Abstract
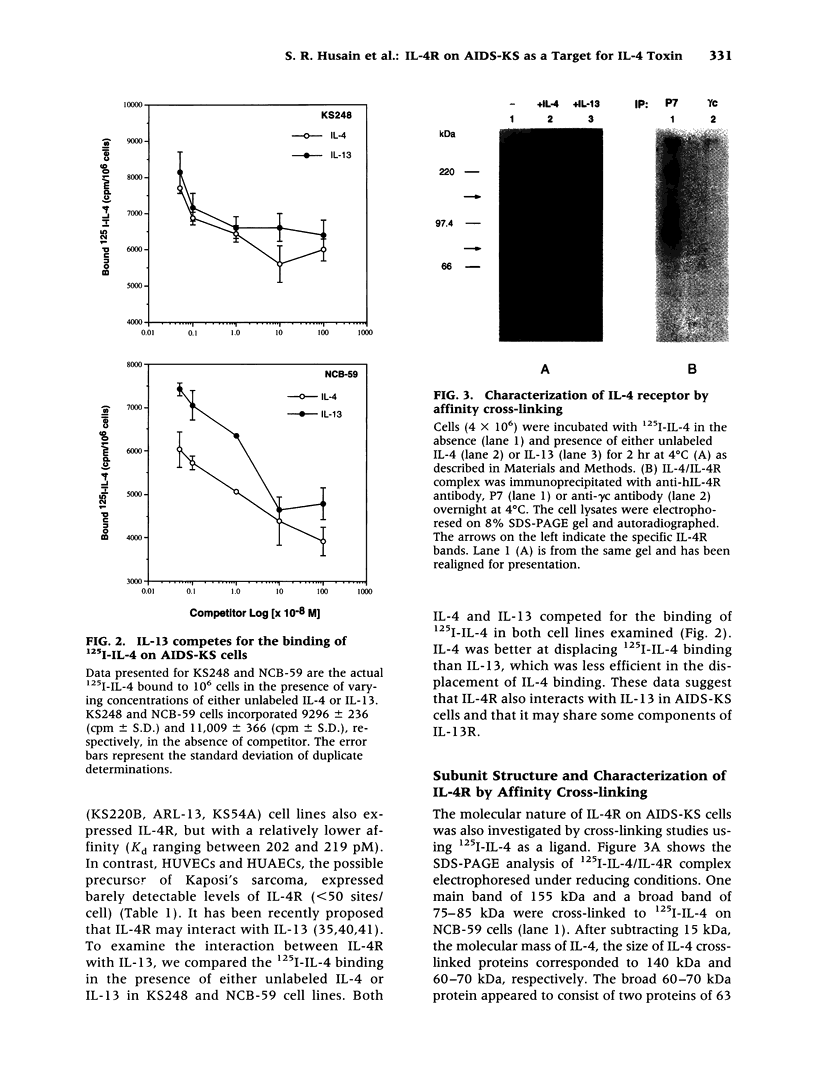
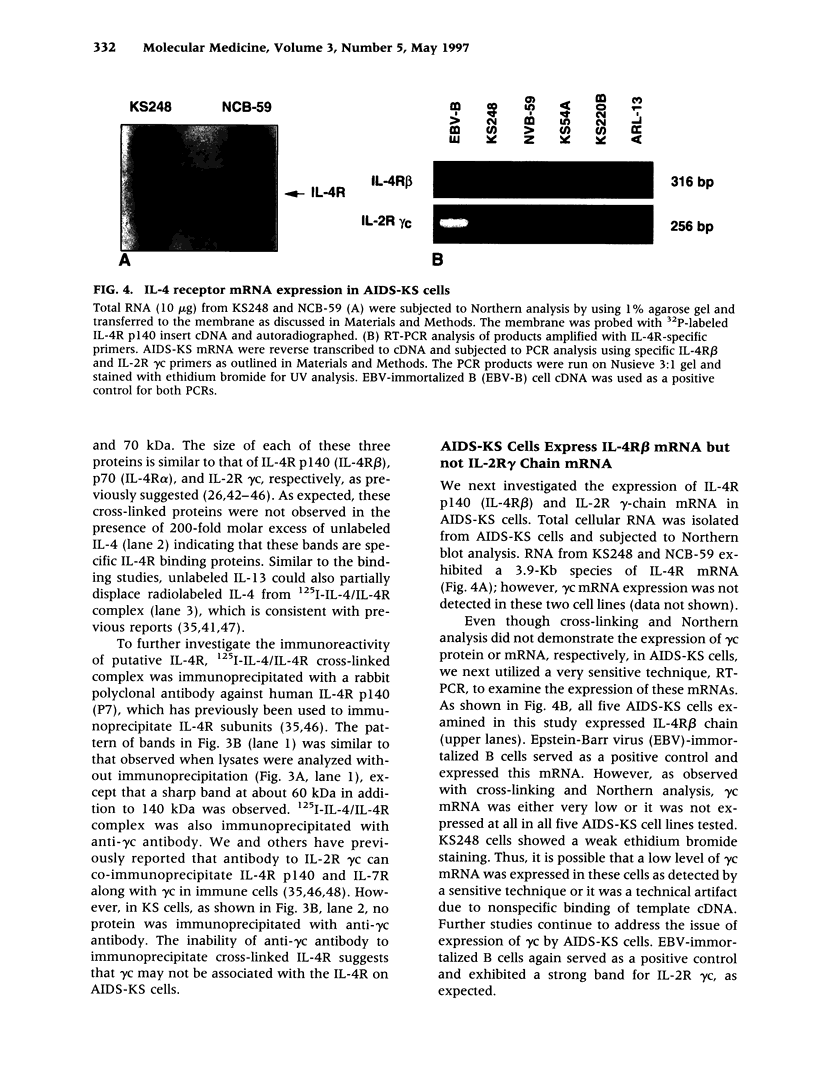
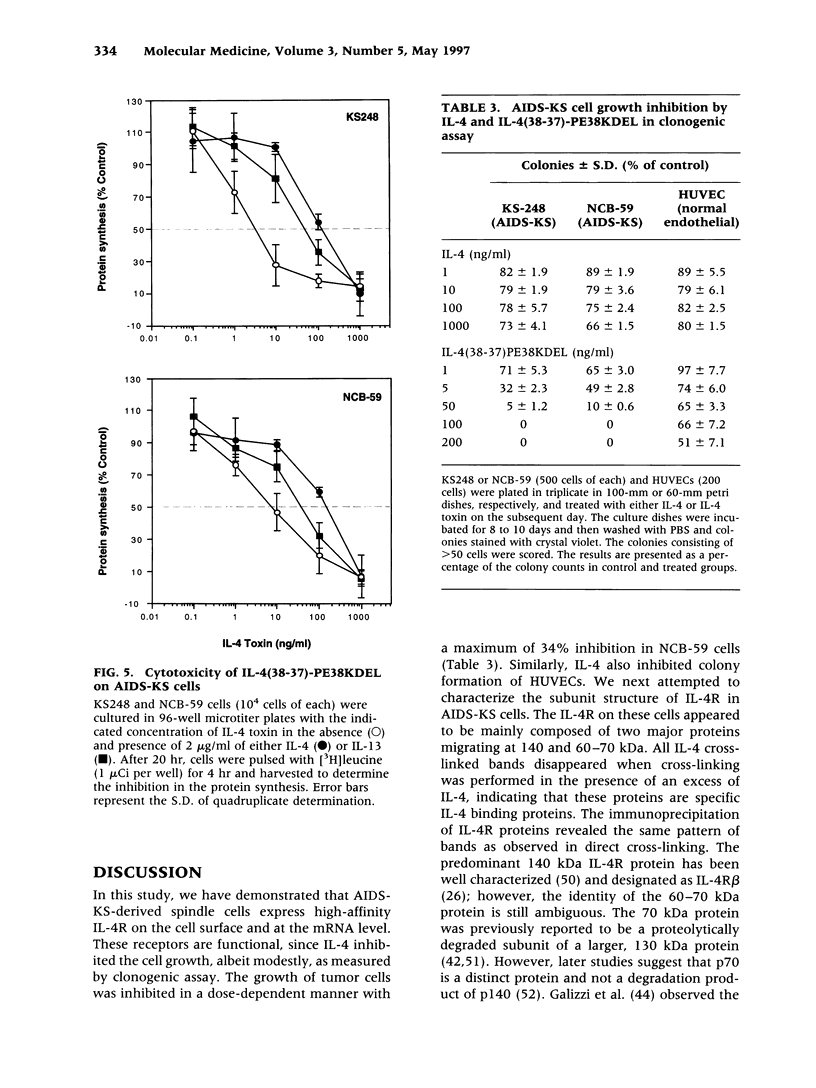
BACKGROUND: AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma (AIDS-KS) represents one of the most common malignancies associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection. To target effective therapeutic agents to AIDS-KS, we have identified a new target in the form of interleukin-4 receptors (IL-4R). MATERIALS AND METHODS: The expression of IL-4R on AIDS-KS cells and their subunit structure was determined by radioligand receptor binding, cross-linking and Northern and RT-PCR analyses. The in vitro effect of IL-4 and recombinant fusion protein made up of circularly permuted IL-4 and a mutated form of Pseudomonas exotoxin, IL-4(38-37)-PE38KDEL, was examined by clonogenic and protein synthesis inhibition assays. RESULTS: Five AIDS-KS cell lines expressed high-affinity IL-4R with a Kd of 23.5-219 pM. IL-4 appeared to cross-link to one major protein corresponding to 140 kDa and a broad band corresponding to 60-70 kDa. Both cross-linked proteins were immunoprecipitated with an antibody to human IL-4R beta chain. AIDS-KS cells exhibited IL-4R beta-specific mRNA. IL-4 caused a modest inhibition (31-34%) of colony formation in two AIDS-KS cell lines tested. IL-4(38-37)-PE38KDEL was found to be highly effective in inhibiting the protein synthesis in all five AIDS-KS examined. The IC50 ranged from 32 to 1225 pM. The cytotoxic action of IL-4 toxin was blocked by an excess of IL-4, exhibiting the specificity of IL-4(38-37)-PE38KDEL. The cytotoxicity of IL-4 toxin observed by a clonogenic assay corroborated well with the IC50 obtained by protein synthesis inhibition assay. Normal human endothelial cells expressed a negligible number of IL-4R (< 50 sites/cell) and were less sensitive or not sensitive to IL-4(38-37)-PE38KDEL. CONCLUSION: The presence of a new plasma membrane protein in the form of IL-4R on AIDS-KS cells may be targeted by IL-4(38-37)-PE38KDEL for its potential implication in the treatment of AIDS-KS.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clerici M., Hakim F. T., Venzon D. J., Blatt S., Hendrix C. W., Wynn T. A., Shearer G. M. Changes in interleukin-2 and interleukin-4 production in asymptomatic, human immunodeficiency virus-seropositive individuals. J Clin Invest. 1993 Mar;91(3):759–765. doi: 10.1172/JCI116294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corbeil J., Evans L. A., Vasak E., Cooper D. A., Penny R. Culture and properties of cells derived from Kaposi sarcoma. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):2972–2976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debinski W., Puri R. K., Kreitman R. J., Pastan I. A wide range of human cancers express interleukin 4 (IL4) receptors that can be targeted with chimeric toxin composed of IL4 and Pseudomonas exotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):14065–14070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debinski W., Puri R. K., Pastan I. Interleukin-4 receptors expressed on tumor cells may serve as a target for anticancer therapy using chimeric Pseudomonas exotoxin. Int J Cancer. 