Abstract
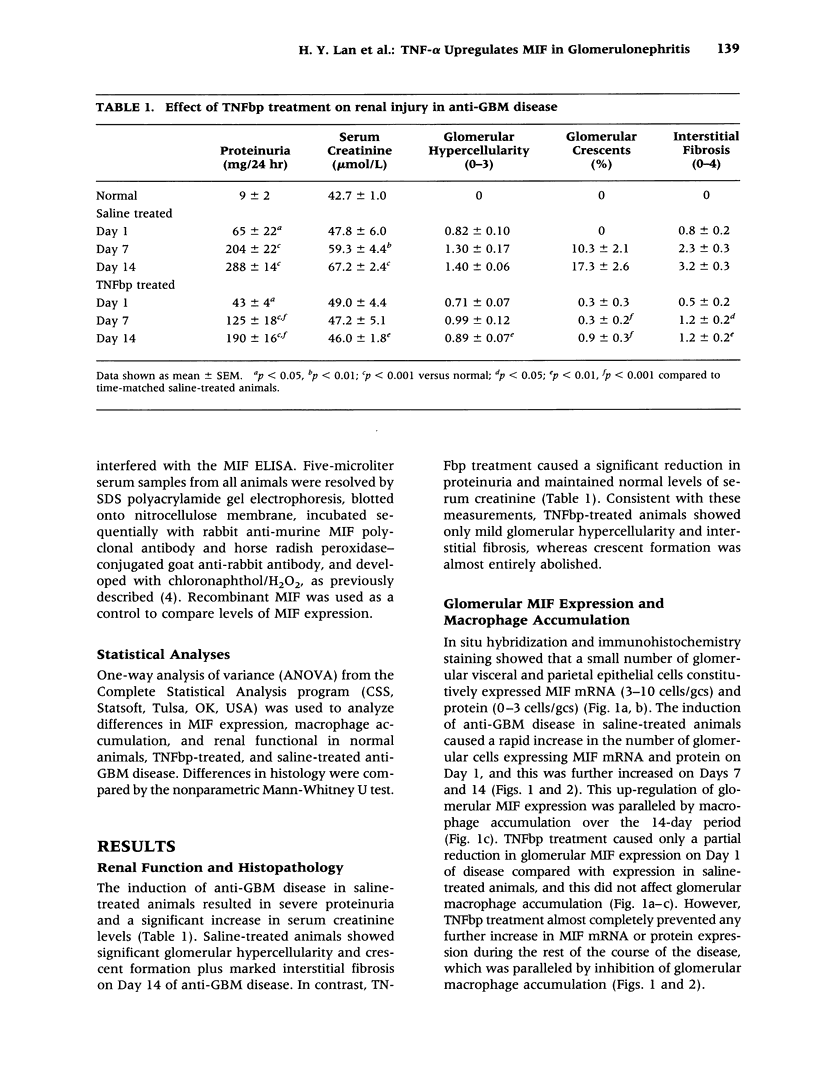
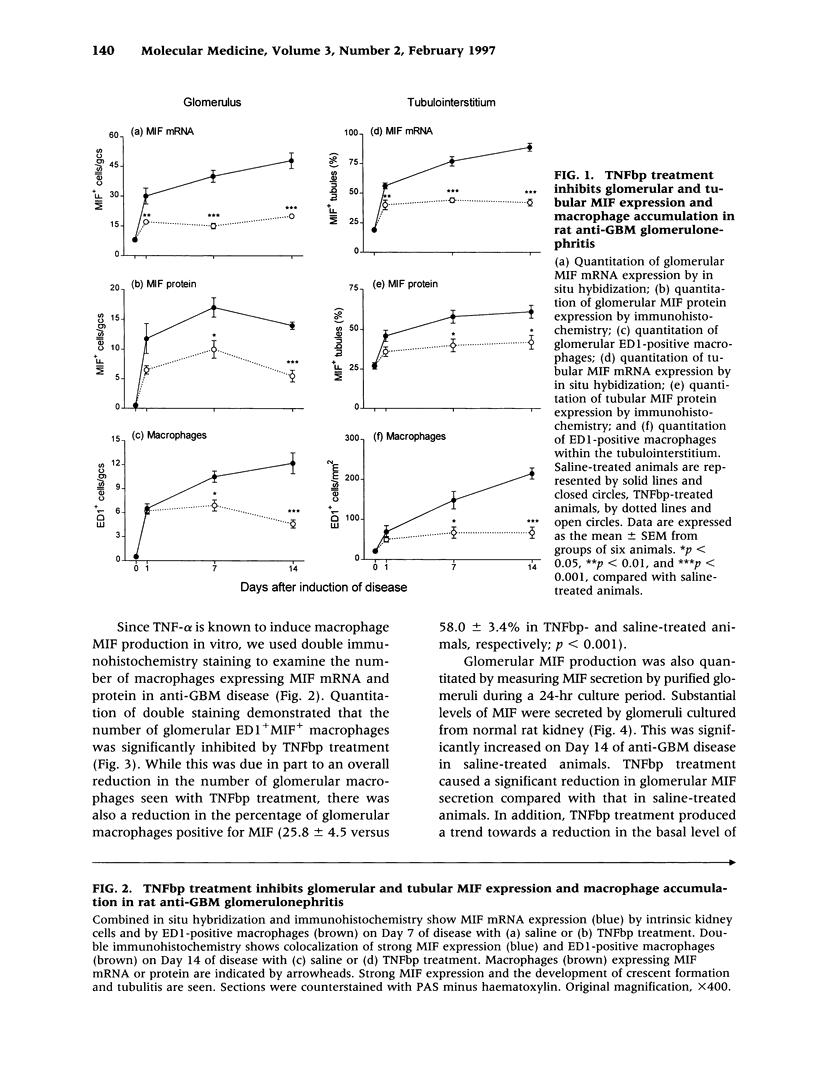
BACKGROUND: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) is a potent proinflammatory mediator that participates in the pathogenesis of endotoxemia and experimental crescentic glomerulonephritis. However, very little is known about how MIF production is regulated in disease. We therefore examined whether tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), a known inducer of MIF expression by macrophages in vitro, up-regulates local and systemic MIF expression in a macrophage-mediated rat model of crescentic glomerulonephritis. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Anti-glomerular basement membrane (GBM) glomerulonephritis was induced in groups of six primed rats. Animals were treated with 1 mg/kg soluble TNF-alpha receptor (TNFbp) or saline from the time of disease induction until they were killed on Days 1, 7, or 14. Renal MIF expression was assessed by in situ hybridization, immunohistochemistry, and ELISA, and compared with macrophage accumulation and indices of renal damage. RESULTS: Although TNFbp treatment on Day 1 of the disease had only a partial effect upon the up-regulation of glomerular MIF expression, on Days 7 to 14 it almost completely abrogated the increase in glomerular and interstitial MIF mRNA and protein expression. In addition, TNFbp treatment significantly inhibited MIF secretion by cultured glomeruli and reduced serum MIF levels. The inhibition of renal MIF expression was paralleled by a significant inhibition of glomerular and interstitial macrophage infiltration (p < 0.001 versus saline treated), a significant suppression of renal injury (proteinuria and serum creatinine), and a marked reduction in histologic damage (glomerular hypercellularity, crescent formation, and interstitial fibrosis; all p < 0.01 versus saline treated). CONCLUSIONS: This study demonstrates for the first time that TNF-alpha up-regulates local MIF expression by both infiltrating macrophages and resident kidney cells in rat crescentic glomerulonephritis. In addition, TNF-alpha regulates systemic MIF production. Thus, TNF-alpha, together with MIF, may play a pathological role in immunologically induced renal disease.
