Abstract
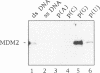
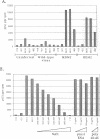
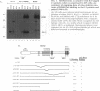
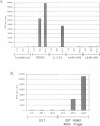
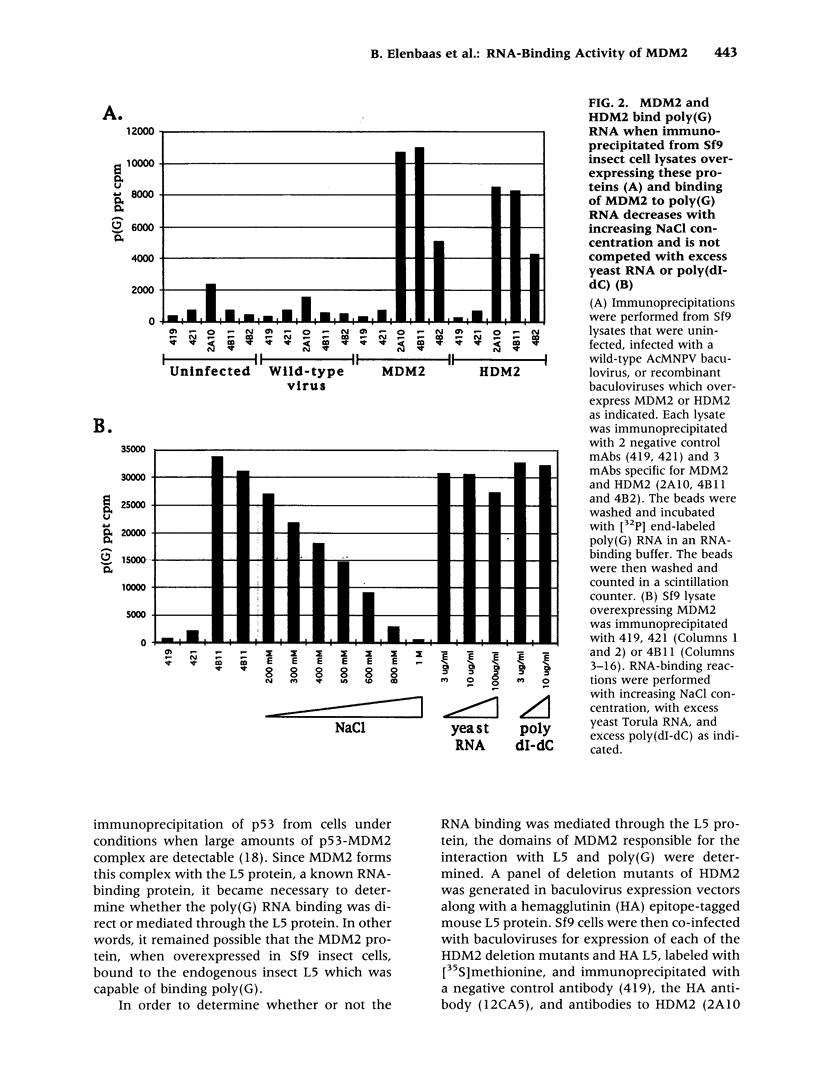
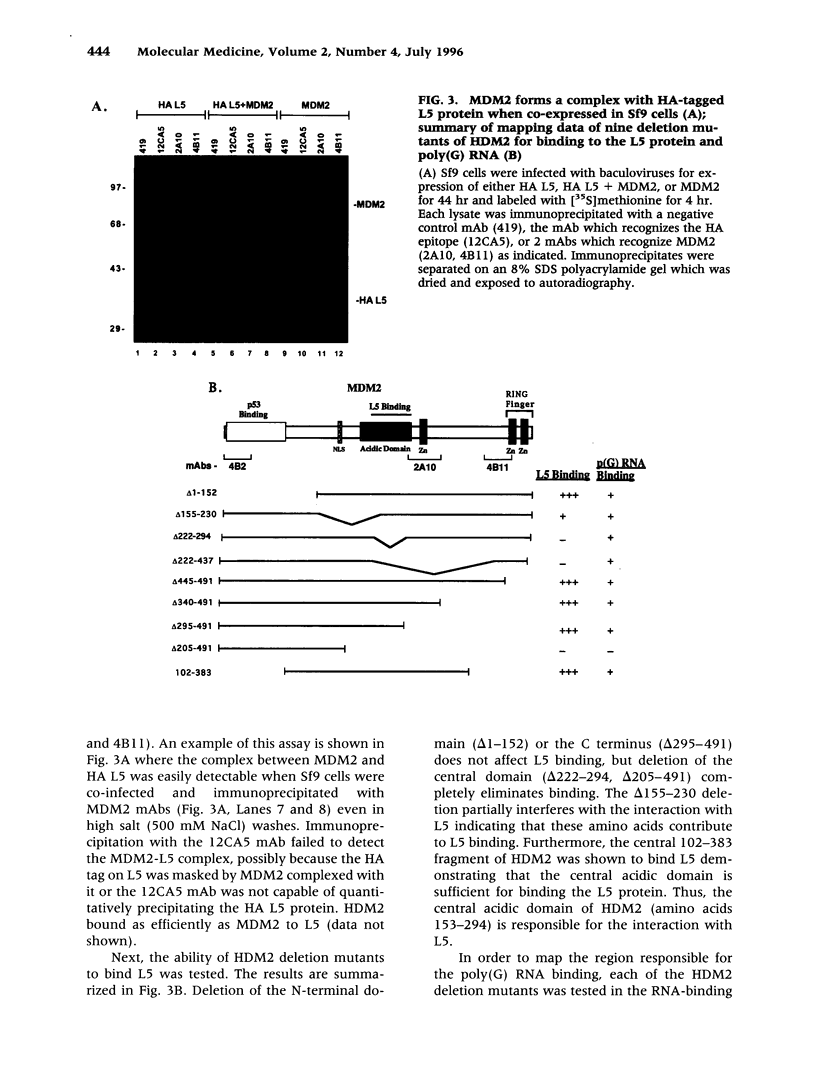
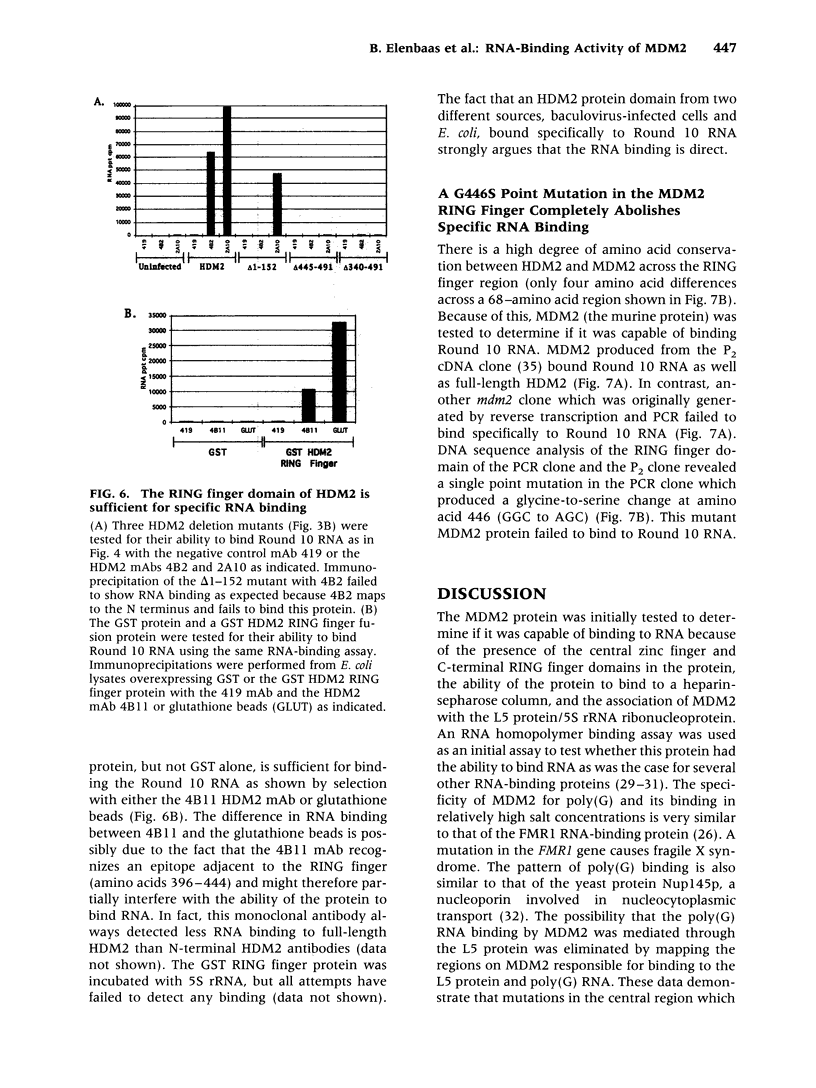
BACKGROUND: The cellular mdm2 gene has transforming activity when overexpressed and is amplified in a variety of human tumors. At least part of the transforming ability of the MDM2 protein is due to binding and inactivating the p53 tumor suppressor protein. Additionally, this protein forms a complex in vivo with the L5 ribosomal protein and its associated 5S ribosomal RNA and may be part of a ribosomal complex. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A RNA homopolymer binding assay and a SELEX procedure have been used to characterize the RNA-binding activity of MDM2. RESULTS: The MDM2 protein binds efficiently to the homopolyribonucleotide poly(G) but not to other homopolyribonucleotides. This binding is independent of the interaction of MDM2 with the L5 protein, which occurs through the central acidic domain of MDM2. An RNA SELEX procedure was performed to identify specific RNA ligands that bind with high affinity to the human MDM2 (HDM2) protein. After 10 rounds of selection and amplification, a subset of RNA molecules that bound efficiently to HDM2 was isolated from a randomized pool. Sequencing of these selected ligands revealed that a small number of sequence motifs were selected. The specific RNA binding occurs through the RING finger domain of the protein. Furthermore, a single amino acid substitution in the RING finger domain, G446S, completely abolishes the specific RNA binding. CONCLUSIONS: These observations, showing that MDM2 binds the L5/5S ribosomal ribonucleoprotein particle and can also bind to specific RNA sequences or structures, suggest a role for MDM2 in translational regulation in a cell.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barak Y., Gottlieb E., Juven-Gershon T., Oren M. Regulation of mdm2 expression by p53: alternative promoters produce transcripts with nonidentical translation potential. Genes Dev. 1994 Aug 1;8(15):1739–1749. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.15.1739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow P. N., Luisi B., Milner A., Elliott M., Everett R. Structure of the C3HC4 domain by 1H-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. A new structural class of zinc-finger. J Mol Biol. 1994 Mar 25;237(2):201–211. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berberich S., Cole M. The mdm-2 oncogene is translocated and overexpressed in a murine plasmacytoma cell line expressing wild-type p53. Oncogene. 1994 May;9(5):1469–1472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddy M. N., Freemont P. S., Borden K. L. The p53-associated protein MDM2 contains a newly characterized zinc-binding domain called the RING finger. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 May;19(5):198–199. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borden K. L., Boddy M. N., Lally J., O'Reilly N. J., Martin S., Howe K., Solomon E., Freemont P. S. The solution structure of the RING finger domain from the acute promyelocytic leukaemia proto-oncoprotein PML. EMBO J. 1995 Apr 3;14(7):1532–1541. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07139.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bueso-Ramos C. E., Yang Y., deLeon E., McCown P., Stass S. A., Albitar M. The human MDM-2 oncogene is overexpressed in leukemias. Blood. 1993 Nov 1;82(9):2617–2623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd C. G., Dreyfuss G. Conserved structures and diversity of functions of RNA-binding proteins. Science. 1994 Jul 29;265(5172):615–621. doi: 10.1126/science.8036511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Lin J., Levine A. J. Regulation of transcription functions of the p53 tumor suppressor by the mdm-2 oncogene. Mol Med. 1995 Jan;1(2):142–152. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Marechal V., Levine A. J. Mapping of the p53 and mdm-2 interaction domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4107–4114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordon-Cardo C., Latres E., Drobnjak M., Oliva M. R., Pollack D., Woodruff J. M., Marechal V., Chen J., Brennan M. F., Levine A. J. Molecular abnormalities of mdm2 and p53 genes in adult soft tissue sarcomas. Cancer Res. 1994 Feb 1;54(3):794–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook N. E., Clem R. J., Miller L. K. An apoptosis-inhibiting baculovirus gene with a zinc finger-like motif. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2168–2174. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2168-2174.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbelstein M., Shenk T. In vitro selection of RNA ligands for the ribosomal L22 protein associated with Epstein-Barr virus-expressed RNA by using randomized and cDNA-derived RNA libraries. J Virol. 1995 Dec;69(12):8027–8034. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.12.8027-8034.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Matunis M. J., Piñol-Roma S., Burd C. G. hnRNP proteins and the biogenesis of mRNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:289–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabre E., Boelens W. C., Wimmer C., Mattaj I. W., Hurt E. C. Nup145p is required for nuclear export of mRNA and binds homopolymeric RNA in vitro via a novel conserved motif. Cell. 1994 Jul 29;78(2):275–289. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fakharzadeh S. S., Trusko S. P., George D. L. Tumorigenic potential associated with enhanced expression of a gene that is amplified in a mouse tumor cell line. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1565–1569. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07676.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A. The mdm-2 oncogene can overcome wild-type p53 suppression of transformed cell growth. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):301–306. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freemont P. S. The RING finger. A novel protein sequence motif related to the zinc finger. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993 Jun 11;684:174–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb32280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goddard A. D., Borrow J., Freemont P. S., Solomon E. Characterization of a zinc finger gene disrupted by the t(15;17) in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1371–1374. doi: 10.1126/science.1720570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. E., Henderson S. T., Petes T. D., Prakash S., Bankmann M., Prakash L. Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAD5-encoded DNA repair protein contains DNA helicase and zinc-binding sequence motifs and affects the stability of simple repetitive sequences in the genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3807–3818. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. N., Roe A. E., Donehower L. A., Bradley A. Rescue of embryonic lethality in Mdm2-deficient mice by absence of p53. Nature. 1995 Nov 9;378(6553):206–208. doi: 10.1038/378206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley R. L., Solovyeva I., Lyman L. M., Richman R., Solovyev V., Kuroda M. I. Expression of msl-2 causes assembly of dosage compensation regulators on the X chromosomes and female lethality in Drosophila. Cell. 1995 Jun 16;81(6):867–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiledjian M., Dreyfuss G. Primary structure and binding activity of the hnRNP U protein: binding RNA through RGG box. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2655–2664. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05331.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladanyi M., Cha C., Lewis R., Jhanwar S. C., Huvos A. G., Healey J. H. MDM2 gene amplification in metastatic osteosarcoma. Cancer Res. 1993 Jan 1;53(1):16–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landers J. E., Haines D. S., Strauss J. F., 3rd, George D. L. Enhanced translation: a novel mechanism of mdm2 oncogene overexpression identified in human tumor cells. Oncogene. 