1994 Sep 1;58(5):744–748. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910580520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Barillari G., Gallo R. C. Pathogenesis of AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 1991 Apr;5(2):281–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensoli B., Nakamura S., Salahuddin S. Z., Biberfeld P., Larsson L., Beaver B., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. AIDS-Kaposi's sarcoma-derived cells express cytokines with autocrine and paracrine growth effects. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):223–226. doi: 10.1126/science.2643161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foxwell B. M., Woerly G., Ryffel B. Identification of interleukin 4 receptor-associated proteins and expression of both high- and low-affinity binding on human lymphoid cells. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Sep;19(9):1637–1641. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman V. H., Shin S. I. Cellular tumorigenicity in nude mice: correlation with cell growth in semi-solid medium. Cell. 1974 Dec;3(4):355–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman-Kien A. E. Disseminated Kaposi's sarcoma syndrome in young homosexual men. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1981 Oct;5(4):468–471. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(81)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galizzi J. P., Castle B., Djossou O., Harada N., Cabrillat H., Yahia S. A., Barrett R., Howard M., Banchereau J. Purification of a 130-kDa T cell glycoprotein that binds human interleukin 4 with high affinity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galizzi J. P., Zuber C. E., Cabrillat H., Djossou O., Banchereau J. Internalization of human interleukin 4 and transient down-regulation of its receptor in the CD23-inducible Jijoye cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6984–6989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D. AIDS. Viruses, cytokines and Kaposi's sarcoma. Curr Biol. 1995 May 1;5(5):469–471. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00093-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill P. S. Pathogenesis of HIV-related malignancies. Curr Opin Oncol. 1991 Oct;3(5):867–871. doi: 10.1097/00001622-199110000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada N., Yang G., Miyajima A., Howard M. Identification of an essential region for growth signal transduction in the cytoplasmic domain of the human interleukin-4 receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):22752–22758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans P., Gori A., Lemone M., Franchioly P., Clumeck N. Possible role of granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) on the rapid progression of AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma lesions in vivo. Br J Haematol. 1994 Jun;87(2):413–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1994.tb04934.