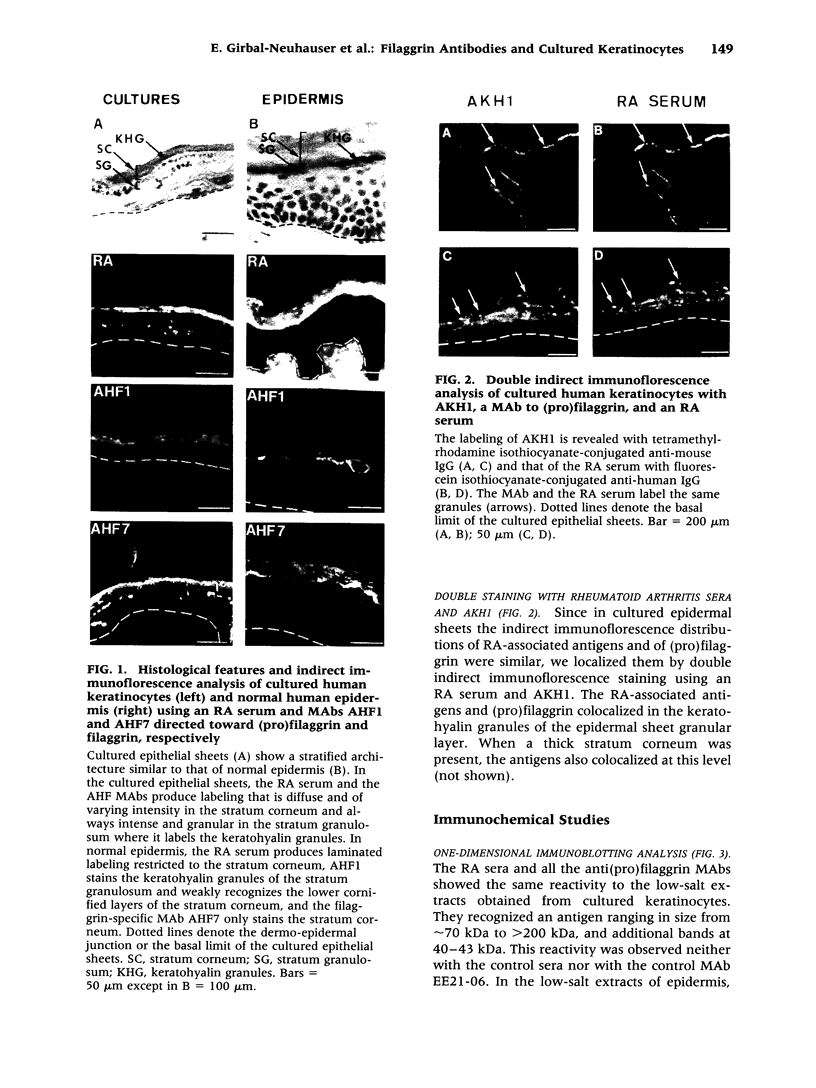
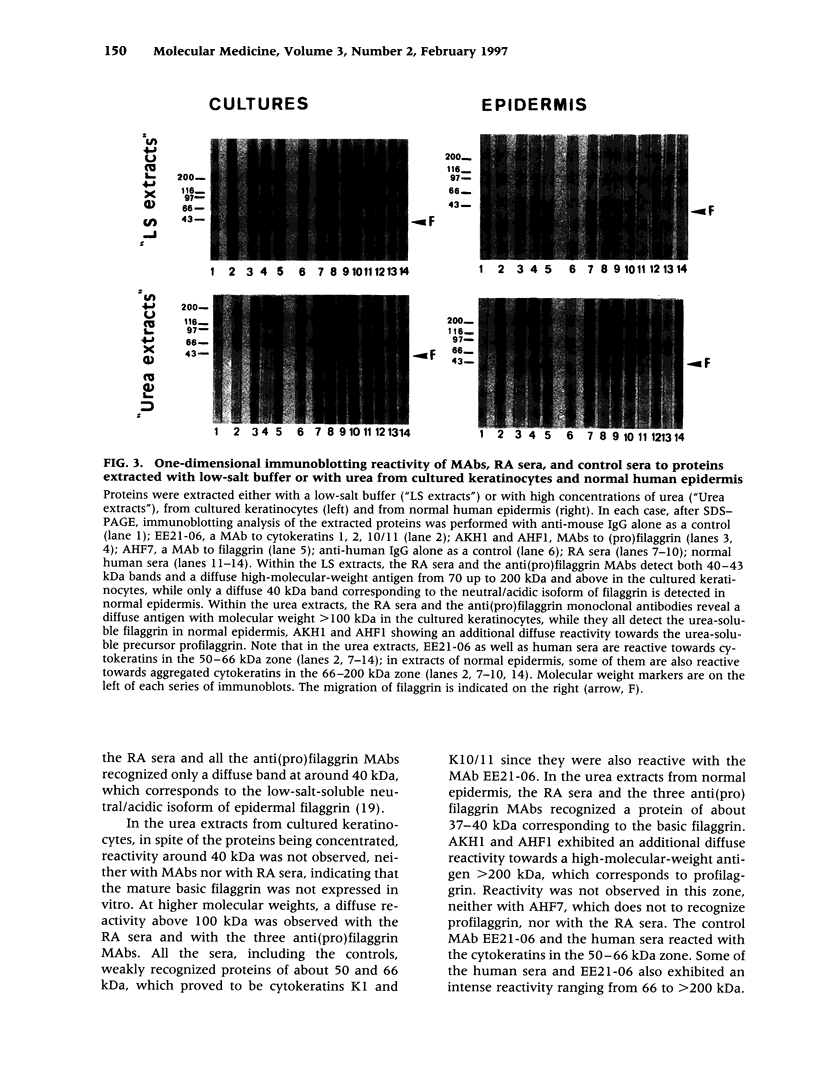
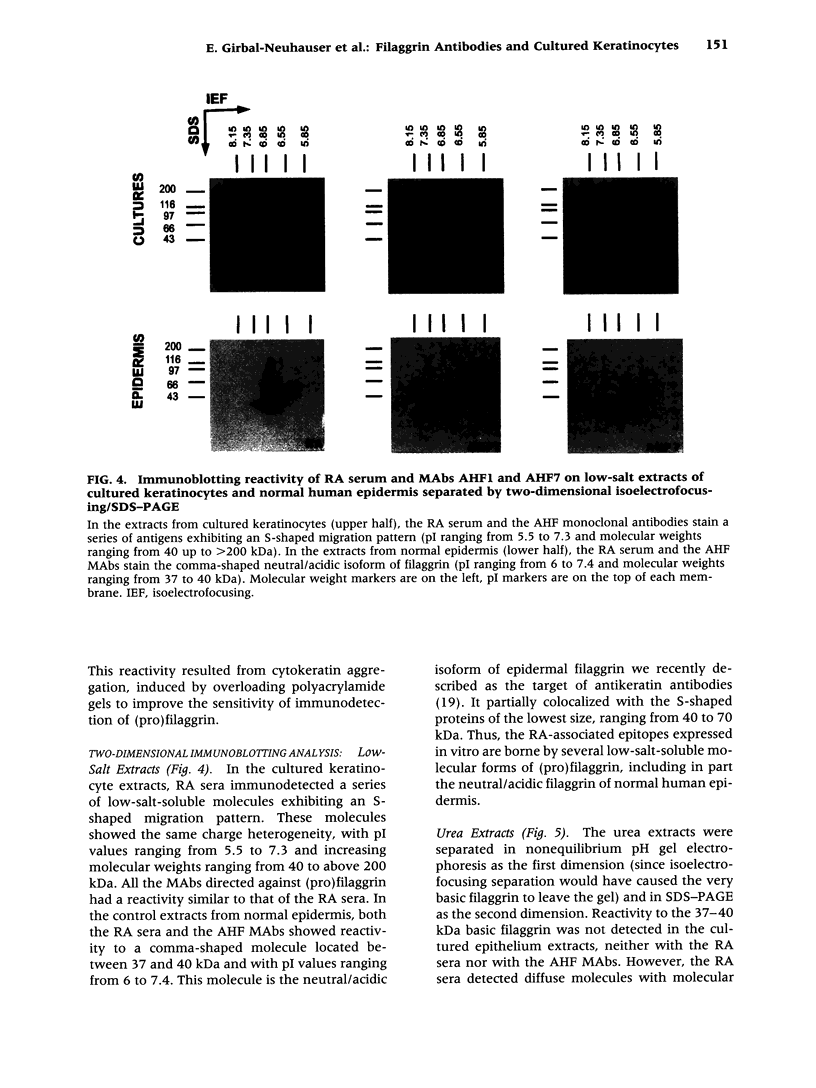




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnett F. C., Edworthy S. M., Bloch D. A., McShane D. J., Fries J. F., Cooper N. S., Healey L. A., Kaplan S. R., Liang M. H., Luthra H. S. The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988 Mar;31(3):315–324. doi: 10.1002/art.1780310302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asselineau D., Dale B. A., Bernard B. A. Filaggrin production by cultured human epidermal keratinocytes and its regulation by retinoic acid. Differentiation. 1990 Dec;45(3):221–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1990.tb00476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asselineau D., Darmon M. Retinoic acid provokes metaplasia of epithelium formed in vitro by adult human epidermal keratinocytes. Differentiation. 1995 Apr;58(4):297–306. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-0436.1995.5840297.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale B. A., Gown A. M., Fleckman P., Kimball J. R., Resing K. A. Characterization of two monoclonal antibodies to human epidermal keratohyalin: reactivity with filaggrin and related proteins. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Mar;88(3):306–313. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12466185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris J., Cooper S., Roessner K., Hochberg M. Antibodies to denatured type II collagen in rheumatoid arthritis: negative association with IgM rheumatoid factor. J Rheumatol. 1990 Jul;17(7):880–884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girbal E., Sebbag M., Gomès-Daudrix V., Simon M., Vincent C., Serre G. Characterisation of the rat oesophagus epithelium antigens defined by the so-called 'antikeratin antibodies', specific for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1993 Oct;52(10):749–757. doi: 10.1136/ard.52.10.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoet R. M., Voorsmit R. A., Van Venrooij W. J. The perinuclear factor, a rheumatoid arthritis-specific autoantigen, is not present in keratohyalin granules of cultured buccal mucosa cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1991 Apr;84(1):59–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb08124.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Carvalho A., Holborow E. J., Goddard D. H., Russell G. Antiperinuclear factor and keratin antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1981 Jun;40(3):263–266. doi: 10.1136/ard.40.3.