1994 Sep;9(9):2745–2750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach F. S., Tokino T., Meltzer P., Burrell M., Oliner J. D., Smith S., Hill D. E., Sidransky D., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. p53 Mutation and MDM2 amplification in human soft tissue sarcomas. Cancer Res. 1993 May 15;53(10 Suppl):2231–2234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovering R., Hanson I. M., Borden K. L., Martin S., O'Reilly N. J., Evan G. I., Rahman D., Pappin D. J., Trowsdale J., Freemont P. S. Identification and preliminary characterization of a protein motif related to the zinc finger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2112–2116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marechal V., Elenbaas B., Piette J., Nicolas J. C., Levine A. J. The ribosomal L5 protein is associated with mdm-2 and mdm-2-p53 complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;14(11):7414–7420. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.11.7414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K., Trouche D., Hagemeier C., Sørensen T. S., La Thangue N. B., Kouzarides T. Stimulation of E2F1/DP1 transcriptional activity by MDM2 oncoprotein. Nature. 1995 Jun 22;375(6533):691–694. doi: 10.1038/375691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miki Y., Swensen J., Shattuck-Eidens D., Futreal P. A., Harshman K., Tavtigian S., Liu Q., Cochran C., Bennett L. M., Ding W. A strong candidate for the breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1. Science. 1994 Oct 7;266(5182):66–71. doi: 10.1126/science.7545954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momand J., Zambetti G. P., Olson D. C., George D., Levine A. J. The mdm-2 oncogene product forms a complex with the p53 protein and inhibits p53-mediated transactivation. Cell. 1992 Jun 26;69(7):1237–1245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90644-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montes de Oca Luna R., Wagner D. S., Lozano G. Rescue of early embryonic lethality in mdm2-deficient mice by deletion of p53. Nature. 1995 Nov 9;378(6553):203–206. doi: 10.1038/378203a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberosler P., Hloch P., Ramsperger U., Stahl H. p53-catalyzed annealing of complementary single-stranded nucleic acids. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2389–2396. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05893.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliner J. D., Kinzler K. W., Meltzer P. S., George D. L., Vogelstein B. Amplification of a gene encoding a p53-associated protein in human sarcomas. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):80–83. doi: 10.1038/358080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliner J. D., Pietenpol J. A., Thiagalingam S., Gyuris J., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Oncoprotein MDM2 conceals the activation domain of tumour suppressor p53. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):857–860. doi: 10.1038/362857a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reifenberger G., Liu L., Ichimura K., Schmidt E. E., Collins V. P. Amplification and overexpression of the MDM2 gene in a subset of human malignant gliomas without p53 mutations. Cancer Res. 1993 Jun 15;53(12):2736–2739. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands M. S., Bogenhagen D. F. The carboxyterminal zinc fingers of TFIIIA interact with the tip of helix V of 5S RNA in the 7S ribonucleoprotein particle. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 25;19(8):1791–1796. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.8.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D., Gold L., Platt T. Selective enrichment of RNA species for tight binding to Escherichia coli rho factor. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):201–207. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.7678562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siomi H., Siomi M. C., Nussbaum R. L., Dreyfuss G. The protein product of the fragile X gene, FMR1, has characteristics of an RNA-binding protein. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90420-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. S., Dreyfuss G. Classification and purification of proteins of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles by RNA-binding specificities. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2237–2241. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theunissen O., Rudt F., Guddat U., Mentzel H., Pieler T. RNA and DNA binding zinc fingers in Xenopus TFIIIA. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):679–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90601-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian Y., Adya N., Wagner S., Giam C. Z., Green M. R., Ellington A. D. Dissecting protein:protein interactions between transcription factors with an RNA aptamer. RNA. 1995 May;1(3):317–326. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk C., MacDougal S., Gold L. RNA pseudoknots that inhibit human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6988–6992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Bayle J. H., Elenbaas B., Pavletich N. P., Levine A. J. Alternatively spliced forms in the carboxy-terminal domain of the p53 protein regulate its ability to promote annealing of complementary single strands of nucleic acids. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jan;15(1):497–504. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.1.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao Z. X., Chen J., Levine A. J., Modjtahedi N., Xing J., Sellers W. R., Livingston D. M. Interaction between the retinoblastoma protein and the oncoprotein MDM2. Nature. 1995 Jun 22;375(6533):694–698. doi: 10.1038/375694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M. Prediction of RNA secondary structure by energy minimization. Methods Mol Biol. 1994;25:267–294. doi: 10.1385/0-89603-276-0:267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]