Full text
PDF


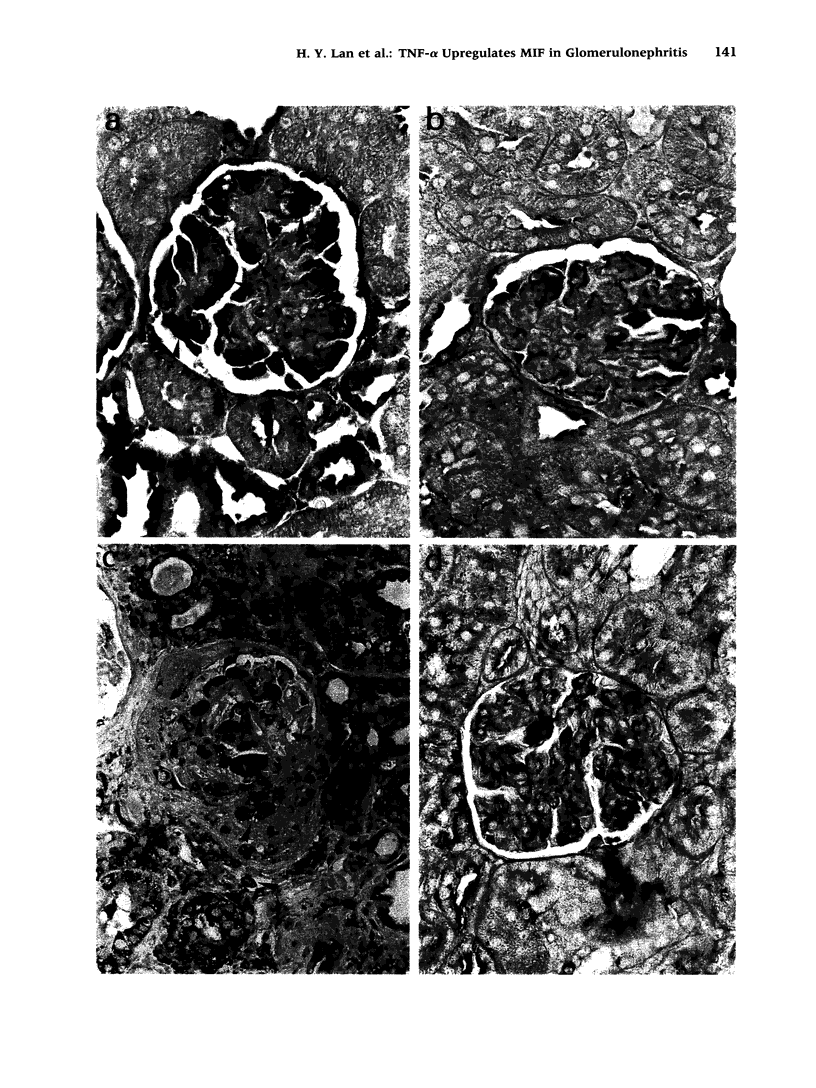
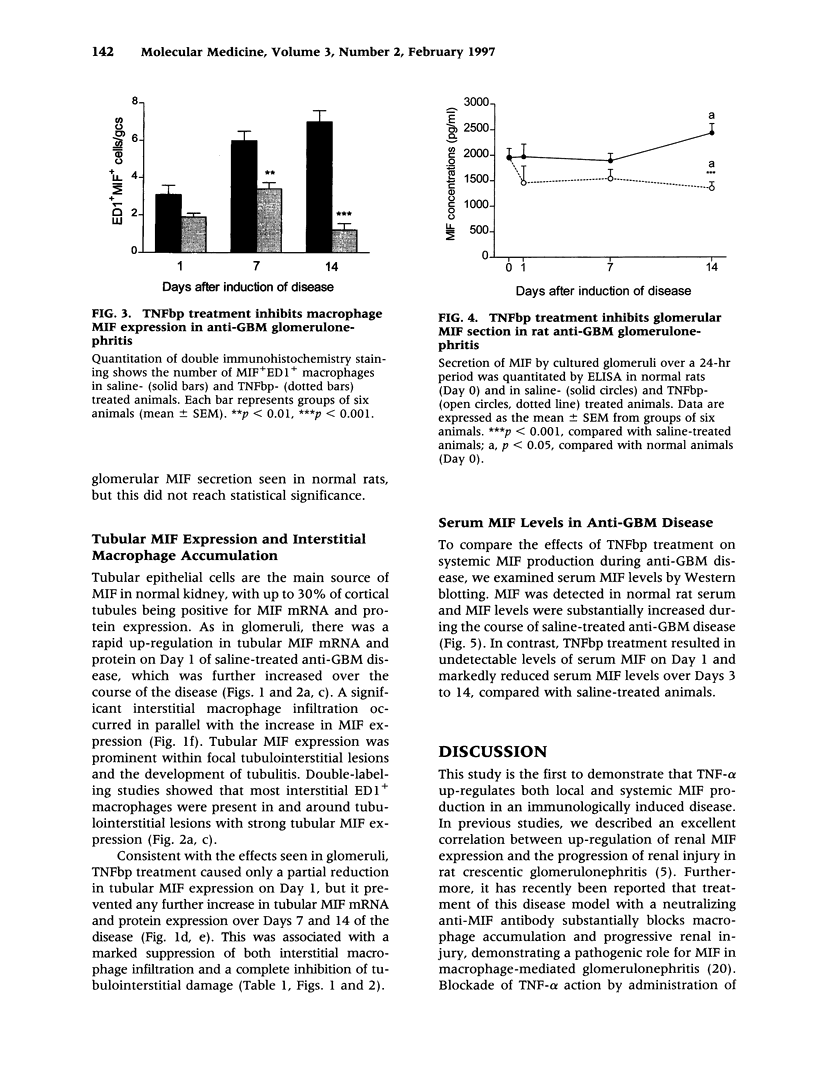


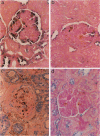
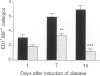
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auphan N., DiDonato J. A., Rosette C., Helmberg A., Karin M. Immunosuppression by glucocorticoids: inhibition of NF-kappa B activity through induction of I kappa B synthesis. Science. 1995 Oct 13;270(5234):286–290. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5234.286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacher M., Meinhardt A., Lan H. Y., Mu W., Metz C. N., Chesney J. A., Calandra T., Gemsa D., Donnelly T., Atkins R. C. Migration inhibitory factor expression in experimentally induced endotoxemia. Am J Pathol. 1997 Jan;150(1):235–246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacher M., Metz C. N., Calandra T., Mayer K., Chesney J., Lohoff M., Gemsa D., Donnelly T., Bucala R. An essential regulatory role for macrophage migration inhibitory factor in T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jul 23;93(15):7849–7854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.15.7849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baud L., Fouqueray B., Philipp C. Involvement of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in glomerular injury. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1994;16(1):53–61. doi: 10.1007/BF00196713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Finco T. S., Nantermet P. V., Baldwin A. S., Jr Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 lead to phosphorylation and loss of I kappa B alpha: a mechanism for NF-kappa B activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3301–3310. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhagen J., Calandra T., Mitchell R. A., Martin S. B., Tracey K. J., Voelter W., Manogue K. R., Cerami A., Bucala R. MIF is a pituitary-derived cytokine that potentiates lethal endotoxaemia. Nature. 1993 Oct 21;365(6448):756–759. doi: 10.1038/365756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Bennett B. Mechanism of a reaction in vitro associated with delayed-type hypersensitivity. Science. 1966 Jul 1;153(3731):80–82. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3731.