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann F., Andreeff M., Gruss H. J., Brach M. A., Lübbert M., Mertelsmann R. Interleukin-4 inhibits growth of multiple myelomas by suppressing interleukin-6 expression. Blood. 1991 Oct 15;78(8):2070–2074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain S. R., Leland P., Aggarwal B. B., Puri R. K. Transcriptional up-regulation of interleukin 4 receptors by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 tat gene. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1996 Sep 20;12(14):1349–1359. doi: 10.1089/aid.1996.12.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan A. D., Beckmann M. P., Park L. S., Paul W. E. The IL-4 receptor: biochemical characterization of IL-4-binding molecules in a T cell line expressing large numbers of receptors. J Immunol. 1991 Apr 1;146(7):2272–2279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan A. D., Nelms K., Wang L. M., Pierce J. H., Paul W. E. Interleukin 4 receptor: signaling mechanisms. Immunol Today. 1994 Sep;15(9):423–432. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreitman R. J., Puri R. K., Pastan I. A circularly permuted recombinant interleukin 4 toxin with increased activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):6889–6893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.6889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreitman R. J., Puri R. K., Pastan I. Increased antitumor activity of a circularly permuted interleukin 4-toxin in mice with interleukin 4 receptor-bearing human carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1995 Aug 1;55(15):3357–3363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masood R., Husain S. R., Rahman A., Gill P. Potentiation of cytotoxicity of Kaposi's sarcoma related to immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) by liposome-encapsulated doxorubicin. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993 Aug;9(8):741–746. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles S. A. Pathogenesis of HIV-related Kaposi's sarcoma. Curr Opin Oncol. 1994 Sep;6(5):497–502. doi: 10.1097/00001622-199409000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosley B., Beckmann M. P., March C. J., Idzerda R. L., Gimpel S. D., VandenBos T., Friend D., Alpert A., Anderson D., Jackson J. The murine interleukin-4 receptor: molecular cloning and characterization of secreted and membrane bound forms. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):335–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90295-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami-Mori K., Taga T., Kishimoto T., Nakamura S. AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) cells express oncostatin M (OM)-specific receptor but not leukemia inhibitory factor/OM receptor or interleukin-6 receptor. Complete block of OM-induced KS cell growth and OM binding by anti-gp130 antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1995 Sep;96(3):1319–1327. doi: 10.1172/JCI118167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata T., Noguchi P. D., Puri R. K. Receptors for interleukin (IL)-4 do not associate with the common gamma chain, and IL-4 induces the phosphorylation of JAK2 tyrosine kinase in human colon carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 22;270(51):30829–30836. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.51.30829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell M. P., Kasiske B. L., Kim Y., Atluru D., Keane W. F. Lovastatin inhibits proliferation of rat mesangial cells. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jan;91(1):83–87. doi: 10.1172/JCI116204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obiri N. I., Debinski W., Leonard W. J., Puri R. K. Receptor for interleukin 13. Interaction with interleukin 4 by a mechanism that does not involve the common gamma chain shared by receptors for interleukins 2, 4, 7, 9, and 15. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 14;270(15):8797–8804. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.15.8797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obiri N. I., Leland P., Murata T., Debinski W., Puri R. K. The IL-13 receptor structure differs on various cell types and may share more than one component with IL-4 receptor. J Immunol. 1997 Jan 15;158(2):756–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obiri N. I., Puri R. K. Characterization of interleukin-4 receptors expressed on human renal cell carcinoma cells. Oncol Res. 1994;6(9):419–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obiri N. I., Siegel J. P., Varricchio F., Puri R. K. Expression of high-affinity IL-4 receptors on human melanoma, ovarian and breast carcinoma cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1994 Jan;95(1):148–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1994.tb06029.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara J. Interleukin-4: molecular structure and biochemical characteristics, biological function, and receptor expression. Year Immunol. 1989;5:126–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park L. S., Friend D., Sassenfeld H. M., Urdal D. L. Characterization of the human B cell stimulatory factor 1 receptor. J Exp Med. 1987 Aug 1;166(2):476–488. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.2.476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E. Interleukin-4: a prototypic immunoregulatory lymphokine. Blood. 1991 May 1;77(9):1859–1870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri R. K., Debinski W., Obiri N., Kreitman R., Pastan I. Human renal cell carcinoma cells are sensitive to the cytotoxic effect of a chimeric protein composed of human interleukin-4 and Pseudomonas exotoxin. Cell Immunol. 1994 Apr 1;154(1):369–379. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1994.1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri R. K., Leland P., Kreitman R. J., Pastan I. Human neurological cancer cells express interleukin-4 (IL-4) receptors which are targets for the toxic effects of IL4-Pseudomonas exotoxin chimeric protein. Int J Cancer. 1994 Aug 15;58(4):574–581. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910580421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri R. K., Leland P., Obiri N. I., Husain S. R., Mule J., Pastan I., Kreitman R. J. An improved circularly permuted interleukin 4-toxin is highly cytotoxic to human renal cell carcinoma cells. Introduction of gamma c chain in RCC cells does not improve sensitivity. Cell Immunol. 