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kautsky M. B., Fleckman P., Dale B. A. Retinoic acid regulates oral epithelial differentiation by two mechanisms. J Invest Dermatol. 1995 Apr;104(4):546–553. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12606058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirstein H., Mathiesen F. K. Antikeratin antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Methods and clinical significance. Scand J Rheumatol. 1987;16(5):331–338. doi: 10.3109/03009748709102504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurki P., Aho K., Palosuo T., Heliövaara M. Immunopathology of rheumatoid arthritis. Antikeratin antibodies precede the clinical disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1992 Aug;35(8):914–917. doi: 10.1002/art.1780350810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonsdale-Eccles J. D., Haugen J. A., Dale B. A. A phosphorylated keratohyalin-derived precursor of epidermal stratum corneum basic protein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2235–2238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynley A. M., Dale B. A. The characterization of human epidermal filaggrin. A histidine-rich, keratin filament-aggregating protein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Apr 14;744(1):28–35. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miossec P., Youinou P., Le Goff P., Moineau M. P. Clinical relevance of antikeratin antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 1982 Sep;1(3):185–189. doi: 10.1007/BF02042772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIENHUIS R. L., MANDEMA E. A NEW SERUM FACTOR IN PATIENTS WITH RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS; THE ANTIPERINUCLEAR FACTOR. Ann Rheum Dis. 1964 Jul;23:302–305. doi: 10.1136/ard.23.4.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paimela L., Gripenberg M., Kurki P., Leirisalo-Repo M. Antikeratin antibodies: diagnostic and prognostic markers for early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Jun;51(6):743–746. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.6.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quismorio F. P., Jr, Kaufman R. L., Beardmore T., Mongan E. S. Reactivity of serum antibodies to the keratin layer of rat esophagus in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Apr;26(4):494–499. doi: 10.1002/art.1780260407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resing K. A., Johnson R. S., Walsh K. A. Characterization of protease processing sites during conversion of rat profilaggrin to filaggrin. Biochemistry. 