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calandra T., Bernhagen J., Metz C. N., Spiegel L. A., Bacher M., Donnelly T., Cerami A., Bucala R. MIF as a glucocorticoid-induced modulator of cytokine production. Nature. 1995 Sep 7;377(6544):68–71. doi: 10.1038/377068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. R. Delayed hypersensitivity in vitro: its mediation by cell-free substances formed by lymphoid cell-antigen interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jul;56(1):72–77. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.1.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dijkstra C. D., Döpp E. A., Joling P., Kraal G. The heterogeneity of mononuclear phagocytes in lymphoid organs: distinct macrophage subpopulations in the rat recognized by monoclonal antibodies ED1, ED2 and ED3. Immunology. 1985 Mar;54(3):589–599. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby Z. W., Shirota K., Jothy S., Lowry R. P. Antiserum against tumor necrosis factor-alpha and a protease inhibitor reduce immune glomerular injury. Kidney Int. 1991 Jul;40(1):43–51. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan H. Y., Mu W., NG Y. Y., Nikolic-Paterson D. J., Atkins R. C. A simple, reliable, and sensitive method for nonradioactive in situ hybridization: use of microwave heating to improve hybridization efficiency and preserve tissue morphology. J Histochem Cytochem. 1996 Mar;44(3):281–287. doi: 10.1177/44.3.8648089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan H. Y., Mu W., Nikolic-Paterson D. J., Atkins R. C. A novel, simple, reliable, and sensitive method for multiple immunoenzyme staining: use of microwave oven heating to block antibody crossreactivity and retrieve antigens. J Histochem Cytochem. 1995 Jan;43(1):97–102. doi: 10.1177/43.1.7822770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan H. Y., Mu W., Yang N., Meinhardt A., Nikolic-Paterson D. J., Ng Y. Y., Bacher M., Atkins R. C., Bucala R. De Novo renal expression of macrophage migration inhibitory factor during the development of rat crescentic glomerulonephritis. Am J Pathol. 1996 Oct;149(4):1119–1127. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan H. Y., Nikolic-Paterson D. J., Mu W., Vannice J. L., Atkins R. C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist halts the progression of established crescentic glomerulonephritis in the rat. Kidney Int. 1995 May;47(5):1303–1309. doi: 10.1038/ki.1995.