1996 Jul 10;171(1):80–86. doi: 10.1006/cimm.1996.0176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puri R. K., Siegel J. P. Interleukin-4 and cancer therapy. Cancer Invest. 1993;11(4):473–486. doi: 10.3109/07357909309018879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinecker H. C., Podolsky D. K. Human intestinal epithelial cells express functional cytokine receptors sharing the common gamma c chain of the interleukin 2 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 29;92(18):8353–8357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.18.8353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. M., Keegan A. D., Harada N., Nakamura Y., Noguchi M., Leland P., Friedmann M. C., Miyajima A., Puri R. K., Paul W. E. Interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain: a functional component of the interleukin-4 receptor. Science. 1993 Dec 17;262(5141):1880–1883. doi: 10.1126/science.8266078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzl M., Roth W. K., Brockmeyer N. H., Zietz C., Speiser B., Hofschneider P. H. Expression of platelet-derived growth factor and its receptor in AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma in vivo suggests paracrine and autocrine mechanisms of tumor maintenance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7046–7050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W., Grogan T. M., Salmon S. E. Effects of interleukin-4 on the in vitro growth of human lymphoid and plasma cell neoplasms. Blood. 1990 Mar 1;75(5):1114–1118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toi M., Bicknell R., Harris A. L. Inhibition of colon and breast carcinoma cell growth by interleukin-4. Cancer Res. 1992 Jan 15;52(2):275–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vita N., Lefort S., Laurent P., Caput D., Ferrara P. Characterization and comparison of the interleukin 13 receptor with the interleukin 4 receptor on several cell types. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 24;270(8):3512–3517. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.8.3512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner S., Hofschneider P. H., Roth W. K. Cells derived from sporadic and AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma reveal identical cytochemical and molecular properties in vitro. Int J Cancer. 1989 Jun 15;43(6):1137–1144. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida D., Piepmeier J., Weinstein M. Estramustine sensitizes human glioblastoma cells to irradiation. Cancer Res. 1994 Mar 15;54(6):1415–1417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski S. M., Vega F., Jr, Huyghe B., Zurawski G. Receptors for interleukin-13 and interleukin-4 are complex and share a novel component that functions in signal transduction. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2663–2670. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05927.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]