1993 Sep 28;32(38):10036–10045. doi: 10.1021/bi00089a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resing K. A., Walsh K. A., Haugen-Scofield J., Dale B. A. Identification of proteolytic cleavage sites in the conversion of profilaggrin to filaggrin in mammalian epidermis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 25;264(3):1837–1845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resing K. A., al-Alawi N., Blomquist C., Fleckman P., Dale B. A. Independent regulation of two cytoplasmic processing stages of the intermediate filament-associated protein filaggrin and role of Ca2+ in the second stage. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):25139–25145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblat G. H., Arbogast L. Y., Ouellette L., Howard B. V. Preparation of delipidized serum protein for use in cell culture systems. In Vitro. 1976 Aug;12(8):554–557. doi: 10.1007/BF02797438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott I. R., Harding C. R. Studies on the synthesis and degradation of a high molecular weight, histidine-rich phosphoprotein from mammalian epidermis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 29;669(1):65–78. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90224-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebbag M., Simon M., Vincent C., Masson-Bessière C., Girbal E., Durieux J. J., Serre G. The antiperinuclear factor and the so-called antikeratin antibodies are the same rheumatoid arthritis-specific autoantibodies. J Clin Invest. 1995 Jun;95(6):2672–2679. doi: 10.1172/JCI117969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serre G., Mils V., Haftek M., Vincent C., Croute F., Réano A., Ouhayoun J. P., Bettinger S., Soleilhavoup J. P. Identification of late differentiation antigens of human cornified epithelia, expressed in re-organized desmosomes and bound to cross-linked envelope. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Dec;97(6):1061–1072. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12492589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serre G., Vincent C., Fournié B., Lapeyre F., Soleilhavoup J. P., Fournié A. Anticorps anti-stratum corneum d'oesophage de rat, auto-anticorps anti-kératines épidermiques et anti-épiderme dans la polyarthrite rhumatoïde et différentes affections rhumatologiques. Intérêt diagnostique, aspects fondamentaux. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic. 1986 Nov;53(11):607–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Girbal E., Sebbag M., Gomès-Daudrix V., Vincent C., Salama G., Serre G. The cytokeratin filament-aggregating protein filaggrin is the target of the so-called "antikeratin antibodies," autoantibodies specific for rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1993 Sep;92(3):1387–1393. doi: 10.1172/JCI116713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Sebbag M., Haftek M., Vincent C., Girbal-Neuhauser E., Rakotoarivony J., Sommé G., Schmitt D., Serre G. Monoclonal antibodies to human epidermal filaggrin, some not recognizing profilaggrin. J Invest Dermatol. 1995 Sep;105(3):432–437. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12321148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Vincent C., Haftek M., Girbal E., Sebbag M., Gomès-Daudrix V., Serre G. The rheumatoid arthritis-associated autoantibodies to filaggrin label the fibrous matrix of the cornified cells but not the profilaggrin-containing keratohyalin granules in human epidermis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1995 Apr;100(1):90–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb03608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner G., Hartmuth K., Skriner K., Maurer-Fogy I., Sinski A., Thalmann E., Hassfeld W., Barta A., Smolen J. S. Purification and partial sequencing of the nuclear autoantigen RA33 shows that it is indistinguishable from the A2 protein of the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein complex. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):1061–1066. doi: 10.1172/JCI115921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent C., Serre G., Lapeyre F., Fournié B., Ayrolles C., Fournié A., Soleilhavoup J. P. High diagnostic value in rheumatoid arthritis of antibodies to the stratum corneum of rat oesophagus epithelium, so-called 'antikeratin antibodies'. Ann Rheum Dis. 1989 Sep;48(9):712–722. doi: 10.1136/ard.48.9.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe F., Cathey M. A., Roberts F. K. The latex test revisited. Rheumatoid factor testing in 8,287 rheumatic disease patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1991 Aug;34(8):951–960. doi: 10.1002/art.1780340804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youinou P., Le Goff P., Colaco C. B., Thivolet J., Tater D., Viac J., Shipley M. Antikeratin antibodies in serum and synovial fluid show specificity for rheumatoid arthritis in a study of connective tissue diseases. Ann Rheum Dis. 1985 Jul;44(7):450–454. doi: 10.1136/ard.44.7.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young B. J., Mallya R. K., Leslie R. D., Clark C. J., Hamblin T. J. Anti-keratin antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J. 1979 Jul 14;2(6182):97–99. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6182.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]