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan H. Y., Paterson D. J., Atkins R. C. Initiation and evolution of interstitial leukocytic infiltration in experimental glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1991 Sep;40(3):425–433. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R., Bacher M., Bernhagen J., Pushkarskaya T., Seldin M. F., Bucala R. Cloning and characterization of the gene for mouse macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF). J Immunol. 1995 Apr 15;154(8):3863–3870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Guo Y. J., Miyasaka M., Tamatani T., Collins A. B., Sy M. S., McCluskey R. T., Andres G. Antibodies to intercellular adhesion molecule 1/lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 prevent crescent formation in rat autoimmune glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1993 Mar 1;177(3):667–677. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.3.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishino T., Bernhagen J., Shiiki H., Calandra T., Dohi K., Bucala R. Localization of macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) to secretory granules within the corticotrophic and thyrotrophic cells of the pituitary gland. Mol Med. 1995 Nov;1(7):781–788. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzi L. A., Weiser W. Y. Human recombinant migration inhibitory factor activates human macrophages to kill tumor cells. Cell Immunol. 1992 Dec;145(2):372–379. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90339-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai M., Nishihira J., Hibiya Y., Koyama Y., Nishi S. Glutathione binding rat liver 13k protein is the homologue of the macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1994 Jun;33(3):439–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang W. W., Qi M., Warren J. S. Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 mediates glomerular macrophage infiltration in anti-GBM Ab GN. Kidney Int. 1996 Aug;50(2):665–671. doi: 10.1038/ki.1996.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trede N. S., Tsytsykova A. V., Chatila T., Goldfeld A. E., Geha R. S. Transcriptional activation of the human TNF-alpha promoter by superantigen in human monocytic cells: role of NF-kappa B. J Immunol. 1995 Jul 15;155(2):902–908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]